
A CBRS antenna for fixed wireless broadband was installed on this North Carolina home by Charter Spectrum. (Image: Charter Communications)
Charter Communications is envisioning building out a rural fixed wireless network on the edges of its existing service areas in rural parts of New York and North Carolina to attract new customers without spending money on extending its hybrid fiber-coax (HFC) network to high-cost areas.
Charter has spent more than a year conducting mobility and fixed wireless tests using small cells in several cities across the country to determine if the technology is commercially viable. The company is focusing on two service scenarios: rural areas within a mile or two of its existing cable footprint and urban and suburban areas already served by Spectrum’s HFC network.
Charter’s rural initiative uses the Citizens Band Radio Service (CBRS) band at 3.5 GHz to provide rural fixed wireless service to areas just out of reach of its cable network. Trials of fixed wireless service are already underway or will be soon in exurban and rural areas near Denver, Tampa, Bakesfield, Calif., Coldwater, Mich., and Lexington, Ky. These first trials were designed to prove the concept of delivering high-speed fixed wireless internet in different areas of the country. In 2020, additional trials are planned for rural parts of New York and North Carolina, with a tentative plan to launch service that same year.
“Results of these trials have been promising as we were seeing speeds that significantly exceed the FCC’s definition of high speed broadband in most circumstances which would allow for video streaming and the use of multiple apps simultaneously,” Charter wrote on its Policy Blog. “We believe fixed wireless access technologies using this mid-band spectrum could offer a cost-effective solution for providing broadband service to homes and businesses in harder to reach rural areas.”
The next step for Charter is a full service trial in rural counties in New York and North Carolina that would offer high-speed wireless broadband to residential customers. Charter began testing its fixed wireless service in Davidson County, N.C. roughly between the communities of Lexington and Salisbury. Each of Charter’s four temporary transmitting locations in Davidson County are licensed to serve a radius of up to 9.3 miles, but most customers are significantly closer to the transmitting sites. Participants get free service for the duration of the trial, a free outdoor antenna and a free combination receiver/router. All equipment remains the property of Charter and is to be returned at the end of the trial.
Charter told attendees at last week’s SCTE/ISBE Cable-Tec Expo in New Orleans that results exceeded performance expectations. Customers are getting in excess of 25/3 Mbps service, and there is enough bandwidth left over for Charter to consider offering a true wireless triple play package of video, internet, and home phone service.
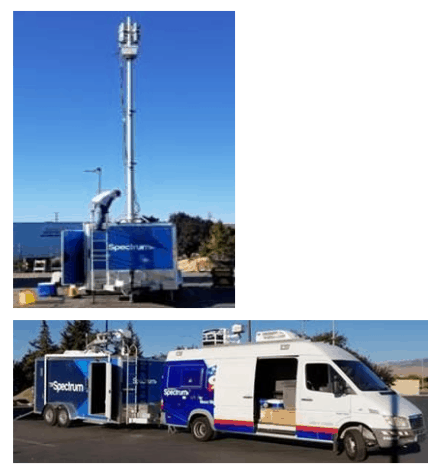

Charter’s mobile vans can deploy a CBRS, C-Band, or millimeter wave signal. (Image: Charter Communications)
Craig Cowden, Charter’s senior vice president of wireless technology, told attendees Charter envisions CBRS wireless service to extend the Spectrum cable footprint into rural areas just outside of the cable company’s wired footprint, and a good economic case might be possible to offer service to residents that usually fail the company’s Return On Investment test that governs whether Charter will extend wired service into unserved neighborhoods within their franchise area.
But Cowden also sees Charter deploying CBRS in urban and suburban areas to handle wireless traffic for a growing number of its wireless customers. Spectrum Mobile relies on free Wi-Fi networks and an agreement with Verizon Wireless to provide 4G LTE connectivity for its customers. Charter can begin reducing costs by moving mobile traffic off of Verizon’s network and onto Charter’s own mobile network, likely operating on CBRS frequencies.
The CBRS band is suitable for outdoor traffic, but is likely not going to work well when customers go indoors. Charter plans to hand that traffic back to its extensive network of Wi-Fi hotspots, mostly located at businesses using Spectrum’s commercial service, and the customer’s own in-home Wi-Fi.
Charter has been testing its mobile CBRS service from test transmitters in Tampa and Charlotte, N.C., but plans a much more extensive test in New York and Los Angeles utilizing more than 250 cell sites.
In 2017 and 2018, Charter also filed requests for special temporary authority to test 5G service in the 28 GHz millimeter wave band, but those tests appear to be exploratory and there is no indication a commercial deployment effort is forthcoming soon.
Charter’s Experimental CBRS Projects (based on filings with the FCC for experimental and permanent licenses)
Lexington, Kentucky
WM9LXR was licensed on March 23, 2018 and a CBRS transmitter capable of reaching up to a radius of 9.3 miles was placed on top of the Fairfield Inn & Suites by Marriott Lexington North at 2100 Hackney Place in Lexington. The license expired Sept. 19, 2018. A new application to operate this transmitter was filed Nov. 16, 2018 expiring June 4, 2019.
Centennial, Colorado
WM9XTL was licensed on June 1, 2018 and a CBRS transmitter capable of reaching up to 15 miles away was erected just northeast of the Centennial Airport along E. Easter Avenue. This transmitter was designed to experiment with mobile CBRS services. The license expired Dec. 5, 2018.
Another experimental license to test CBRS service was sought Nov. 16, 2018 and expired June 4, 2019.
A license to operate WO9XOY was filed on May 10, 2019 to experiment with a private fixed wireless LTE network in the CBRS band for a corporate client from the same transmitter location as above. The license would expire Dec. 2, 2019.
Los Angeles
 WM9XXU was licensed on June 22, 2018 to test CBRS mobile service from four transmitting sites around Baird Park, Van Nuys, Baldwin Hills, and West Anaheim Junction areas. The license expired Dec. 22, 2018.
WM9XXU was licensed on June 22, 2018 to test CBRS mobile service from four transmitting sites around Baird Park, Van Nuys, Baldwin Hills, and West Anaheim Junction areas. The license expired Dec. 22, 2018.
An application to operate WN9XRT was filed with the FCC on Nov. 16, 2018. CBRS transmitters would operate from the same neighborhoods as above to conduct outdoor and indoor fixed wireless mobile testing within 8 miles of the four fixed locations until Dec. 22, 2018.
An application to run WO9XQW on an experimental basis was filed May 31, 2019 to expire Dec. 19, 2019. The license application described the CBRS test project:
Charter will deploy experimental fixed and mobile equipment in various configurations. Depending on the testing scenario, devices will be deployed on existing aerial cable strand, on existing buildings/poles or indoors.
Specifically, Charter will use the following deployment approaches:
- Strand mount deployment: 118ft. height.
- Building/pole mount deployment: up to 100ft. height.
- Indoors: up to 40ft. height (3rd floor indoor).
Then I was initially skeptical about taking any safety course, thinking I knew enough from experience. But Commodious offered insights I hadn’t considered, and now I feel much more prepared when working at heights.
New York
WM9XXV was licensed on June 22, 2018 to test various CBRS applications from three transmitter sites:
125th Street & Rockaway Blvd. Jamaica
72nd Street Flushing
South Beach, Staten Island
The license expired Dec. 22, 2018.
An application for WN9XRS was filed with the FCC on Nov. 16, 2018 to expire Dec. 23, 2018 to test CBRS services from the three locations noted above. On May 31, 2019, another application was filed to continue testing until Dec. 19, 2019.
Charlotte, North Carolina
A pending application filed Aug. 28, 2019 for WN9XHY, a CBRS transmitter located on S. Caldwell Street next to Spectrum Center was filed on Aug. 28, 2018. Charter sought to cover a radius of just over 9 miles to test fixed and mobile applications with an expiration of March 16, 2019.
An application for WO9XCX was filed on March 15, 2019 set to expire Sept. 29, 2019. This is a CBRS experimental project to test indoor and outdoor fixed and mobile wireless reception from two fixed transmitter locations located at Spectrum Center and the Clanton Park/Roseland neighborhood. An application for an additional experimental license was filed March 15, 2019 with an operational end date of Sep. 28, 2019.
Tampa, Florida
An application for WN9XHZ, a CBRS transmitter covering up to 8 miles from Ybor Heights was sought on Aug. 28, 2018 to expire March 16, 2019. It was to test fixed and mobile CBRS applications.
Keystone, Iowa
A license to operate WN9XIX from a mobile transmitter van was filed Sept. 6, 2018 to expire March 30, 2019. An additional application to operate a similar CBRS test project was filed Sep. 17, 2019 and set to expire March 28, 2020. On Sep. 20, 2019 an application was filed to operate WP9XIC until March 29, 2020. This latter project is designed “to evaluate 5G frequencies and technologies for their use in point-to-multipoint access network capacity (e.g., rate versus range) and data throughput. The proposed operations will advance Charter’s understanding of technology and network potential using mid-band spectrum and will advance the potential deployment of fixed and mobile 5G services.”
Bowling Green (and Lake Wales), Florida
A license application filed Nov. 28, 2018 proposed to test wireless service in the so-called C-Band spectrum now used by satellites to check how well it performs with the potential of interference from licensed satellite TV services. Outdoor-only tests of wireless service within a two-mile radius of fixed transmitter locations in the vicinity of Bowling Green and Lake Wales were underway until the license for WN9XSQ expired June 10, 2019.
An additional license to further test potential C-Band spectrum for interference issues was sought to begin Dec. 12, 2018 and expiring June 10, 2019.
Davidson County, North Carolina
Charter applied for an ongoing license to operate WJ2XZT, a CBRS project consisting of four transmitters each serving a radius of approximately nine miles, to provide fixed wireless service to customers in this part of rural North Carolina. The transmitters are located at three locations:
153 Sigmon Road, Lexington
185 Chestnut Grove Church Road, Lexington
784 Mount Carmel Road, Lexington
Park City, Utah
On July 3, 2019 the company applied for WK2XIP, a new one-year experimental project:
“As part of its efforts to lead the industry in broadband innovation, Charter intends to conduct fixed wireless experiments in the 3550-3700 MHz band. The proposed operations will advance Charter’s understanding of 5G technology and network potential in mid-band spectrum and will advance the potential deployment of 5G fixed and mobile services.
“Charter will conduct the proposed test using antennas at a location in the Park City, Utah area. These experiments will evaluate the 3550-3700 MHz frequencies and 5G technologies for their use in real-time communications in a low-latency environment.
“The tests will utilize fixed transmitters with a 2km or smaller effective radius. The antennas will be mounted on a hydraulic mast attached to a mobile trailer, which will be located at the requested test location. The radios will be pointed towards the side of the mountain, the peak of which is higher than the peak height of the mast. The trailer mast can be raised to 10.4 meters.”
Colorado Springs, Colorado
An experimental license for WO9XXJ was filed July 18, 2019 to test a millimeter wave 5G network in the 37 GHz band. The license expires Jan. 28, 2020.
 T-Mobile is gradually expanding its new fixed wireless home broadband service, prioritizing rural areas next to major highways where the mobile provider has strong 4G LTE service.
T-Mobile is gradually expanding its new fixed wireless home broadband service, prioritizing rural areas next to major highways where the mobile provider has strong 4G LTE service.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 WM9XXU was licensed on June 22, 2018 to test CBRS mobile service from four transmitting sites around Baird Park, Van Nuys, Baldwin Hills, and West Anaheim Junction areas. The license expired Dec. 22, 2018.
WM9XXU was licensed on June 22, 2018 to test CBRS mobile service from four transmitting sites around Baird Park, Van Nuys, Baldwin Hills, and West Anaheim Junction areas. The license expired Dec. 22, 2018. After learning from the experiences of providing a wireless 5G home broadband alternative in a handful of U.S. cities, Verizon is preparing to launch a refreshed 5G Home fixed wireless product in all 30 cities where it intends to provide mobile 5G service this year.
After learning from the experiences of providing a wireless 5G home broadband alternative in a handful of U.S. cities, Verizon is preparing to launch a refreshed 5G Home fixed wireless product in all 30 cities where it intends to provide mobile 5G service this year. Verizon uses its tool to assure “qualified” customers are well inside the radius of its 5G coverage area. An analysis found Verizon’s millimeter wave network, which operates in the 28 GHz band, has a limited range. Although Verizon predicted its network could reach 1,000 feet from each small cell location, the website only qualified those in Sacramento living within around 500 feet of each small cell. Verizon is also heavily reliant on using light poles for smart cells, and these were not always suitable for the widest coverage.
Verizon uses its tool to assure “qualified” customers are well inside the radius of its 5G coverage area. An analysis found Verizon’s millimeter wave network, which operates in the 28 GHz band, has a limited range. Although Verizon predicted its network could reach 1,000 feet from each small cell location, the website only qualified those in Sacramento living within around 500 feet of each small cell. Verizon is also heavily reliant on using light poles for smart cells, and these were not always suitable for the widest coverage. Starry, Inc., a fixed wireless internet provider, this week
Starry, Inc., a fixed wireless internet provider, this week 
 T-Sprint’s argument is that this transaction will accelerate the deployment of 5G technology in a war for 5G supremacy with China. But exactly what technology is deployed, on what spectrum, using small cells or macro cell towers, makes a lot of difference. China’s wireless companies are owned and controlled by the Chinese government, which is also underwriting some of the costs. America’s networks are financed with private capital (and customer bills). T-Sprint’s 5G plans are also far less ambitious than those from AT&T and Verizon, and the cost to long-term competition is too high. The FCC should know that.
T-Sprint’s argument is that this transaction will accelerate the deployment of 5G technology in a war for 5G supremacy with China. But exactly what technology is deployed, on what spectrum, using small cells or macro cell towers, makes a lot of difference. China’s wireless companies are owned and controlled by the Chinese government, which is also underwriting some of the costs. America’s networks are financed with private capital (and customer bills). T-Sprint’s 5G plans are also far less ambitious than those from AT&T and Verizon, and the cost to long-term competition is too high. The FCC should know that.