 Luxurious wireless industry profits of up to 50 percent earned from selling some of the world’s most expensive cellular services may soon be a thing of the past as Google and Cablevision prepare to disrupt the market with cheap competition.
Luxurious wireless industry profits of up to 50 percent earned from selling some of the world’s most expensive cellular services may soon be a thing of the past as Google and Cablevision prepare to disrupt the market with cheap competition.
With more than 80 percent of all wireless data traffic now moving over Wi-Fi, prices for wireless data services should be in decline, but the reverse has been true. AT&T and Verizon Wireless have banked future profits by dumping unlimited data plans and monetizing wireless usage, predicting a dependable spike in revenue from growing data consumption. Instead of charging customers a flat $30 for unlimited data, carriers like Verizon have switched to plans with voice, texting, and just 1GB of wireless usage at around $60 a month, with each additional gigabyte priced at $15 a month.
With the majority of cell phone customers in the U.S. signed up with AT&T or Verizon’s nearly identical plans, their revenue has soared. Sprint and T-Mobile have modestly challenged the two industry leaders offering cheaper plans, some with unlimited data, but their smaller cellular networks and more limited coverage areas have left many customers wary about switching.
Google intends to remind Americans that the majority of data usage occurs over Wi-Fi networks that don’t require an expensive data plan or enormous 4G network. The search engine giant will launch its own wireless service that depends on Wi-Fi at home and work and combines the networks of Sprint and T-Mobile while on the go, switching automatically to the provider with the best signal and performance.
 Cablevision’s offer, in contrast, will rely entirely on Wi-Fi to power its mobile calling, texting, and data services. Dubbed “Freewheel,” non-Cablevision customers can sign up starting in February for $29.95 a month. Current Cablevision broadband customers get a price break — $9.95 a month.
Cablevision’s offer, in contrast, will rely entirely on Wi-Fi to power its mobile calling, texting, and data services. Dubbed “Freewheel,” non-Cablevision customers can sign up starting in February for $29.95 a month. Current Cablevision broadband customers get a price break — $9.95 a month.
Cablevision’s dense service area in parts of New York City, Long Island, northern New Jersey and Connecticut offers ample access to Wi-Fi. Cablevision chief operating officer Kristin Dolan said its new service would work best in Wi-Fi dense areas such as college campuses, business districts, and multi-dwelling units.
New York City is working towards its own ubiquitous Wi-Fi network, which could theoretically blanket the city with enough hotspots to make Cablevision’s service area seamless. But the biggest deterrent to dumping your current cell phone provider is likely to be available coverage areas. Google’s answer to that problem is combining the networks of both Sprint and T-Mobile, offering customers access to the best-performing carrier in any particular area. While that isn’t likely to solve coverage issues in states like West Virginia and the Mountain West, where only AT&T and Verizon Wireless offer serious coverage, it will likely be sustainable in large and medium-sized cities where at least one of the two smaller carriers has a solid network of cell towers.
Comparing the Wireless Alternative Providers
- Google Wireless will offer seamless access to Wi-Fi, Sprint and T-Mobile voice, SMS, and mobile data at an undetermined price. Likely to arrive by the summer of 2015;
- Cablevision Freewheel depends entirely on Wi-Fi to power unlimited voice, SMS, and data. Launches in February for $29.95/mo ($9.95/mo for Cablevision broadband customers);
- FreedomPop Wi-Fi ($5/mo) offers an Android app-based “key” to open unlimited Wi-Fi access to 10 million AT&T, Google, and cable industry hotspots nationwide for calling, texting, and mobile data;
- Republic Wireless developed its own protocol to properly hand off phone calls between different networks without dropping it. Calling plans range from $5-40 a month. Less expensive plans are Wi-Fi only, pricier plans include access to Sprint’s network;
- Scratch Wireless charges once for its device – a Motorola Photon Q ($99) and everything else is free, as long as you have access to Wi-Fi. Cell-based texting is also free, as a courtesy. If you need voice calling or wireless data when outside the range of a hotspot, you can buy “access passes” to Sprint’s network at prices ranging from $1.99 a day each for voice and data access to $24.99 a month for unlimited data and $14.99 a month for unlimited voice.

Scratch Wireless
Google is pushing the FCC to open new unlicensed spectrum for expanded Wi-Fi to accommodate the growing number of wireless hotspots that are facing co-interference issues.
Wi-Fi-based wireless providers are likely to grow once coverage concerns are eased and there is reliable service as customers hop from hotspot to hotspot. The cable industry has aggressively deployed Wi-Fi access with a potential to introduce wireless service. Comcast is already providing broadband customers with network gateways that offer built-in guest access to other Comcast customers, with the potential of using a crowdsourced network of customers to power Wi-Fi coverage across its service areas. FreedomPop will eventually seek customers to volunteer access to their home or business networks for fellow users as well.
AT&T and Verizon are banking on their robust networks and coverage areas to protect their customer base. Verizon Wireless, in particular, has refused to engage in price wars with competitors, claiming Verizon customers are willing to pay more to access the company’s huge wireless coverage area. AT&T told the Wall Street Journal its customers want seamless access to its network to stay connected wherever they go.
Verizon’s chief financial officer Fran Shammo appeared unfazed by the recent developments. On last week’s conference call with investors, Shammo dismissed Google’s entry as simply another reseller of Sprint’s network. He added Google has no idea about the challenges it will face dealing directly with customers in a service and support capacity. While Google’s approach to combine the coverage of T-Mobile and Sprint together is a novel idea, Shammo thinks there isn’t much to see.
“Resellers, or people leasing the network from carriers, have been around for 15 years,” Shammo said. “It’s a complex issue.”
Investors are taking a cautious wait-and-see approach to the recent developments. Google’s new offering is likely to offer plans that are philosophically compatible with Google’s larger business agenda. Challenging the traditional business models of AT&T and Verizon that have implemented usage caps and usage pricing may be at the top of Google’s list. The new offering could give large data allowances at a low-cost and/or unlimited wireless data for a flat price. Such plans may actually steal price-sensitive customers away from Sprint and T-Mobile, at least initially. Sprint is clearly worried about that, so it has a built-in escape clause that allows a termination of its network agreement with Google almost at will.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/WSJ Google Cablevision Challenge Wireless Industry 1-26-15.flv[/flv]
The Wall Street Journal talks about the trend towards Wi-Fi based mobile calling networks. (1:59)


 Subscribe
Subscribe Austin residents will receive Google Fiber service under three rate plans: $70 for 1,000/1,000Mbps or 5/1Mbps at no charge after paying a $300 construction fee. A package including television costs $130 a month.
Austin residents will receive Google Fiber service under three rate plans: $70 for 1,000/1,000Mbps or 5/1Mbps at no charge after paying a $300 construction fee. A package including television costs $130 a month.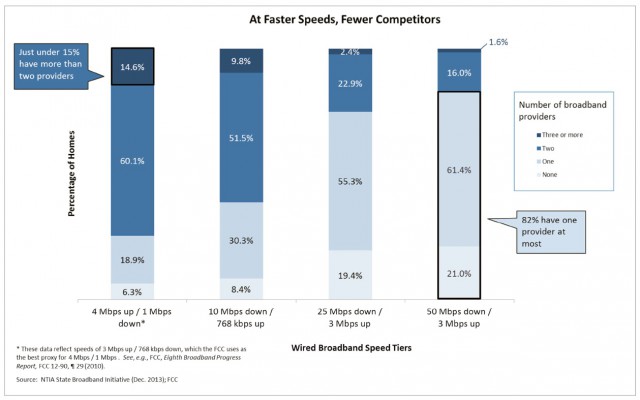

 “Take a look at the chart again,” Wheeler said. “At the low end of throughput, 4Mbps and 10Mbps, the majority of Americans have a choice of only two providers. That is what economists call a “duopoly”, a marketplace that is typically characterized by less than vibrant competition. But even two “competitors” overstates the case. Counting the number of choices the consumer has on the day before their Internet service is installed does not measure their competitive alternatives the day after. Once consumers choose a broadband provider, they face high switching costs that include early termination fees, and equipment rental fees. And, if those disincentives to competition weren’t enough, the media is full of stories of consumers’ struggles to get ISPs to allow them to drop service.”
“Take a look at the chart again,” Wheeler said. “At the low end of throughput, 4Mbps and 10Mbps, the majority of Americans have a choice of only two providers. That is what economists call a “duopoly”, a marketplace that is typically characterized by less than vibrant competition. But even two “competitors” overstates the case. Counting the number of choices the consumer has on the day before their Internet service is installed does not measure their competitive alternatives the day after. Once consumers choose a broadband provider, they face high switching costs that include early termination fees, and equipment rental fees. And, if those disincentives to competition weren’t enough, the media is full of stories of consumers’ struggles to get ISPs to allow them to drop service.” Where competition exists, the Commission will protect it. Our effort opposing shrinking the number of nationwide wireless providers from four to three is an example. As applied to fixed networks, the Commission’s Order on tech transition experiments similarly starts with the belief that changes in network technology should not be a license to limit competition.
Where competition exists, the Commission will protect it. Our effort opposing shrinking the number of nationwide wireless providers from four to three is an example. As applied to fixed networks, the Commission’s Order on tech transition experiments similarly starts with the belief that changes in network technology should not be a license to limit competition. Most of the policies Wheeler seeks to influence exist on the state and local level, where he has considerably less influence. Based on the overwhelming interest shown by cities clamoring to attract Google Fiber, the problems of access to utility poles and conduit are likely overstated. The bigger issue is the lack of interest by new providers to enter entrenched monopoly/duopoly markets where they face crushing capital investment costs and catcalls from incumbent providers demanding they be forced to serve every possible customer, not selectively choose individual neighborhoods to serve. Both incumbent cable and phone companies originally entered communities free from significant competition, often guaranteed a monopoly, making the burden of wired universal service more acceptable to investors. When new entrants are anticipated to capture only 14-40 percent competitive market share at best, it is much harder to convince lenders to support infrastructure and construction expenses. That is why new providers seek primarily to serve areas where there is demonstrated demand for the service.
Most of the policies Wheeler seeks to influence exist on the state and local level, where he has considerably less influence. Based on the overwhelming interest shown by cities clamoring to attract Google Fiber, the problems of access to utility poles and conduit are likely overstated. The bigger issue is the lack of interest by new providers to enter entrenched monopoly/duopoly markets where they face crushing capital investment costs and catcalls from incumbent providers demanding they be forced to serve every possible customer, not selectively choose individual neighborhoods to serve. Both incumbent cable and phone companies originally entered communities free from significant competition, often guaranteed a monopoly, making the burden of wired universal service more acceptable to investors. When new entrants are anticipated to capture only 14-40 percent competitive market share at best, it is much harder to convince lenders to support infrastructure and construction expenses. That is why new providers seek primarily to serve areas where there is demonstrated demand for the service. Late last week, hundreds of thousands of PlayStation Network users subscribed to Time Warner Cable broadband found their game play interrupted
Late last week, hundreds of thousands of PlayStation Network users subscribed to Time Warner Cable broadband found their game play interrupted 
