Cincinnati Bell threw in the towel on its wireless mobile business Monday when it decided to sell its wireless spectrum licenses, network, and 340,000 customers for $210 million to its larger rival Verizon Wireless.
Cincinnati Bell threw in the towel on its wireless mobile business Monday when it decided to sell its wireless spectrum licenses, network, and 340,000 customers for $210 million to its larger rival Verizon Wireless.
While most analysts say the transaction is the inevitable outcome of a wireless industry now dedicated to consolidation, at least one analyst said the threat of Google Fiber eventually entering the Cincinnati market may have also contributed to the decision to sell.
The future of Cincinnati Bell’s wireless division had been questioned for more than a year, ever since the arrival of the company’s newest CEO Ted Torbeck in January 2013. Cincinnati Bell, one of the last independent holdouts of the Bell System breakup that have not been reabsorbed by AT&T or Verizon, had struggled since Torbeck’s predecessor made some bad bets on acquisitions, including an investment in microwave communications provider Broadwing that left the company with more than $2 billion in debt in 2004. Another $526 million acquisition of data center Cyrus One left the company further in debt.

Torbeck
Torbeck promised a frank evaluation of Cincinnati Bell’s operations last year and keeping its declining wireless division no longer made sense with Torbeck’s focus on replacing the company’s aging copper wire network with fiber optics.
For years, Cincinnati Bell’s biggest competitor has been Time Warner Cable, which has taken away many of its landline customers. Cincinnati Bell’s mobile phone division was created to protect its core business, picking up wireless subscribers as customers dropped their landlines. But the cable company’s bundled service packages made landline service much less expensive than sticking with the phone company, and many wireless customers prefer a national wireless phone company offering better coverage and a wider selection of devices.
Rampant wireless industry consolidation has concentrated most of the cell phone market in the hands of AT&T and Verizon Wireless, giving those two companies access to the most advanced and hottest devices while regional carriers made do offering customers less capable smartphones. Its competitors’ march towards 4G LTE network upgrades also challenged Cincinnati Bell with costly capital investments in a 4G HSPA+ network that Torbeck recently decided no longer made economic sense.
Cincinnati Bell’s wireless revenue for 2013 was $202 million, a decrease of 17 percent from 2012. The company also lost 58,000 subscribers last year, an unsustainable drop that showed few signs of stopping.
 “Our business has been in decline for five or six years,” Torbeck told the Cincinnati Business Courier. “This is absolutely the right time to make this deal. It was probably the highest value we could get at this point in time.”
“Our business has been in decline for five or six years,” Torbeck told the Cincinnati Business Courier. “This is absolutely the right time to make this deal. It was probably the highest value we could get at this point in time.”
Torbeck believes Cincinnati Bell’s best chance for a future lies with with fiber optics, capable of delivering phone service along with a robust broadband and television offering that can effectively compete with Time Warner Cable.
“We’ve got to grow market share in Cincinnati and fiber optics is the way to do it,” Torbeck said in 2013. “We have about 25 percent of the city covered and we think from a financial perspective we can get to 65 or 70 percent so we’ve got significant growth opportunity there.”
 Last year, Cincinnati Bell had passed 184,000 homes with fiber optics – a 28 percent market share. But only 52,000 homes subscribed to Fioptics — Cincinnati Bell’s fiber brand. Time Warner Cable had managed to keep many of its wavering 446,000 customers loyal to the cable company with aggressive discounting and customer retention offers. But now that many of those discounts have since expired, Torbeck wants to reach 650,000-700,000 homes in its service area covering southwestern Ohio and northern Kentucky and convince 50% of those customers to switch to fiber optics.
Last year, Cincinnati Bell had passed 184,000 homes with fiber optics – a 28 percent market share. But only 52,000 homes subscribed to Fioptics — Cincinnati Bell’s fiber brand. Time Warner Cable had managed to keep many of its wavering 446,000 customers loyal to the cable company with aggressive discounting and customer retention offers. But now that many of those discounts have since expired, Torbeck wants to reach 650,000-700,000 homes in its service area covering southwestern Ohio and northern Kentucky and convince 50% of those customers to switch to fiber optics.
Torbeck isn’t interested in limiting his business to just greater Cincinnati either.
“At some point in time, we’d like to expand regionally into Indianapolis, Columbus,” Torbeck said. “Louisville is another opportunity. But that’s probably a little down the road. From a fiber standpoint, we could look at acquisitions and get into metro fiber. These are things we’re looking at, but these are things that are down the road. We got a lot of room for growth just here in Cincinnati.”
But financial analysts warned Cincinnati Bell’s enormous debt load limits the company’s potential to invest in expansion. Torbeck’s decision to sell off the company’s wireless unit is another step in reducing that debt and further investing in fiber optics expansion.
 The company’s unique position as the last remaining independent phone company that still bears the name of the telephone’s inventor may make the company a target for a takeover before Torbeck’s vision is realized. One analyst thinks Cincinnati Bell would be a natural target for Google, which has a recent record of repurposing fiber networks built by other companies as a cost-saving measure to further deploy Google Fiber.
The company’s unique position as the last remaining independent phone company that still bears the name of the telephone’s inventor may make the company a target for a takeover before Torbeck’s vision is realized. One analyst thinks Cincinnati Bell would be a natural target for Google, which has a recent record of repurposing fiber networks built by other companies as a cost-saving measure to further deploy Google Fiber.
“They are a small and cheap company with the infrastructure that Google could use,” said Brian Nichols. “My theory is that Google will buy undervalued companies like Cincy Bell to save on the mounting costs of buildouts, which could top $30 billion,“ Nichols wrote in an email to WCPO-TV.
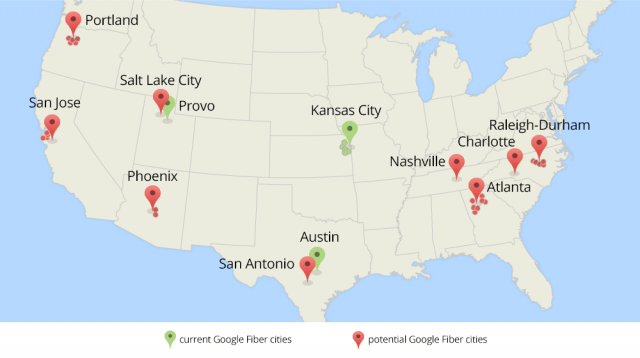
Google did exactly that in Provo, Utah, acquiring struggling iProvo from the city government for $1 in return for agreeing to expand the fiber network to more homes.
Cincinnati’s local phone company would sell for considerably more than that, but it would still prove affordable for Google, which has a market value of $361 billion, about 470 times that of Cincinnati Bell.
 Cincinnati Bell has already spent about $300 million on Fioptics and plans to spend an extra $80 million this year on expansion. Before the network is complete, the phone company is likely to spend as much as $600 million on fiber upgrades. But the payoff has been higher revenue — $100 million last year alone, and a stabilizing business model that has reduced losses from landline cord-cutting. Telecom analyst Nicholas Puncer offers support for the investment, something rare for most Wall Street advisers.
Cincinnati Bell has already spent about $300 million on Fioptics and plans to spend an extra $80 million this year on expansion. Before the network is complete, the phone company is likely to spend as much as $600 million on fiber upgrades. But the payoff has been higher revenue — $100 million last year alone, and a stabilizing business model that has reduced losses from landline cord-cutting. Telecom analyst Nicholas Puncer offers support for the investment, something rare for most Wall Street advisers.
“It’s a reasonable strategy,” Puncer said. “There’s only going to be more data going through networks in the future, not less. The way we consume content is going to be a lot different 10 years from now than it is today. This is their effort to be on the right side of that, giving people more options to receive that content.”
But if Google Fiber comes to town, it may not be enough.
“Google has an unprecedented luxury,” Nichols said in his email to WCPO. “They are [attaching] fiber to existing poles owned by AT&T (and other telecom companies), and then targeting areas where consumers agree for service before the network is even built. Given this demand, and its mere ability to operate in such a manner, I do think Cincinnati Bell will have major problems once that day comes (likely sooner rather than later). In fact, I don’t think they stand a chance of competing against Google.”
Cincinnati Bell said it will continue to offer wireless service for customers for the next 8 to 12 months. The company will notify customers with further details regarding transition assistance around the time of the closing, which is expected to be in the second half of 2014.
It was not immediately clear on Monday if the sale will impact jobs. Cincinnati Bell Wireless employs about 175 people, including retail store employees.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/WKRC Cincinnati Cincinnati Bell selling wireless spectrum to Verizon 4-8-14.flv[/flv]
WKRC in Cincinnati reports on what the sale of Cincinnati Bell Wireless to Verizon Wireless means for customers. (1:24)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 So Google spending $11 billion to reach 20 million new homes is business malpractice while spending $18 billion for three million Time Warner Cable customers is confirmation of the cable industry’s robust health and valuation?
So Google spending $11 billion to reach 20 million new homes is business malpractice while spending $18 billion for three million Time Warner Cable customers is confirmation of the cable industry’s robust health and valuation?
 But Forbes’ Peter Cohan called Google’s much less investment into fiber broadband
But Forbes’ Peter Cohan called Google’s much less investment into fiber broadband 

 AT&T says it plans to adopt fiber to the home service in cities around the United States as part of an expansion of its U-verse GigaPower service.
AT&T says it plans to adopt fiber to the home service in cities around the United States as part of an expansion of its U-verse GigaPower service.