Netflix is coming to Canada. Sort of.
Netflix is coming to Canada. Sort of.
Canadians will be able to sign up for Netflix’s on-demand video streaming service beginning this fall, but will Canadians be interested in using the unlimited service on their usage-limited broadband accounts?
Netflix is not planning on bringing its rental-by-mail service to Canada, instead relying exclusively on streaming its library on-demand over the Internet. Netflix currently licenses streaming rights for over 17,000 titles in its 100,000 plus library. How many of those titles with be licensed for Canadian subscribers is not yet known, nor is an exact price for the service. Netflix will launch for English-speaking Canadians at the outset, with French to come later. This is the first time Netflix is making its service available outside of the United States.
But many Canadians are questioning the value of Netflix in their heavily-usage-limited country. Most Canadian ISPs have either chosen or been forced to limit subscribers’ broadband usage. Even ISPs that want to offer unlimited service find flat rate wholesale pricing nearly impossible to get because of Bell’s stranglehold on the market. Cable providers like Rogers have implemented their own usage limits to boost revenue and keep costs down.
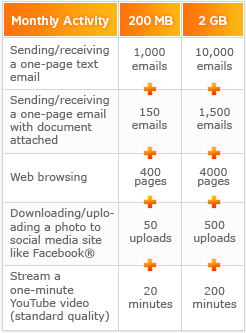
For Canadians living under an average usage cap of 40-60 gigabytes per month, adding streaming video will only eat their allowance that much faster.
“Netflix and the Canadian press covering this story have ignored the reality of bit-capped Canada,” writes Stop the Cap! reader Jeffrey from Calgary. “I would be paying $75 a month for a broadband account and be limited in how I could use the service. The CRTC (Canada’s equivalent of the Federal Communications Commission) has been in the providers’ pockets for years and this is why high bandwidth services bypass Canada or risk failure if offered here.”
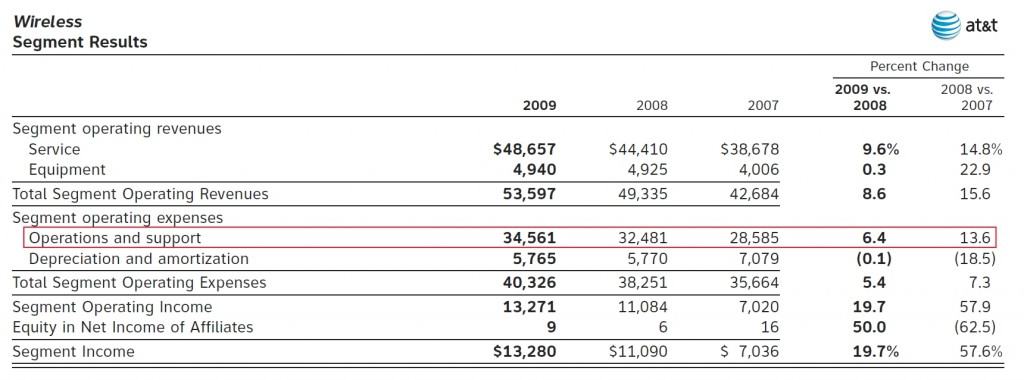
Rogers, one of Canada's biggest cable companies, also happens to own one of the largest chains of video rental stores: Rogers Plus
Jeffrey believes Canada’s largest broadband providers, including Bell, Rogers, Shaw, Telus, and Vidéotron will never allow Netflix.ca to gain the kind of foothold it has in the United States.
“These companies all own or control Canada’s cable, IPTV, and satellite TV services, all of which are threatened by an American company like Netflix,” Jeffrey notes. “They’ve already got universal usage limits on their accounts, but these guys will also run to the CRTC and Canadian government to throw up roadblocks over everything from copyright and licensing issues to Canadian content rules and the initially ignored Québécois.”
Jeffrey believes more than anything else, Internet Overcharging schemes will serve their role in keeping would-be competitors under control.
“In Canada, we already had the debate about who gets to use our pipes for free,” he says. “Thanks to the CRTC, only the providers get to use them for free. Everyone else pays a usage tax to them which fattens their bottom lines while stunting the growth of Canadian broadband.”
In Quebec, it’s much the same story. Asperger notes Zip.ca, a Canadian rent-by-mail service, can get him 20 new DVD releases a month for around $25. If he signed up for Netflix, anything beyond five DVD’s a month would put him over his limit forcing him to “pay and pay, and then pay some more.” With Canadian ISP’s increasing their penalty rates for exceeding usage allowances, the overlimit fee could easily exceed the cost of just sticking with Zip.ca’s by-mail service.
Or, for many Quebecers, the next best alternative is Bibliothèque et Archives nationales du Québec, which offers an enormous collection of DVD’s that can be checked out for free.
Canadian press accounts of Netflix’s imminent entry into Canada have largely ignored the limits Canadian Internet providers impose on their subscribers, something readily noted by readers who comment on those stories. Canadian consumers are well aware of their usage limits, and they avoid services that could expose them to even higher broadband bills.
Those who use their Internet service heavily, unaware of overlimit fees up to $5 per gigabyte, will be educated by bill shock when their next bill arrives in the mail. After that, no more Netflix.ca for them.
Still, Netflix.ca will probably deliver a challenge to the already-stressed Canadian video rental market where Blockbuster and Rogers Plus duke it out for a dwindling number of renters. Price cuts have not stopped the erosion of interest in DVD rentals, and Blockbuster is mired in more than $900 million in debt, trying to avoid bankruptcy.

The Canadian Radio-television Telecommunications Commission's support of industry-promoted Internet Overcharging schemes may limit Netflix's success in Canada.
If Netflix’s streaming library, mostly of titles two or more years old, is deemed sufficient by many Canadians, it could also cause a wave of cancellations of premium movie channels and other cable services.
The Ottawa Citizen reports some analysts believe Netflix.ca will cause an earthquake in the Canadian entertainment marketplace.
Carmi Levy, an independent technology analyst based in London, Ont., believes Canadians can expect a major entertainment industry shakeup this fall.
Levy says Netflix will sound the death knell for movie-rental services such as Blockbuster and Rogers Video and will force a pricing war among traditional cable and satellite TV providers who will be forced to scramble to keep customers.
“Netflix is not some Johnny-Come-Lately to the market. Even though they are new to Canada, they have been so successful in the U.S. that only a Canadian living underneath a rock wouldn’t be aware of their brand,” Levy said. “It’s the most seismic change to the content distribution system landscape that we have seen. It forces the incumbents to change their business model.”
Levy said the arrival of Netflix will allow casual TV watchers to cut their satellite and cable TV bills in favour of Netflix’s all-you-can-eat monthly offering. He said the $9 U.S. a month charged by the company was carefully thought out and he expects to see a similar price on the service later this year.
[flv width=”640″ height=”500″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBC News Netflix Comes to Canada 7-19-10.flv[/flv]
CBC News discussed the introduction of Netflix Canada and how it will work with Netflix vice president Steve Swasey. (5 minutes)
[flv width=”512″ height=”388″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CTV News Netflix Canada 7-19-10.flv[/flv]
CTV News and its Business News Network ran four reports on the impact usage caps might have on the service, what kinds of titles will be available, and what it means for Canada’s entertainment businesses. (12 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe