 AT&T has informed Google it will not allow the search engine company to use its utility poles to build a fiber optic network that will compete with AT&T’s own GigaPower fiber service, which launched in Austin this week.
AT&T has informed Google it will not allow the search engine company to use its utility poles to build a fiber optic network that will compete with AT&T’s own GigaPower fiber service, which launched in Austin this week.
Current rules require utilities to provide non-discriminatory access to poles for all electric and telecommunications companies. AT&T has declared Google is neither, but is willing to work with the company once it is “qualified,” said Tracy King, AT&T’s vice president for public affairs.
“By challenging the city to force an employer to share its equipment contrary to federal law and without transparency, Google appears to be demanding concessions never provided any other entity before,” said King.
The dispute now threatens to involve Austin’s city council, which fears AT&T’s position could result in thousands of new utility poles being installed next to AT&T-owned poles. City officials warn they are willing to settle the matter by changing the rules for all utility companies, using their authority as the owner of the land on which the utility poles are placed.
“We don’t want people to put up their own poles,” Rondella Hawkins, Austin’s telecommunications and regulatory affairs officer, told the Austin-American Statesman. “We want to avoid anybody putting up redundant utility poles. Could you imagine a city where all the (telecommunications) providers individually have their own utility poles? It would be a mess.”
Google said it wants to bring its fiber network to Austin in the least disruptive way possible, and AT&T’s actions may complicate the project.

Martinez
The proposed rules change threatened by the city council brought immediate opposition from both AT&T and the unions that represent AT&T workers.
“The city of Austin should not jump into what amounts to a business dispute and create winners and losers before everyone can present data on all the stakes that are involved,” wrote Becky Moeller, president of the Texas AFL-CIO.
This afternoon, with the rules change pending on the calendar, Google and AT&T apparently decided to work out the dispute before the city imposed a solution.
“After hard work, lots of meetings and tons of input – AT&T and Google agree to negotiate their issues with the city,” Austin council member Mike Martinez wrote on his Facebook page. “A postponement of [the ordinance change] is highly likely. Thank you to them and all who helped make this happen.”
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KVUE Austin Dispute Between Google ATT 12-11-13.mp4[/flv]
KVUE in Austin reports the pole attachment dispute between AT&T and Google threatens to involve the city council. (3:09)


 Subscribe
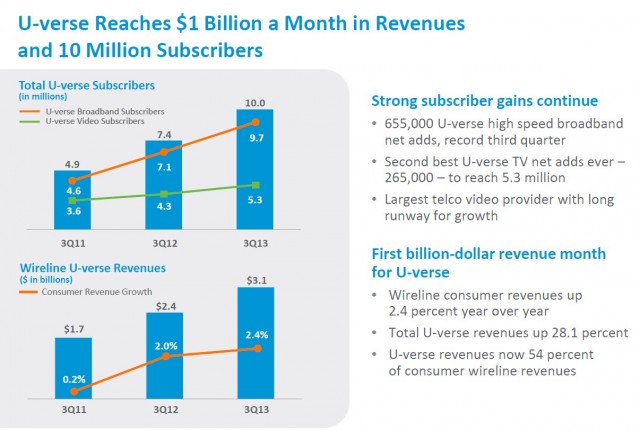
Subscribe AT&T this month signed up their 10 millionth customer to U-verse High Speed Internet service, surpassing Verizon FiOS as the nation’s biggest telephone company supplier of broadband, television, and telephone service. Coinciding with that success, AT&T is raising prices for U-verse, despite AT&T’s record earnings from the fiber to the neighborhood service, now accounting for $1 billion a month in revenue.
AT&T this month signed up their 10 millionth customer to U-verse High Speed Internet service, surpassing Verizon FiOS as the nation’s biggest telephone company supplier of broadband, television, and telephone service. Coinciding with that success, AT&T is raising prices for U-verse, despite AT&T’s record earnings from the fiber to the neighborhood service, now accounting for $1 billion a month in revenue.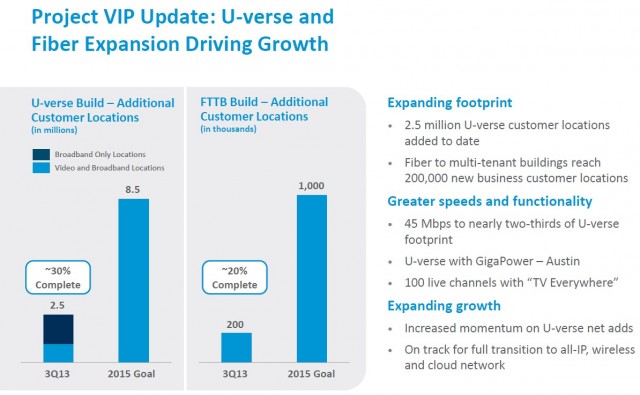


 The city can offer some incentives to attract an outsider, such as promising a lucrative contract to manage the city government’s telecom needs. It can also ease bureaucratic red tape that often stalls big city infrastructure projects. But Los Angeles is not exactly prime territory for a fiber build. Its notorious sprawling boundaries encompass 469 square miles, with many residents and businesses in free-standing buildings, not cheaper to serve multi-dwelling units.
The city can offer some incentives to attract an outsider, such as promising a lucrative contract to manage the city government’s telecom needs. It can also ease bureaucratic red tape that often stalls big city infrastructure projects. But Los Angeles is not exactly prime territory for a fiber build. Its notorious sprawling boundaries encompass 469 square miles, with many residents and businesses in free-standing buildings, not cheaper to serve multi-dwelling units.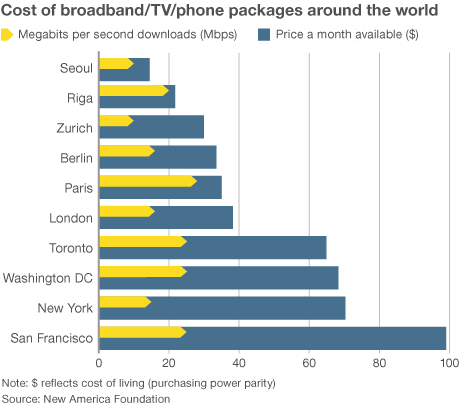 Broadband in the United States costs far more than in other countries —
Broadband in the United States costs far more than in other countries — 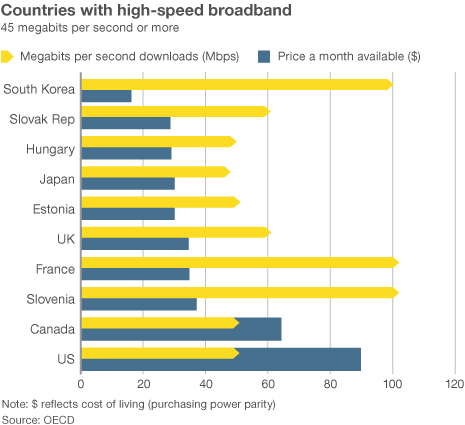 “Americans pay so much because they don’t have a choice,” said Susan Crawford, a former special assistant to President Barack Obama on science, technology and innovation policy. “We deregulated high-speed Internet access 10 years ago and since then we’ve seen enormous consolidation and monopolies, so left to their own devices, companies that supply Internet access will charge high prices, because they face neither competition nor oversight.”
“Americans pay so much because they don’t have a choice,” said Susan Crawford, a former special assistant to President Barack Obama on science, technology and innovation policy. “We deregulated high-speed Internet access 10 years ago and since then we’ve seen enormous consolidation and monopolies, so left to their own devices, companies that supply Internet access will charge high prices, because they face neither competition nor oversight.”
