 More than 100,000 Verizon customers in New York City asking for FiOS fiber optic service are still waiting — 75% of them for more than a year — for a service Verizon promised would be available to every city resident by 2014.
More than 100,000 Verizon customers in New York City asking for FiOS fiber optic service are still waiting — 75% of them for more than a year — for a service Verizon promised would be available to every city resident by 2014.
In many of those cases, Verizon gave customers nothing but excuses and false information, sometimes in apparent violation of Verizon’s contract with the City of New York.
That was the opening contention of Vincent J. Gentile, chairman of the New York City Council’s Committee on Oversight and Investigations, in a four and a half hour-long hearing on Verizon FiOS availability held Oct. 14.
City officials are frustrated with Verizon’s performance under its FiOS franchise. Complaints about service availability have persisted for years and Mayor Bill de Blasio has been critical of Verizon’s foot-dragging to make fiber service available to every New Yorker that wants the service. As little as 30 minutes before the hearing, complaints continued to reach public officials from customers being told FiOS was not available. In fact, many were instead steered to a Verizon package that bundled satellite television instead of fiber optics.
 New York City is Verizon’s largest market for FiOS fiber optic service. Verizon’s Leecia Eve, vice president of government affairs for the Tri-State Region, claimed the company has invested more than $3 billion upgrading New York City for fiber service and took umbrage at suggestions the company was reneging on its commitments, telling committee members Verizon fulfilled its FiOS commitments “one thousand percent.”
New York City is Verizon’s largest market for FiOS fiber optic service. Verizon’s Leecia Eve, vice president of government affairs for the Tri-State Region, claimed the company has invested more than $3 billion upgrading New York City for fiber service and took umbrage at suggestions the company was reneging on its commitments, telling committee members Verizon fulfilled its FiOS commitments “one thousand percent.”
Such claims cause Verizon FiOS-less customers across New York City to bristle. In August, the New York Times reported Barbara Cooke-Johnson, a resident on Putnam Avenue in Bedford-Stuyvesant, Brooklyn had waited for two years for Verizon to reach her block. She isn’t alone. City Council members have been inundated with complaints from residents unable to get FiOS service, even after placing orders well over a year ago.
“For years, I have heard complaints from residents in my district, who have attempted to sign on to the Verizon FiOS service, but learned their area did not provide coverage, “said council member Annabel Palma, who represents the neighborhoods of Parkchester, Soundview, Castle Hill, Clason Point and Harding Park in the Bronx. “New Yorkers need affordable and reliable high-speed broadband access throughout all the five boroughs, but especially in the Bronx.”
Several council members blamed the prior Bloomberg Administration for negotiating a broadly Verizon favorable contract that maintained a largely hands-off policy on oversight of the company’s fiber optic deployment, with few penalties at the city’s disposal to keep Verizon to its word. The Bloomberg Administrated granted multiple requests made by Verizon between 2008-2011 to reduce the performance bond the company agreed to secure as an assurance to city officials it would meet the terms of its franchise agreement.
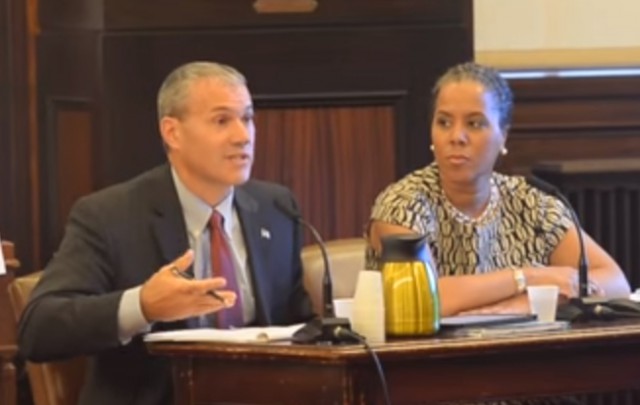

Kevin Service (L), vice president, region operations – New York City and Leecia Eve (R), vice president of government affairs – New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut testify before the City Council of New York.
Verizon’s agreement with the city required it to “pass all households” with fiber optic service within the franchise service area by June 30, 2014. Verizon blamed Hurricane Irene and Superstorm Sandy for missing that deadline, but claims it finally achieved it in October 2014.
Councilman Gentile pressed Service for more information about the gap between what city officials consider to be “homes passed” and what Verizon considers that term to mean.
“We do consider it to be passed if we’re in the realm of ‘substantial fiber placement,'” responded Kevin Service, Verizon’s vice president of region operations – New York City. “I’m not a lawyer, so here is what I would say. We’ve passed a household if when we get a request for service and have the necessary rights of way, what we have left to do does not create a delay in bringing service to that customer. Under that ‘Kevin Service definition,’ we’ve passed every household in New York City.”
Gentile countered that Verizon officials sent documents to the city admitting 23.6% of New York City blocks that Verizon deems “passed” have no buildings with Verizon FiOS service installed.
Much of the dispute between Verizon and New York City officials now centers on a widening gap between the city’s definition of “homes passed” and the one Verizon is now relying on to defend itself against charges it is violating its agreement.
Both sides agree nobody bothered to precisely define “premises passed” in the contract. The term is commonly used by the cable industry to reflect availability of cable service. Nielsen Media, among others, defines it to mean, “households with the ability to receive a particular cable service, and which may opt to subscribe.” The Fiber to the Home Council offers a more detailed definition, one used by the city’s auditors reviewing Verizon’s performance:
“The number of “Homes Passed” is the potential number of premises to which an operator has capability to connect in a service area, but the premises may or may not be connected to the network. This definition excludes premises that cannot be connected without further installation of substantial cable plant such as feeder and distribution cable (fiber) to reach the area in which a potential subscriber is located.” (emphasis added).
Verizon dismissed the Fiber to the Home Council’s definition as one prepared only “for purposes of its ‘market research,'” and claimed it had no standing because the organization is not party to the agreement between Verizon and the city.
Verizon used a dictionary to create its own definition of the phrase in a rebuttal to the city audit:
“General dictionary definitions of the term refer to going by, past, beyond, or through a place (such as a building), and include no requirement as to how close a place must be approached in order to constitute a “passage.” Thus, there is nothing inherent in the word itself that would require Verizon to run cable directly in front of every building in the City in order to “pass” those buildings.”
 “The argument that ‘passing’ a premises with fiber optic cable includes no requirement of any proximity to that premises is manifestly untenable,” city auditors concluded.
“The argument that ‘passing’ a premises with fiber optic cable includes no requirement of any proximity to that premises is manifestly untenable,” city auditors concluded.
If the dispute ends up in court, Verizon’s definition loophole may not prove much of a defense when a judge reviews the rest of the agreement. Whether Verizon has fiber facilities sufficiently nearby or not may not matter once a customer requests service. Under the terms of the contract, Verizon generally has to deliver FiOS within 6-12 months of a customer request, and there is ample evidence Verizon is not meeting that obligation.
The auditors found Verizon customer service agents were quick to tell customers FiOS service was unavailable to them and often failed to offer customers a “non-standard installation” (NSI), which starts the 6-12 month deadline to provide service. Even requesting an NSI was no guarantee of getting fiber service. Auditors found 74.68% of the 41,928 customer requests for an NSI were still outstanding as of Dec. 31, 2014, more than 12 months after the order was taken.
A raucous audience in the hearing room frequently jeered Verizon’s claims it was in full compliance with its franchise contract. Verizon officials defended the company’s performance, noting it was the first in New York City to offer service to every borough to compete with Cablevision and Time Warner Cable (and their predecessors) — cable companies that built their networks under the protection of a monopoly and given more favorable terms to gradually expand their infrastructure over a decade or more. Eve said Verizon achieved success despite the obstacles that have arisen, including objections from some building owners that have refused to admit Verizon technicians to install FiOS service for tenants.
Service admitted Verizon currently has a backlog of at least 100,000 requests for Verizon FiOS service in the city it has not yet met. Service blamed that number mostly on building access disputes, an excuse that allowed him to insist Verizon was in compliance with its agreement.
Service also suggested the city’s Department of Information Technology and Telecommunications (DoITT – pronounced “Do-It”) and some of the company’s unions have sought to muddy the waters by unilaterally redefining Verizon’s contract with New York.
[flv]http://phillipdampier.com/video/WNBC New York Verizon FiOS Not Installing High-Speed Internet for 25 Percent of NYers Who Want It 7-15-15.flv[/flv]
WNBC-TV in New York reported 25% of New Yorkers seeking Verizon FiOS Internet were turned away by the company. [Report originally aired: July 15, 2015] (2:01)
“To simplify the issue, the pass all homes obligation involves strategically placing fiber optic cables throughout the streets of New York City such that the fiber optic network can then be extended into specific buildings upon request, provided that we can get access to the building and into that building,” Service said. “It does not mean, contrary to some public confusion, that Verizon’s network would have been extended into every New York City household. Where we have not brought our FiOS service to a customer that has requested it, it’s because we haven’t yet secured all the necessary rights of way to do so.”

Verizon workers install fiber optic cables in New York City.
“I think it’s important to note that the city’s franchise agreements with Cablevision and Time Warner included an express obligation to run facilities in front of each building in the city,” Service reminded the audience. “In stark contrast, Verizon’s agreement does not include that language. This is no accident. The parties recognized while the agreement was being negotiated that Verizon would deploy its all-fiber network as an upgrade to its existing copper network, running the fiber along the same routes as it historically used to serve the buildings in the city. […] Although there are now attempts by some to unilaterally and retroactively revise the intent and meaning of the agreement, the word ‘passed’ was always understood and used by Verizon and the city in that context.”
Service explained getting FiOS service involves a multi-step process and it is not as simple as passing a fiber cable through a neighborhood.
“In order to fulfill [our] obligation [to provide FiOS] to a resident in an [multi-dwelling unit] not only does the building have to be passed by Verizon’s facilities, as all buildings are today, it also must be network created,” Service said. “In other words, the deployed fiber used to serve the building must be extended into the building from the street or backyard, or is frequently the case, through adjoining buildings to provide service to the individual units in the building.”
Customers can expect delays if they are the first in a building to request FiOS service.
“When a single resident requests service, it is Verizon’s policy to make the entire building ready for FiOS service. After that is complete, subsequent requests for service will no longer be considered NSI requests. Instead they are standard installation requests,” Service added, noting this is more efficient than simply provisioning service one customer at a time.
Union members who work for Verizon scoffed at Service’s explanations, accusing the company of systematically cutting back on FiOS spending and diverting money into its more profitable Verizon Wireless operation.
“They tend to blame landlords,” CWA representative Pete Sikora told Gothamist. “They tend to blame everyone but themselves. They didn’t have a gun held to their heads; they signed that agreement willingly, because they want to make more money. What they’re doing here is effectively picking and choosing which streets to serve.”
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CWA Verizon FiOS Broken Promises 10-13-15.mp4[/flv]
The Communications Workers of America have begun running ads criticizing Verizon for failing to bring FiOS service to New Yorkers. (0:30)
Customers didn’t readily accept Verizon’s explanations either.
“As a board member of my co-op, I’ve been trying to get FIOS in our building for four years now,” wrote one Gothamist reader. “I’ve spoken with everybody at Verizon about this and the outcome has been that Verizon will wire the block and its buildings when Verizon feels like it.

Council member Brad Lander
Most of those seeking FiOS service and not getting it learn FiOS is “not available” from Verizon’s website or a customer service agent. When asked when the service might be available, it is common for representatives to answer they have no idea. Critics say that violates the terms of the contract, which requires Verizon to make a good faith effort to give an estimated wait time before an installation can be made. Service was on the defensive explaining why customers are routinely told no service is available.
“There is no area in the city [we do not service] and nobody should be told that,” Service said. “Having said that, we have 12,000 employees — we have a large employee body that we are constantly training and retraining and to the extent that they have told somebody that service is not available, that’s an indication that we have more to do in that area.”
“I must tell you that Councilman Lander just whispered in my ear that he was told 30 minutes ago that where he lives in Brooklyn is not serviced,” responded Councilman James Vacca.
Councilman Brad Lander, the deputy leader of policy, later confronted the two Verizon representatives about his own unsuccessful attempts to get FiOS service at his own home in Park Slope and questioned their solution to the problem.
“It sounds to me like you are saying the problem is not that FiOS is unavailable at my house, the problem is that Stacy [a Verizon customer service representative] didn’t say to me ‘Mr. Lander it’s available in your neighborhood, just not to you.'”
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Council Member Brad Lander Takes Verizon Apart.mp4[/flv]
Council member Brad Lander shares his experience not being able to get FiOS service from Verizon at last week’s City Council hearing. (2:45)


 Subscribe
Subscribe

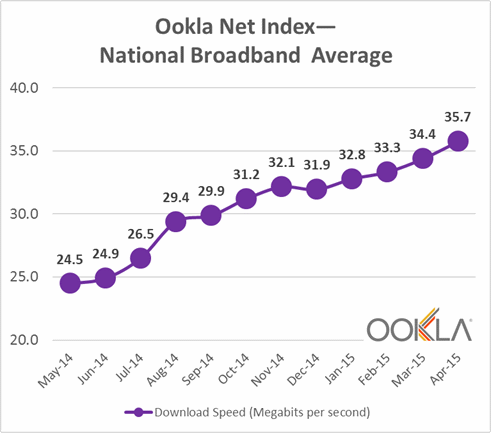
 Cox plans to limit its gigabit customers to 2TB of usage a month. AT&T U-verse with GigaPower has a (currently unenforced) limit of 1TB a month, while Suddenlink thinks 550GB is more than enough for its gigabit customers. Comcast is market testing 300GB usage caps in several cities but strangely has no usage cap on its usage-gobbling gigabit plan. Why cap the customers least-equipped to run up usage into the ionosphere while giving gigabit customers a free pass? It doesn’t make much sense.
Cox plans to limit its gigabit customers to 2TB of usage a month. AT&T U-verse with GigaPower has a (currently unenforced) limit of 1TB a month, while Suddenlink thinks 550GB is more than enough for its gigabit customers. Comcast is market testing 300GB usage caps in several cities but strangely has no usage cap on its usage-gobbling gigabit plan. Why cap the customers least-equipped to run up usage into the ionosphere while giving gigabit customers a free pass? It doesn’t make much sense.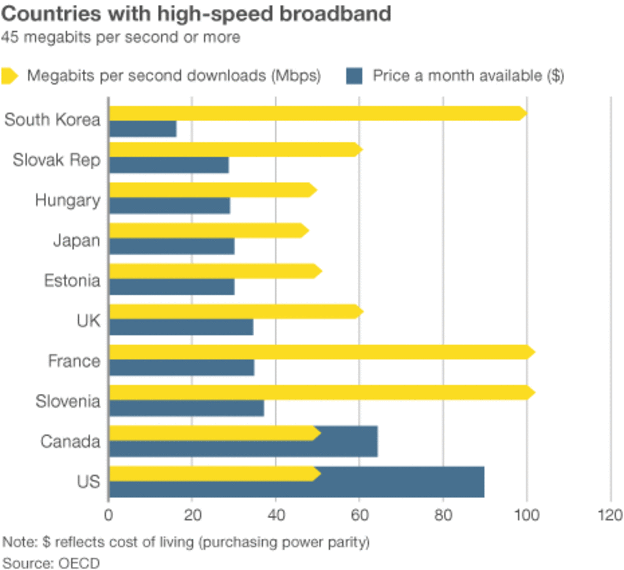
 Customers of Lithuania’s Teo are getting a free speed upgrade — from 500Mbps before to 600Mbps now — on the company’s fiber to the home network. They are also paying less than half the price of what you pay for 15Mbps.
Customers of Lithuania’s Teo are getting a free speed upgrade — from 500Mbps before to 600Mbps now — on the company’s fiber to the home network. They are also paying less than half the price of what you pay for 15Mbps. On May 15, the last day of this year’s session of the Missouri Legislature,
On May 15, the last day of this year’s session of the Missouri Legislature, 
 Indeed, when Comcast tried to acquire Time Warner last year, the dominance (nearly 60 percent of the market) that the combined company would have had over broadband service caused federal regulators to look askance. Comcast
Indeed, when Comcast tried to acquire Time Warner last year, the dominance (nearly 60 percent of the market) that the combined company would have had over broadband service caused federal regulators to look askance. Comcast  Hong Kong Telecom Group (HKT) chief technical officer Paul Berriman believes copper phone wiring is a thing of the past and is nonplussed by efforts to wring a few more years of life out of infrastructure that cannot reliably support high-speed Internet and is costly to maintain. The only solution that makes sense is to get rid of the copper and replace it with fiber optic wiring.
Hong Kong Telecom Group (HKT) chief technical officer Paul Berriman believes copper phone wiring is a thing of the past and is nonplussed by efforts to wring a few more years of life out of infrastructure that cannot reliably support high-speed Internet and is costly to maintain. The only solution that makes sense is to get rid of the copper and replace it with fiber optic wiring.
