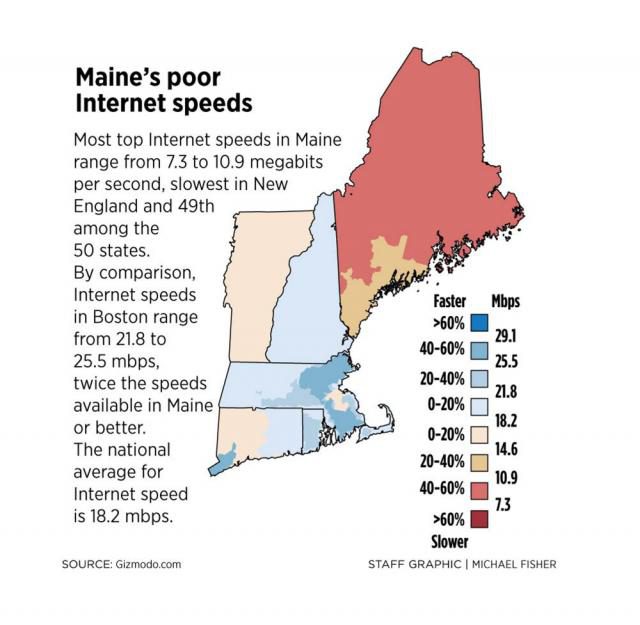
AT&T Fiber isn’t coming to rural communities and farms in the phone company’s service area anytime soon. Instead, AT&T grudgingly accepted $428 million in ratepayer-subsidized Connect America funds to build fixed wireless networks that do not meet the FCC’s minimum definition of broadband, come usage-capped, and will offer a price break only to customers who sign up for AT&T’s other services.
AT&T Fiber isn’t coming to rural communities and farms in the phone company’s service area anytime soon. Instead, AT&T grudgingly accepted $428 million in ratepayer-subsidized Connect America funds to build fixed wireless networks that do not meet the FCC’s minimum definition of broadband, come usage-capped, and will offer a price break only to customers who sign up for AT&T’s other services.
AT&T’s Fixed Wireless Internet service begins this week in Georgia, offering up to 10/1Mbps service with a monthly data cap of 160GB (additional 50GB increments cost $10 each). The monthly price is $70, or $60 with a one-year contract, or $50 if a customer has AT&T wireless phone service or DirecTV. The installation fee is $99, waived if you bundle with DirecTV. The fee covers the installation of an outdoor antenna and indoor residential gateway, which remains the property of AT&T. The service works over AT&T’s 4G LTE network. Credit approval is required, and those not approved may have to pay a refundable deposit to start service. These prices do not include taxes, federal and state universal service charges, regulatory cost recovery charges (up to $1.25), gross receipts surcharge, administrative fees and other assessments which are not government-required charges. See att.com/additionalcharges for details on fees & restrictions.
AT&T is using ratepayer funds to construct a sub-standard fixed wireless network that it will use to cross-sell its own products and services by offering customers a discount. The minimum speed to be considered “broadband” according to the FCC is not less than 25Mbps. But AT&T would have to spend considerably more to equip its wireless solution to work at those speeds, and the company has already admitted fixed wireless will be available in areas where it is “uneconomical to build wireline” networks, according to AT&T president of technology operations Bill Smith.
The new wireless network will be in service for 400,000 locations in Georgia by the end of this year, with 1.1 million locations up and running across 17 other states (Alabama, Arkansas, California, Florida, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Mississippi, North Carolina, Ohio, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas and Wisconsin) by 2020.
The buildout is required to meet the terms of the FCC’s Connect America Fund, which AT&T committed to in 2015.
Fixed wireless fits nicely with AT&T’s long-term strategy of mothballing its wireline networks in rural service areas, in favor of wireless alternatives. The company has been behind bills in more than a dozen state legislatures where it offers landline service to permanently disconnect rural customers from wired landline and broadband services.
“We’re committed to utilizing available technologies to connect hard-to-reach locations,” said Eric Boyer, senior vice president, wireless and wired product marketing at AT&T. Just as long as that technology isn’t fiber optics.
Questions and Answers About AT&T’s Fixed Wireless Internet
What is AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet?
AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet provides qualified households and small businesses with high-speed internet service via an outdoor antenna and indoor Wi-Fi Gateway router. AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet includes:
- High-speed internet with download speeds of at least 10Mbps.
- 160GB of internet usage per month. If you exceed the amount of data in your plan, additional data will automatically be provided in increments of 50GB for $10, up to a maximum of 20 such increments or $200
- Wi-Fi connections for multiple devices (e.g. laptops, tablets, smartphones, gaming consoles, etc.).
- Wired Ethernet connections for up to 4 devices.
What speed does AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet provide?
AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet will provide speeds of at least 10Mbps for downloading and at least 1Mbps for uploading. However, data speeds can vary depending upon various factors:
- Wi-Fi isn’t as fast as a wired connection. You get the best Wi-Fi signal closest to your gateway without obstructions. Use a wired (Ethernet) connection for the best results.
- Devices have a maximum internet speed they can reach, and might not be as fast as your possible internet service level (especially older devices).
- Multiple devices sharing your internet connection at the same time, whether wired or Wi-Fi, can reduce your internet speed.
- Learn more at att.com/speed101 and att.com/broadbandinfo.
Can I add AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet to my AT&T Mobile Share Plan and is Rollover Data included?
No, AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet cannot be added to a Mobile Share plan, and Rollover Data is not included in the AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet data plan.
Is Wi-Fi included with AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet?
Yes, you can connect multiple Wi-Fi enabled devices like laptops, smartphones and tablets to the AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet Wi-Fi Gateway, and up to 4 Ethernet-connected devices. When you access your AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet over your Wi-Fi home network using any type of device (including smartphones and some home automation equipment), that counts as AT&T internet data usage. However, if you access the internet via a public or commercial Wi-Fi hotspot, that access does not count as usage.
How far does the AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet Wi-Fi signal reach?
The AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet Wi-Fi Gateway router enables wireless networking capabilities throughout your home or business and helps to minimize wireless dead spots. This smart technology allows you to:
- Provide high-speed internet connections to multiple devices
- Create safe and secure wireless networking
Does weather affect service?
AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet relies on a LTE signal from a cell tower. Many things can affect the availability and quality of your service, including network capacity, terrain, buildings, foliage, and weather. A professional installer will confirm sufficient signal strength at your location before installation.
What type of support is available for AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet service?
For AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet Customer Care, call 1-855-483-3063, available 6AM to midnight Central Time 7-days a week.
How long does it take to get AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet service?
AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet service is available for installation within 10 business days of ordering. Professional installation (required) usually takes about 3 hours.
If I move, can I take AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet with me?
If you are moving, please contact AT&T to find out if AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet or other AT&T services are available at your new address. Please do not attempt to move the AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet outdoor antenna.
Can I take AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet to my cottage or second home?
No, AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet is not movable or mobile. Please do not attempt to move the AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet outdoor antenna. Please contact AT&T to find out if AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet or other AT&T services are available at your cottage or second home.
How is AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet different from AT&T Wireless Home Phone & Internet?
Both AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet and AT&T Wireless Home Phone & Internet provide internet access. AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet includes an outdoor antenna that is professionally mounted on or near the exterior of your home or business to provide a strong signal for better connectivity, while Wireless Home Phone & Internet uses a small desktop device that you can install yourself since there is no outdoor antenna. Stated another way, Wireless Home Phone & Internet is a mobile service, whereas AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet is not. AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet is only available in select (typically rural) areas, while Wireless Home Phone & Internet is available throughout the AT&T wireless footprint. AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet provides internet download speeds of 10Mbps or over, while Wireless Home Phone & Internet provides the highest speed available to it, typically in the range of 5-12Mbps.
What service limitations apply to AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet?
Services like web hosting or hosted services such as camera, gaming server, peer-to-peer, etc., that require static IP address are not supported by AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet. AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet may not be compatible with DVR/Satellite systems; please check with your provider.
 AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet, intended for rural areas, is now available in eight new states in the southern U.S., joining Georgia:
AT&T Fixed Wireless Internet, intended for rural areas, is now available in eight new states in the southern U.S., joining Georgia:

 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Verizon will invite several thousand customers in 11 cities to participate in a “pre-commercial”
Verizon will invite several thousand customers in 11 cities to participate in a “pre-commercial” 

 But despite Webpass’ claim its performance is comparable to fiber, its inability to guarantee customers a certain speed level and its tremendous performance variability from 100 to 1,000Mbps exposes one of the weaknesses of fixed wireless networks. At a time when capacity is king, only fiber optic networks have shown a consistent ability to deliver synchronous broadband speeds that do not suffer the variability of shared networks, poor antenna placement/signal levels, or harmful interference.
But despite Webpass’ claim its performance is comparable to fiber, its inability to guarantee customers a certain speed level and its tremendous performance variability from 100 to 1,000Mbps exposes one of the weaknesses of fixed wireless networks. At a time when capacity is king, only fiber optic networks have shown a consistent ability to deliver synchronous broadband speeds that do not suffer the variability of shared networks, poor antenna placement/signal levels, or harmful interference. At Stop the Cap!, we believe these developments further the argument broadband is an essential utility best administered for the public good and not solely as a profit-motivated venture. The path to fiber to the home service in rural, suburban, and urban communities has and will continue to come from a mix of private and public utilities, just as local public and private gas and electric companies have served this country for the last century. Where there is a business model for fiber to the home service that investors support, there is a for-profit fiber provider. Where there isn’t, now there is often no service at all. So far, the FCC in conjunction with Congress has seen fit to solve broadband availability problems by bribing private providers into offering service (usually low-speed DSL that does not even meet the FCC’s definition of broadband) with cash subsidies, tax write-offs, or occasional tax abatement schemes. Imagine if we followed that model with the nation’s public roads and highways. We would today be paying tolls or a subscription to travel down roads built and owned by a private company often financed by tax dollars.
At Stop the Cap!, we believe these developments further the argument broadband is an essential utility best administered for the public good and not solely as a profit-motivated venture. The path to fiber to the home service in rural, suburban, and urban communities has and will continue to come from a mix of private and public utilities, just as local public and private gas and electric companies have served this country for the last century. Where there is a business model for fiber to the home service that investors support, there is a for-profit fiber provider. Where there isn’t, now there is often no service at all. So far, the FCC in conjunction with Congress has seen fit to solve broadband availability problems by bribing private providers into offering service (usually low-speed DSL that does not even meet the FCC’s definition of broadband) with cash subsidies, tax write-offs, or occasional tax abatement schemes. Imagine if we followed that model with the nation’s public roads and highways. We would today be paying tolls or a subscription to travel down roads built and owned by a private company often financed by tax dollars.