Your bundle is bigger than ever.
A-la-carte TV is still dead. Long live the super-sized bundle!
If AT&T and Time Warner wanted to deliver a message to the cable industry as a result of their now-approved blockbuster merger deal, it is one that promises hundreds, if not thousands of more TV channels, movies and shows headed your way in the coming days, bundled into super-sized pricier packages of television, telephone, and internet service.
Despite the fact consumers claim they want to pick and pay only for the entertainment options they specifically want, in reality people are paying for more bundled packages and services — usually from multiple online streaming services — than ever before, with no possibility they will ever watch everything these services have to offer.
AT&T and Time Warner are well aware customers are now subscribing to cable television -and- streaming video services like Hulu and Netflix. But many customers are also buying streaming live cable TV alternatives, despite the fact they already subscribe to a cable television package. Given the option of selling you an inexpensive package of a dozen cable channels you claim to want or selling you much larger and more expensive bundles of services many are actually buying, AT&T will follow the money every time.
What will be different as a result of this merger is where you buy that programming. Before, you may have purchased AT&T Fiber internet access, AT&T wireless mobile phone service, a HBO GO subscription through DirecTV Now, a cable TV alternative, and Netflix. Now, with the exception of Netflix, all of that money will go directly to AT&T. The company will also be able to enhance their bottom line by monetizing content viewed over mobile devices. After taking control of Time Warner’s vast entertainment offerings, which range from HBO to Turner Broadcasting networks like CNN and TNT, AT&T will generously bestow liberal (or possibly free) access to this content for its broadband and wireless customers, while those served by other providers will have to pay up to watch. AT&T will ultimately set the terms of its licensing agreements. AT&T Wireless customers with unlimited data plans already have a sample of this with a free year of DirecTV Now, which customers of other wireless companies have to pay to watch.
AT&T plans to offer the best deals to customers who bundle everything through AT&T. The “quad play” bundle of TV, internet, home phone, and wireless phone will offer customers discounts on each element of the package, but some may experience sticker shock even with the discounts.
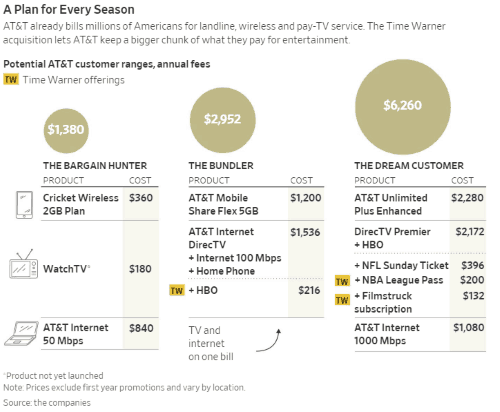
The Wall Street Journal noted a premium AT&T customer could pay more than $500 a month for AT&T’s best package — that’s more than $6,000 a year. Most bundled AT&T customers will pay about half that — around $246 a month for a package of 100 Mbps internet, a home phone line, wireless phone and a limited TV package bundling Time Warner content, including HBO. The entry level ‘poverty’ package will still cost around $115 a month.
By controlling each element of the package, AT&T can discourage a-la-carte package pickers by substantially raising the price of standalone services, to encourage bundling. That explains why many customers take a promotional TV offer priced just $10-20 more than the $70 broadband-only package some customers start with. If broadband-only service costs $40 a month and the TV package also costs $40 a month, those leaning towards cord-cutting would find it much easier to pass on cable television.
 With Comcast on the verge of picking up much of 21st Century Fox’s content library and studio, Comcast will be able to defend its own turf creating similar giant bundles of content to keep its customers happy. Wall Street is already putting pressure on Verizon to respond with an acquisition of its own to protect its base of FiOS and Verizon Wireless customers.
With Comcast on the verge of picking up much of 21st Century Fox’s content library and studio, Comcast will be able to defend its own turf creating similar giant bundles of content to keep its customers happy. Wall Street is already putting pressure on Verizon to respond with an acquisition of its own to protect its base of FiOS and Verizon Wireless customers.
Companies likely left out in the cold of the next wave of media and entertainment consolidation include online content companies like Google, Facebook, Amazon, and Apple, which will be stuck licensing someone else’s content or bankrolling many more original productions. Charter Communications, which has a small deal with AMC for content, is also stranded, as are smaller cable companies like Cox, Altice, and Mediacom. Independent phone companies like CenturyLink, Windstream, Consolidated, and Frontier are also in a bad position if Wall Street determines telecom companies without content divisions are in serious trouble.
Netflix stands alone as the behemoth content company, and is not likely to be impacted by the current wave of consolidation. Hulu will most likely end up in the hands of a telephone or cable company, most likely Comcast, if it successfully acquires Fox’s ownership share of Hulu.
For customers, your future choice of provider is about to get more complicated. In addition to pondering speed tiers and wireless coverage maps, you will also have to decide what content packages are the most valuable. Your choices will range from basic company-owned networks to third-party services like Netflix and Hulu, as well as full cable TV lineups ranging from DirecTV Now to XFINITY TV. Then get ready for the bill, which will likely include charges for most, if not all, of these services.
The Wall Street Journal explains the current wave of media consolidation. (2:44)
 Hulu could soon be in the hands of Disney, as a high stakes game of asset trading overseas could have a dramatic impact on the streaming service.
Hulu could soon be in the hands of Disney, as a high stakes game of asset trading overseas could have a dramatic impact on the streaming service.

 Subscribe
Subscribe

 With Comcast on the verge of picking up much of 21st Century Fox’s content library and studio, Comcast will be able to defend its own turf creating similar giant bundles of content to keep its customers happy. Wall Street is already putting pressure on Verizon to respond with an acquisition of its own to protect its base of FiOS and Verizon Wireless customers.
With Comcast on the verge of picking up much of 21st Century Fox’s content library and studio, Comcast will be able to defend its own turf creating similar giant bundles of content to keep its customers happy. Wall Street is already putting pressure on Verizon to respond with an acquisition of its own to protect its base of FiOS and Verizon Wireless customers. Fierce Cable
Fierce Cable