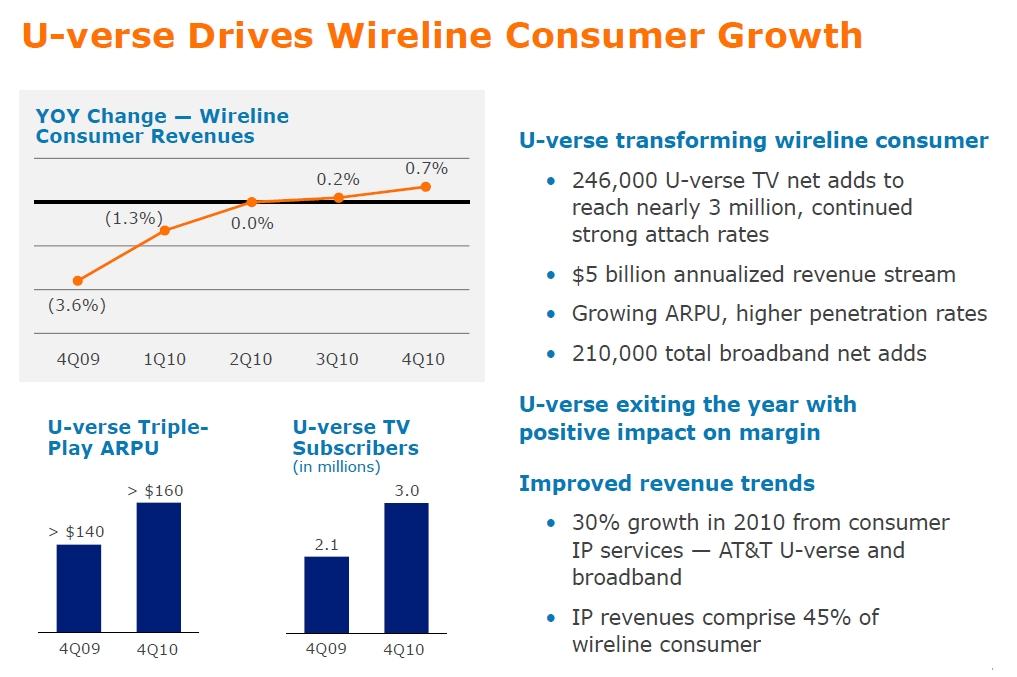
Rep. Marilyn Avila (R-Time Warner Cable) is coming under increasing scrutiny across North Carolina as her cable lobbyist-written, anti-community broadband bill — H.129 — faces negative reviews in the media across the state.
Avila’s bill would set conditions under which community-owned broadband networks could operate, while specifically exempting existing cable and phone companies. Most observers on the ground predict Avila’s bill would kill any further expansion of public broadband networks in the state and tie the hands of those already in operation, which would inevitably drive them out of business. Avila’s bill, ghost-written by the state’s cable companies, even has the prescience to allow the fiber systems to be sold off to cable and phone companies at fire-sale prices for as little as pennies on the dollar, without a public vote.
Last week, the state legislature’s Finance Committee put Avila’s bill on a temporary hold “to allow public input” on the bill, but also to permit scrambling by lobbyists to deal with several surprise amendments that attempt to exempt existing community networks.
That time-out has given the press a chance to examine the proposed legislation and its impact on North Carolina’s efforts to improve its mediocre broadband rankings, now 41st in the country. More than a few in the media do not like what they see in H.129.
The Associated Press notes the state legislature was finally allowing the public to weigh in on a matter that directly impacts their Internet experience:
North Carolina lawmakers aiming to stop cities from building their own broadband networks decided Thursday to allow public comments the next time they consider the latest effort by telecom companies to keep local governments out of the business.
The House Finance Committee will hear from the public next Wednesday as it reviews legislation that would sharply restrict the chances for municipalities to step in when cable and phone companies decide not to build high-speed Internet systems in lightly populated areas. Opponents say telecom companies aren’t extending super-fast Internet at reasonable prices, and that keeps smaller communities behind in the wired world of commerce.
 “They don’t want to provide these services in a lot of areas because it’s expensive, and they don’t want municipalities to offer these services. That’s an unlevel playing field for our citizens,” said Rep. Deborah Ross, D-Wake.
“They don’t want to provide these services in a lot of areas because it’s expensive, and they don’t want municipalities to offer these services. That’s an unlevel playing field for our citizens,” said Rep. Deborah Ross, D-Wake.
Legislation unveiled Thursday was changed to ease the rules for communities in which at least half the households have no access to high-speed Internet except through a satellite provider. Another change ensures the new rules don’t affect the municipal networks already established in Wilson, Salisbury, Morganton and Iredell County, which have borrowed to build their systems.
Cable and phone companies have been urging the General Assembly to restrict municipal broadband services since a 2005 state appeals court ruling upheld the right of towns and cities to offer their residents broadband. Companies argue that local governments have an unfair advantage because they don’t have to pay taxes and can subsidize their rates by shifting profits from their electricity or gas customers, undercutting the corporate competitors.
Except community broadband providers in North Carolina are not doing any of those things.
In fact, smaller providers start at a competitive disadvantage because they cannot enjoy the savings larger providers get from their extensive buying power — winning lower costs on everything from programming to equipment and services.
Community providers are not winning most of their customers from “underpricing” their service — they are earning them by delivering better service, which was precisely the point.
The original argument communities like Wilson and Salisbury had with state cable and phone companies was with the quality and level of service offered in their communities. They solved the problem themselves with the development of fiber optic service that provides ultra-fast broadband connections that residents and small businesses simply could not get from other providers.
Some lawmakers believe community networks get in the way of cable jobs and phone company investment, and they want to “clear the playing field for business.” But for many communities in the state, the playing field is empty and will remain so indefinitely.
Broadband: Utility or Convenience
For some lawmakers, the debate is both generational and philosophical. Ruth Samuelson (R-Mecklenburg), told the AP she doesn’t believe providing broadband is a core part of government.
Among the older population who have not grown up with the Internet, broadband can be seen more as a luxury and less of a utility. A few generations earlier, a similar debate erupted over telephone and electric service, which faced identical controversy in regions underserved by private utilities.
A reminder of these earlier challenges was part of the Winston-Salem Journal’s argument against H.129’s adoption:
 “The broadband battle is not being waged in the heavily populated portions of the state such as the Triad. Here, the for-profit companies moved in a long time ago. They can make a very nice profit here because the population density is adequate to provide a good return on the infrastructure needed for high-speed Internet service.
“The broadband battle is not being waged in the heavily populated portions of the state such as the Triad. Here, the for-profit companies moved in a long time ago. They can make a very nice profit here because the population density is adequate to provide a good return on the infrastructure needed for high-speed Internet service.
“Over the past decade, however, North Carolina’s smaller municipalities, such as Wilson, Salisbury and Morganton, have built their own systems because their leaders recognized that broadband Internet is now an essential utility, just as electricity and natural gas are. The Internet-service providers did not step up to provide that essential service, so the municipalities did. In doing so, the cities followed a path they took nearly a century ago when the biggest electrical power companies did not provide service to these areas.”
North Carolina blogger-activist Mark Turner wrote in the News & Observer broadband has the capacity to transform North Carolina’s economic future in much the same way power and phone service did a century earlier:
While farm life has never been easy, at one time it was significantly harder. In the mid-1930s, over 97 percent of North Carolina farms had no electricity, many because private electric companies couldn’t make enough money from them to justify running the lines.
Aware of the transformational effect of electrification and recognizing the need to do something, visionary North Carolina leaders created rural electric cooperatives, beating passage of FDR’s Rural Electrification Act by one month. Through the state’s granting local communities the power to provide for their own needs where others would not, over 98 percent of farms had electricity by 1963, and our state has prospered.
The Internet is no less transformational than electricity. Through this world-changing technology, lives are being shared, distance learning taking place and innovative new businesses springing up. Sadly just as in the days before electrification, many North Carolina communities (particularly rural ones) are being left behind, stuck in the Internet slow lane.
 The Journal argues Internet Service Providers essentially want to keep these communities in the slow lane, with a powerful cartel that doesn’t deliver service, and does not want cities to provide it either. The cable and phone companies can’t have it both ways, the paper says. “They can’t delay bringing high-speed service to North Carolina communities but then turn around and lobby the legislature to deny local governments the authority to establish municipal service if their residents want it,” the paper editorializes.
The Journal argues Internet Service Providers essentially want to keep these communities in the slow lane, with a powerful cartel that doesn’t deliver service, and does not want cities to provide it either. The cable and phone companies can’t have it both ways, the paper says. “They can’t delay bringing high-speed service to North Carolina communities but then turn around and lobby the legislature to deny local governments the authority to establish municipal service if their residents want it,” the paper editorializes.
“The private providers are trying to make a big-government argument here, one that includes clichés about unfairness and Big Brother. But that is not the case. In this situation, residents and businesses are tired of waiting for Internet-service providers to arrive, so they’ve exercised their democratic rights to seek an alternative solution through their local governments.
“Had the private companies tried to make their argument 15 years ago, they might have deserved some sympathy. But not in 2011. The Internet and high-speed access to it have now been available in North Carolina homes for well more than a decade.
“They ignored a market, and local governments stepped in to provide a critical service. The legislature should kill this bill.”
Mark Turner in the News & Observer argues nothing about H.129 is really an ideological right or left-wing debate. He reminds readers the Internet itself was a government invention delivered through public rights-of-way established by local and state government, or over airwaves that are literally owned by the public.
“Like the electric lines that were once strung by hand to all corners of our state, our cities should retain the right to bring Internet service to their communities – especially where the private providers will not,” Turner wrote.
The Rural-Urban Disconnect: Choices in Raleigh, Sneaking Onto Wi-Fi in Spruce Pine

Spruce Pine, N.C., where one of the most popular hangouts in town is a parking lot where Wi-Fi signals deliver the only Internet service some residents can get.
The Journal points out North Carolina’s broadband debate is taking place in the state capital – Raleigh, a city much like the Triad region, served by both cable and phone companies. Against that backdrop, legislators may assume ubiquitous urban and suburban broadband leaves local governments with few excuses for getting into the business in the first place — an argument the cable lobby is using to its advantage with some legislators. But as soon as one ventures off Interstates 40, 77, or 95 — it does not take too long to find oneself in a broadband backwater.
“Here in Spruce Pine, broadband is a fabled, magical thing we read about, but don’t have — a big reason why my 17 year old son cannot wait to move out of here,” shares Stop the Cap! reader Morgan. “Everything you see on television shows with people using the Internet for practically everything just does not happen here.”
Morgan shares one of the community’s broadband secrets: local hotels and other business establishments have parking lots filled with cars with people still in them sneaking online.
“They are hopping on board business and motel Wi-Fi connections to pay their bills, apply for jobs, or just complete homework assignments that require an Internet connection,” Morgan shares. “Some businesses have locked down their Wi-Fi with passwords to stop the traffic, so there is an active underground trade of passwords of different wireless connections around the area.”
Morgan called the phone company wondering when DSL service might reach her house.
“Never, came the eventual reply — and the guy was laughing about it,” Morgan says. “He told me if I want something better, I should probably move.”
“What burns me up is these state legislators on the other end of the state are spending their time and energy defending the companies in the broadband shortage business. If they spent half as much time working for better broadband in western North Carolina, we would not be in this position today,” Morgan writes. “I mean we’re at the point where people take Internet access for granted in this society and they treat places like Spruce Pine as an escape from that technology ‘to get away from it all,’ all while we live in that world perpetually.”
Morgan is hardly alone living a life without broadband. In communities from Mars Hill to Marshall, large sections of the state simply go without. Avila’s bill does nothing to help — it actually hurts.
The Public-Private Partnership: A Solution for North Carolina’s Unserved?
![]() In some areas of the state, public-private partnerships (PPP’s) — also rejected in Avila’s bill — are making a difference getting broadband into rural North Carolina, reports Craig Settles, a broadband activist.
In some areas of the state, public-private partnerships (PPP’s) — also rejected in Avila’s bill — are making a difference getting broadband into rural North Carolina, reports Craig Settles, a broadband activist.
“Last year, North Carolina broadband advocates began formulating policy recommendations to make PPPs something of a standard in business models for communities that want better broadband,” Settles writes in a piece for Government Technology. “When legislation was introduced earlier this year that would effectively end further development of municipal networks in the state, this seemed like the right time to promote PPPs. Unfortunately the legislators pushing the bill effectively shut out these muni-network proponents from offering a compromise in separate negotiations.”
PPPs over some creative solutions to rural broadband challenges — especially in addressing return-on-investment concerns that keep private providers from building out networks to reach rural populations. A community or non-profit collaborative finances and builds the infrastructure to supply the service with a much longer payback period. While many commercial companies want a return within five years, co-ops have been comfortable paying off infrastructure projects over 10, 20, or even 25 years. Then, the private company can hop on board the constructed network at a wholesale price that helps pay off construction costs, and allows the provider to market its services and run its own business. The only requirement, and the one some private companies hate, is that the network is operated in the public interest and good, meaning -any- competitor can compete over the same facilities.

A successful public-private partnership in western New York could be a model to help rural North Carolina get broadband.
In the Finger Lakes Region of western New York, a hallmark PPP project has brought Ontario County a fiber network that can deliver faster broadband than anything available in nearby Rochester. And it has the support of TW Telecom, Verizon, Frontier Communications and other companies who can use it as part of their business plans.
“This is a winning scenario,” said Ed Hemminger, CIO of Ontario County, N.Y., and CEO of Axcess Ontario, the county’s 180-mile fiber network project. “It’s the only way some communities may be able to get fiber broadband. They can finance the buildout with bond financing with a 25-year payback term. If a muni is going to partner in this manner, be extremely cautious and ensure that it’s a true open access model that not only benefits providers in the area, but also allows others to come in and compete.”
“The beauty of this scenario is that it enables private-sector companies to overcome one of their biggest hurdles to deploying networks in rural and low-income areas: the cost of laying fiber or building wireless infrastructure,” Settles writes. “Municipalities, if they’re able to swing the financing, can take up to 25 years to pay off the debt. Providers, on the other hand, have to make their money back in three to five years.”
Rebuilding America’s Economy: Investing in Infrastructure
Providing suitable broadband infrastructure is increasingly important in small cities that are afterthoughts for many cable and telephone company providers. For Wilson, N.C., creating the infrastructure of a 21st century broadband network is part of an investment to attract future jobs for a city reinventing itself.
“The city council realized that it would be a very competitive world to attract and retain the best jobs in the future,” Grant Goings, Wilson city manager told The Sun News. “Well, you can’t talk about jobs without talking about the infrastructure that brings them and keeps them. Short and simple advanced broadband is critical infrastructure.”
 The Sun News reports on the state’s broadband controversies from the epicenter — Wilson is the first city in the state to deliver a fiber optic-based broadband network that beats all the others on speed.
The Sun News reports on the state’s broadband controversies from the epicenter — Wilson is the first city in the state to deliver a fiber optic-based broadband network that beats all the others on speed.
This year, Wilson signed on its first 100 megabits per second residential customers and is the first to have residents using the highest speeds available in North Carolina, said Brian Bowman, Wilson public affairs manager.
For Wilson and other communities building out better broadband networks, using fiber optics was a natural decision because of its capacity and future ease of upgrades. The cable industry has long argued broadband is a constantly-changing business and cities have a poor track record of keeping up, but Wilson’s GreenLight service has turned the tables on that argument, leaving Time Warner Cable — the state’s largest operator — well behind the municipal provider cable interests predicted would be a failure.
Wally Bowen, founder and executive director of the nonprofit Mountain Area Information Network (MAIN), which provides broadband services in and around Asheville, says this year’s anti-broadband bill, like the others, leaves cities vulnerable to political posturing and special interest legislation. He’s tried to outmaneuver legislators who work for the interests of Time Warner and CenturyLink by building non-profit or co-op ownership into the infrastructure, if only to protect networks from being forced to play defense year after year as private companies try to pick them off in the state legislature.
“Government-owned infrastructure creates political vulnerabilities given how incumbents are behaving,” Bowen said. “Our nonprofits are comprised of representatives from private-sector companies, private colleges, hospitals and so forth, in addition to local government. So there are limited legal grounds for attacking the nonprofit via laws passed in the legislature.” Some incumbent Internet service providers still will try these tactics anyway, but the makeup of these nonprofits can give them a stronger position from which to defend themselves.”
For many voters in the state, watching certain legislators toil on behalf of billion-dollar phone and cable companies while ignoring North Carolina’s broadband problems should bring consequences.
“My friends and I continue to watch these events with interest and will vote against those legislators who obviously would feel more comfortable working inside Time Warner Cable’s headquarters, because they are effectively on their payroll already,” Morgan says.


 Subscribe
Subscribe