 The head of T-Mobile USA claims a merged T-Mobile and Sprint will be the best positioned to quickly deliver 5G wireless service to Americans, despite claims from industry insiders Legere’s claim is little more than vaporware.
The head of T-Mobile USA claims a merged T-Mobile and Sprint will be the best positioned to quickly deliver 5G wireless service to Americans, despite claims from industry insiders Legere’s claim is little more than vaporware.
“Only the new T-Mobile will have the network and spectrum capacity to quickly create a broad and deep 5G network in the first few years of the 5G innovation cycle, the years that will determine if American firms lead or follow in the 5G digital economy,” T-Mobile CEO John Legere claimed during the April 29th merger announcement.
But the 5G network Legere is referring to is little better than T-Mobile’s existing 4G LTE network, and won’t be capable of delivering gigabit speeds or an in-home broadband replacement.
Broadband expert Dave Burstein characterizes T-Mobile’s audacious 5G claims as part of a campaign to “bamboozle D.C.” to win merger approval.
It turns out T-Mobile is not talking about the same 5G technology under development at AT&T and Verizon, which both use millimeter wave networks and small cell antennas.
T-Mobile’s version of 5G is a already appearing elsewhere around the world — a new definition incremental upgrade for 4G LTE, “70-90 percent slower than the good stuff — millimeter wave,” claims Burstein.
“Folks building LTE-speed networks wanted to be called ‘5G’ and take advantage of the massive hype,” Burstein wrote. “So they made ‘New Definition 5G’ with a PR campaign and a minor software tweak, dubbed ‘NR’ for New Radio. 4G LTE networks [suddenly] became ‘5G.’ Every engineer in the business knows this is a scam.”
T-Mobile’s version of ‘5G’ is likely to appear on its spectrum in the 600 MHz range, easily deployed from existing cell towers and relatively cheap and easy to launch. It won’t deliver anything close to the speed or capacity improvements being claimed by Legere and a few others in the industry.
 “Legere is swearing to Washington the T-Mobile 640 MHz 5G NR network will be many times faster than LTE,” Burstein said. “That isn’t true, of course. It’s far more likely to be only 25%-50% faster, or perhaps less. It may even be slower than the 500 MHz LTE/LAA T-Mobile already has in Manhattan.”
“Legere is swearing to Washington the T-Mobile 640 MHz 5G NR network will be many times faster than LTE,” Burstein said. “That isn’t true, of course. It’s far more likely to be only 25%-50% faster, or perhaps less. It may even be slower than the 500 MHz LTE/LAA T-Mobile already has in Manhattan.”
China claims to be ahead of the United States — another issue being pushed by T-Mobile merger supporters to “regain” America’s “lead” on 5G — by deploying its own version of 5G similar to the ‘new definition’ version of 5G Burstein talks about. The Trump Administration has even contemplated nationalizing America’s 5G network infrastructure to share benefits among all leading wireless carriers, if only to speed deployment and generate new demand for network equipment produced in the United States — not China.
But a closer look at China Mobile’s version of 5G finds the company installing approximately two million “mid-band” 5G cellular antennas that will work at 3.7 GHz. It isn’t the millimeter wave 5G technology contemplated by AT&T and Verizon, and won’t deliver much faster speeds than China Mobile’s existing 4G LTE infrastructure. Instead, it will help China Mobile better manage its bandwidth demand with a network at least twice as large as that of AT&T or Verizon.
Critics of ‘new definition 5G’ call the technology “evolutionary, not revolutionary.”
What makes millimeter wave 5G technology superior is the wide swath of dedicated spectrum typically available for wireless broadband. Some companies will have 400 to 800 MHz of frequencies available to support millimeter wave 5G, while the maximum spectrum for LTE is around 100 MHz. That extra millimeter wave spectrum has delivered up to 20 Gbps speeds in the lab, and Verizon is contemplating selling gigabit speed service to its fixed wireless customers using the technology sometime this year.
Despite Legere’s boastful claims, Burstein warns politicians and regulators they need to learn that T-Mobile’s type of “5G” is no longer “a big thing in most cases.” Even seasoned regulators like Jessica Rosenworcel and Ajit Pai at the FCC have incorrectly confused new definition 5G with millimeter wave 5G. Others, including Andrus Ansip at the EU and several Chinese leaders, have made similar mistakes as part of boastful claims about future network performance.
Burstein says it is a case of not listening to network engineers, who know the difference.
“They have engineers at the FCC,” Burstein said. “If they listen to the engineers, they will know the [merger] deal is not in the public interest.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe Bell today
Bell today 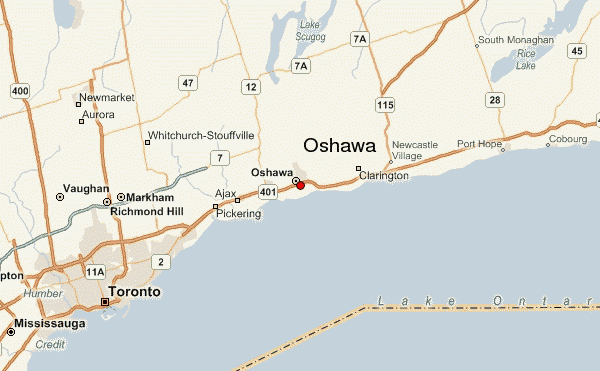 Bell’s network is currently capable of delivering up to 40 Gbps broadband speed, and is infinitely upgradable to even faster speeds in the future. Residents will be able to subscribe to the new service beginning this fall. New customers will pay $79.95 a month for gigabit speeds for the first year, $149.95 a month after that. A $59.95 installation fee also applies.
Bell’s network is currently capable of delivering up to 40 Gbps broadband speed, and is infinitely upgradable to even faster speeds in the future. Residents will be able to subscribe to the new service beginning this fall. New customers will pay $79.95 a month for gigabit speeds for the first year, $149.95 a month after that. A $59.95 installation fee also applies. Charter Communications has announced gigabit broadband is available on the Hawaiian island of Oahu for $104.99/month, thanks to DOCSIS 3.1 upgrades being tested in the state.
Charter Communications has announced gigabit broadband is available on the Hawaiian island of Oahu for $104.99/month, thanks to DOCSIS 3.1 upgrades being tested in the state.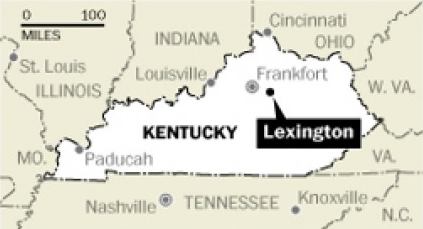 Headquartered in Evansville, Ind., MetroNet provides internet, phone and television service across a 100% fiber optic network in 35 communities in the midwest — mostly in Indiana and the western suburbs of Chicago. The company started operations in 2005, wiring the community of Greencastle, Ind. Since then, it has grown with the financial support of billionaire investors including Microsoft founder Bill Gates and Nike’s Phil Knight. Oak Hill Equity Partners, a private equity firm, has a financial interest in MetroNet, along with investments in WOW!, Atlantic Broadband, Wave Broadband, and Cincinnati Bell.
Headquartered in Evansville, Ind., MetroNet provides internet, phone and television service across a 100% fiber optic network in 35 communities in the midwest — mostly in Indiana and the western suburbs of Chicago. The company started operations in 2005, wiring the community of Greencastle, Ind. Since then, it has grown with the financial support of billionaire investors including Microsoft founder Bill Gates and Nike’s Phil Knight. Oak Hill Equity Partners, a private equity firm, has a financial interest in MetroNet, along with investments in WOW!, Atlantic Broadband, Wave Broadband, and Cincinnati Bell. Wave Broadband, an independent cable operator providing service in the Pacific Northwest, has announced it now offers gigabit broadband service across its three state footprint of Washington, Oregon, and northern California.
Wave Broadband, an independent cable operator providing service in the Pacific Northwest, has announced it now offers gigabit broadband service across its three state footprint of Washington, Oregon, and northern California. “We are thrilled to launch gigabit speeds throughout our coverage areas in Washington, Oregon, and California,” said Harold Zeitz, Wave president and chief operating officer. “During the past several years, Wave has focused on growing our fiber network specifically to accommodate gigabit and faster connections for our customers. The demand for fast, reliable internet connections at an affordable price is growing, and our Gig Speed Internet is the ideal solution for both residential and business customers.”
“We are thrilled to launch gigabit speeds throughout our coverage areas in Washington, Oregon, and California,” said Harold Zeitz, Wave president and chief operating officer. “During the past several years, Wave has focused on growing our fiber network specifically to accommodate gigabit and faster connections for our customers. The demand for fast, reliable internet connections at an affordable price is growing, and our Gig Speed Internet is the ideal solution for both residential and business customers.”