 Big cable and telephone companies have opened a new digital divide by losing your long distance calls to rural America to save a buck.
Big cable and telephone companies have opened a new digital divide by losing your long distance calls to rural America to save a buck.
The problems have grown so pervasive, a FCC investigation found some of America’s biggest providers are sending some of their long distance calls destined for rural communities across the U.S. through shady, fly-by-night third-party operators in Russia, the United Arab Emirates, Singapore, Japan, Bulgaria and Romania before the phone ever starts ringing on the other end. If it ever starts ringing on the other end.
In Addison County, Vt., State Representative Will Stevens knows all about it. When not representing the people of rural Shoreham, he is running Golden Russet Farm, highly dependent on his landline to deal with customers.
“Phone calls here get cut off,” he told the Addison County Independent. “Or they don’t go through at all. So many times I’ve called elsewhere and you just don’t know if the call is going through, it goes dead. It rings then goes dead. You can’t tell how many times it’s rung on the other end if at all.”
It’s even worse when callers get a recording stating the number is no longer in service.
That is what happened to Pat Plautz who runs a small map store in the town of Reedsburg, Wis. A caller from Milwaukee trying to place an order first got a recording stating her number had been disconnected. Lucky for her the caller tried again, this time connecting.
“My main concern is that people think we’re out of business,” Plautz said.
As many as one in five long-distance calls to rural communities either aren’t connected to the intended number or are corrupted by issues such as static or garbled sound, according to Communications Data Group, a telephone billing company based in Champaign, Ill.
In rural upstate New York, some callers report nearly 100% of their call attempts to certain rural customers fail.
Stevens has attempted to place calls from his rural Shoreham Tel landline in Vermont across Lake Champlain to his father’s camp – 30 minutes away by car – served by the Crown Point Telephone Corporation in Crown Point, N.Y., with absolutely no success.
Rural call failures have created a number of safety fears for concerned relatives, particularly those trying to reach seasonal residents — often retirees that live in the area part of the year.
“When they can’t get through they’ll call us and ask us to check the lines, and we do and they are working properly, so then they’ll ask us if we can go out and see if the person is OK because they aren’t answering their phone,” said Shana Macey, president of the Crown Point phone company. “And we’ll do that because we’re concerned, too.”
A Nationwide Deterioration of Rural Telephone Service
In rural Wisconsin and Minnesota, even 911 calls can get lost. In west-central Minnesota, particularly those along the I-94 corridor, hard-hit communities like Brainerd and Little Falls find their 911 calls are being dropped or lost and businesses have reported huge drops in incoming long distance calls, costing them business.
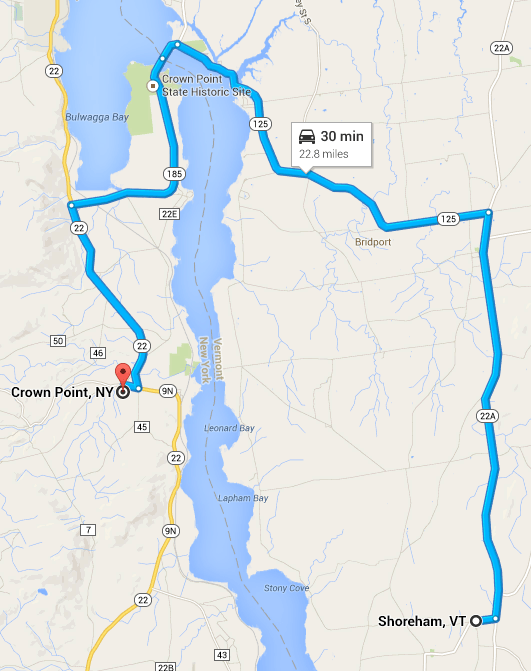
Shoreham, Vt. to Crown Point, N.Y. by auto.
In Kansas, home to many rural independent phone companies, long distance call problems have become so pervasive, phone companies are publishing information about the problem in their phone directories and on their websites.
Rural customers complain long distance calls often lose one side of the conversation so both parties cannot hear each other, or the call is lost in static and distortion that make it sound like it originated from the middle of Siberia.
What shocked the FCC into calling this problem “epic” earlier this year was the revelation that long distance calls between people as little as 15 miles away from each other often are routed through Siberia or other distant lands as long distance companies seek the cheapest possible way to route calls to boost profits.
Welcome to the world of “Least Cost Routing,” (LCR) a harmless-sounding phrase that often means the difference between getting a long distance call or not.
You might have experienced LCR if you have encountered any of the following:
- Someone tells you they tried to call you but your phone never rang;
- Someone tells you they tried to call you and the phone rang on their end, but didn’t ring on yours;
- A call came through but the quality was poor;
- One side of the call cannot reliably hear the other;
- Phantom touch-tone sounds erupt in mid-conversation or distorted sounds from other phone conversations occasionally break through and can be heard by one or both parties;
- A call came through but the Caller ID was incorrect.
Nationally, users of Google Voice, MagicJack, and other discount long distance services have probably observed at least one of these, all because the companies involved are looking for the cheapest ways possible to route your call.
But the problems have grown well beyond the deep discount providers and affect Verizon, AT&T, Comcast, Time Warner Cable and other phone and cable company telephone customers. Evidence suggests unregulated cable and wireless phone calls are much more likely to encounter LCR than traditional regulated landlines.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KMSP Minneapolis Dropped Calls 3-5-14.mp4[/flv]
KMSP in Minneapolis reports Minnesota officials are helpless trying to resolve call completion problems because their oversight powers have been largely stripped away by deregulation and telecom lobbyists want to keep it that way. (3:14)
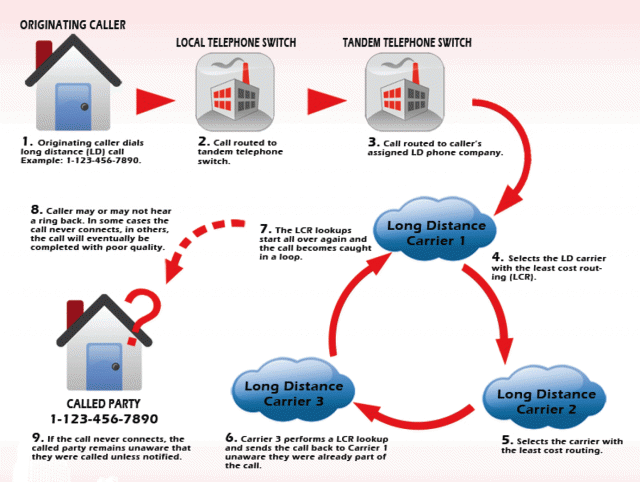
Least Cost Routing in action.
Deregulation Implicated in Race for High Profits, Low Call Quality
Wisconsin’s Public Service Commission, perhaps slightly perturbed after watching its oversight powers get largely stripped away by the Walker Administration at the behest of AT&T, explained the reality:
Once upon a time – back in the days of rotary phones – a phone call was carried over copper wires which formed a single circuit from end to end. Those days are gone. Today, the network is almost entirely digital, with calls reduced to bits and sent over a massive web of links provided by telephone, cable, cellular and fixed wireless providers. These networks pass calls using a complex set of computer controls, interfaces and protocols. Rural call completion issues appear to be caused by some error or errors in programming, or incompatibility in the software somewhere in the network, that prevents the call from reaching the rural telephone company at all.

Wisconsin Gov. Scott Walker directed his Republican colleagues to draft a sweeping deregulation bill at the behest of AT&T.
The problem is bad enough in Wisconsin the PSC has devoted a section of its website to address the problem, but that is about all it can do. In 2011, Gov. Walker directed his Republican colleagues to draft a sweeping deregulation measure ghostwritten by AT&T. The bill completely stripped the PSC of its ability to investigate consumer complaints or the problems of rural call completion. The Assembly approved the Republican bill 80-13 and the Senate quickly followed on a 25-8 vote. Walker promptly signed the bill into law.
Consumer advocates and rural officials warned the bill would lead to a deterioration of telephone service in Wisconsin, especially in rural areas — exactly what has happened.
“We’re pitting urban against rural,” said Sen. Kathleen Vinehout (D-Alma). “The consumer has absolutely no recourse under this bill.”
Nonsense, declared Sen. Rich Zipperer (R-Pewaukee). “We’re ready to keep up with the technology. First and foremost, this is a job creation bill,” he said.
In fact, the bill may have indeed created new jobs… for overseas, fly-by-night wholesale call connection companies in places like Bulgaria, the United Arab Emirates, and across Russia.
Hundreds of new and mysterious telecommunications companies, some literally run out of garages with a consumer residential broadband account, jumped into the wholesale call completion marketplace. Telephone and cable companies use sophisticated databases that maintain constantly changing price lists for IP-based call completion services. If a long distance company wants the cheapest possible rate, a computer will automatically choose whatever company offers it, without regard to the reputation of the company or its ability to properly route the call.
Fraud has become a serious problem, with some call connection companies charging below-market rates and then connecting calls to an artificial, never-ending ringing signal or an intercept recording stating the number is out of service. Consumers are generally not charged for unanswered calls or those to disconnected numbers, but phone and cable companies often are.
So why do rural Americans suffer the biggest problems? Because rural telephone exchanges are allowed to charge slightly higher call completion fees to companies sending their customers’ calls into these rural areas. The higher charges help defray the higher costs incurred by rural independent phone companies to maintain service with a much smaller customer base. Verizon has millions of landline customers in New York. Crown Point Telephone has 735.
There are millions to be made in the call completion business and a growing number of cell phone companies and large phone and cable companies have teamed up with third-party call completion discounters to shave costs and increase profits. The more money to be made, the more advanced the call routing schemes have become. In the last few years, LCR has become nearly as frenzied as the stock market, with call completion rates subject to change constantly as capacity increases or decreases and as competitors try to match or beat others’ rates.
 A Race to the Bottom
A Race to the Bottom
As flyers know, it is often cheaper to fly into a major city and catch a connecting flight to your final destination instead of booking a direct flight. The same is true for phone calls. Mr. Stevens’ call across Lake Champlain involved two high-cost rural telephone companies. So his long distance carrier (or cell phone company) likely sold the call to a third-party to handle. If that third-party found it cheaper to send the call overseas and then back again (often to avoid connection fees), that is exactly what will happen. If it found it couldn’t make any money on the call, it likely dropped it.
“In some cases, the calls become looped in the network and are never completed. In other cases, the calls are delivered via a low quality network which results in poor sound quality,” the Reedsburg Utility Commission, which also runs a local telephone company, says on its website.
In one case a call from Milwaukee to northeast Wisconsin was routed through carriers in Singapore, Dubai, and parts of Europe including Russia.
“It just kept getting shipped everywhere. It was insane,” Peter Jahn, of the Wisconsin Public Service Commission’s Division of Business and Communications Services, told the Journal-Sentinel.
These third-party operators have no responsibility to guarantee calls will be connected, and when their algorithm discovers it has been saddled with a money-losing call that will cost more to complete than the company is charging, it simply drops it, leaving the caller with dead silence, an artificial busy signal, or a dial tone.
“It’s something that’s been going on for years, and it’s very difficult to identify the bad actors. … Some of them could be fly-by-night operations,” admitted Bill Esbeck, executive director of the Wisconsin State Telecommunications Association, which represents telephone companies.
The Murky World of Grey Routes
 In fact, the industry has a different name for this type of call handling – grey routes.
In fact, the industry has a different name for this type of call handling – grey routes.
“The grey route is, literally, a sub-par phone line or phone company who is intentionally selling phone service in areas that should be expensive but is cutting corners to be able to provide the service for less,” says 2600hz, a Voice over IP service provider. “An example of a grey route, in it’s simplest form, might be someone buying 50 phone lines that were on special from the phone company for six months – and putting those phone lines in their garage. Then they buy an Internet connection and funnel calls from the Internet to those cheap phone lines all day long.”
The company says grey routes are responsible for a lot of the problems will call completion and quality.
“They’re most likely using a poor quality Internet connection, poor quality equipment and aren’t interested in debugging or fixing problems with their setup – as long as they can keep you on the line long enough to bill the other party,” says the company.
“How do they achieve that? They pitch the route to the phone company who’s losing money on expensive phone calls and falsely promise them great quality. In essence, the theory goes that if only 5% of your calls go over a ‘grey route’ then phone companies can save literally millions of dollars and most customers will ‘tolerate’ the poor quality because it only occurs on such a small number of calls. Unfortunately, the side effects of such behavior range from broken Caller ID and touchtone transmission to audio quality cut-outs and generally poor sounding calls.”

Fly-by-Night Least Cost Call Routing
Because many of these providers are unsophisticated, mistakes in call routing are common.
In one instance, all calls intended for an area in northern Wisconsin instead were routed to a car dealership, which was deluged with wrong-number calls.
“It took months and months to figure out who had screwed this up,” Jahn told the newspaper.
Unfortunately, it isn’t just the discount long distance providers that occasionally hand off calls to grey routes. The biggest cell phone and cable companies also use them.
For months, Pat Fretschel of Reedsburg had trouble getting calls from Milwaukee. Her callers would assume she wasn’t home and would hang up, when in fact the phone wasn’t ringing at her end of the line.
The problem only affected callers using Time Warner Cable phone service.
“Time Warner kept trying to tell me the calls were being hijacked out of California. I could never wrap my head around that,” Fretschel told the Journal-Sentinel.
Back in New England, Jackie Ambrozaitis is thankful she has a website to advertise her Falkenbury Farm Guest House, because she has no idea how many long distance calls she is missing.
Molly Worden, Jackie’s daughter who lives in Connecticut, reports to the Addison County Independent that she has problems every month reaching both her mother and a sister who also lives in Benson.

Rural first responders can’t respond if they don’t get the call.
“I call Shoreham Tel and they test the line and they say it’s my phone; they tell me my phone looks for the cheapest way to send the call,” Worden says. “I’ve had people over to the house and called from several different carriers with their cell phones, I’ve tried Verizon, Sprint, Nextel, and I still can’t get through. It will ring 20 times without answer or it goes to busy. Sometimes five, six days in a row I can’t get through.”
Worden’s young children get frustrated when they can’t talk to their grandparents in Vermont, and Ambrozaitis’s 90-year-old father-in-law in Connecticut gets distressed when he can’t reach the family.
Your Health and Safety at Risk?
But the problem isn’t just annoying for friends and family trying to stay in touch.
Doctors “have been unable to reach patients, hospitals have been unable to reach on-call emergency surgeons, and there is a reported instance in which a 911 call center was unable to make emergency call backs,” the National Exchange Carrier Association, which represents rural telecom companies, said in an Aug. 18 letter to the Federal Communications Commission.
“I’m concerned we’ll have a major event where perhaps a first responder doesn’t know that they were called out,” says Steve Head, engineer at HEADSolutions, consultant to the telecommunications industry. Head is working with Waitsfield Telecom, and has been instrumental in recognizing and revealing the extent of the rural connectivity problem nationwide. “We had at least one incident of a hospital trying to get ahold of a patient to schedule surgery and could not get through, and if they had not been able to get ahold of him for this surgery opening it was not going to be able to be done for some time,” he said. “That was major.”
“I Have Regulatory Authority Over Telegraph Lines” – State Regulators Helpless to Intervene
Trying to resolve this problem has fallen largely on the FCC in Washington as telephone company oversight and consumer protection laws in the states have not kept up with technology or have been wiped off the books in deregulation measures.

Rothman
“I have regulatory authority over telegraph lines,” complained Minnesota Commerce Commissioner Mike Rothman. “Currently, wholesale transport providers are not defined in statute, they’re unknown.”
In Minnesota, attempts at wholesale deregulation have not been successful, and landline phone companies still fall under some state regulation. Cell phones are covered by the FCC, and, as Rothman explained, cable is pretty much a free-for-all.
Any attempt to place oversight or regulation on telecom companies rings alarm bells and the lobbyists quickly arrive in Rothman’s office, “all lined up, someone from Verizon, another from Sprint, and a representative from a trade group representing cable.”
“Regulation worked for a long time but customers didn’t have a choice. Now they have a choice, but the quality of calls may have declined,” said Rob Souza, senior vice president of Otelco, the Maine-based communication company that bought Shoreham Tel 13 months ago. “I’ve been in this business 40 years, and the modernization of the telecommunications system has been extraordinary. It’s a good, solid reliable system. But when people don’t play by the rules, you get more service problems. That’s not an indictment of the system, but on some people who are trying to shave every penny out of it.”
Inadequate FCC Fines Are Just the Cost of Maintaining a Very Profitable Business
Among those include Matrix Telecom Inc. of Irving, Tex., fined $875,000 by the FCC to resolve a call-completion investigation. Similar agreements were reached with Level 3 Communications LLC for $975,000 in March and Windstream Corp. for $2.5 million in February.
But those amounts are miniscule in comparison to the potential financial benefits reaped from LCR.
“In the short-term, it’s going to take the FCC cracking down and making those fines larger, so the cost of not doing what the carriers are supposed to do is greater than doing what they’re supposed to,” said Reedsburg Utility Commission general manager Brett Schuppner.
But the FCC isn’t immune to lobbying either, and powerhouse AT&T is at the front of the line fiercely fighting to weaken new FCC rules to a level that would qualify them as homeopathic.
CommLawBlog fingered AT&T as the worst offender. The phone company recently filed a petition to change FCC rules designed to find and track the source of degradation of rural calls. The company also wants waivers for its wireless traffic and intaLATA toll calls (those placed to nearby areas outside of a customer’s local toll-free calling zone). They are also seeking a six month extension of a reporting deadline. This is significant, CommLawBlog says, because AT&T is the largest interexchange carrier with the most traffic sent to many rural areas in the country. Letting them effectively “opt out” could nullify many of the benefits of the new rural call completion rules.
Those suggested changes from AT&T are getting a cold response from groups like the National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners, which complain that rural call completion problems have been ongoing for years and now is not the time to weaken FCC rules.
On a separate front, Sen. Tim Johnson (D-S.D.) has introduced a bill requiring the FCC to keep a registry of the companies responsible for routing long-distance calls. It also would set service quality standards for the carriers.
The bill has little chance of being passed because of significant Republican opposition.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KTVM Montana Incomplete Calls Madison County 4-24-14.mp4[/flv]
In rural Montana, long distance telephone calls often don’t reach homes and businesses. KTVM talks with a business owner in Madison County who thinks it’s unfair rural America is stuck with substandard service. (1:40)
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/You Might Have to Call Again If I Live in Rural America.flv[/flv]
David Lewis, CEO of ANPI talks about Rural Call Completion at the IP Possibilities Conference and Expo. Lewis goes into greater detail about how this problem developed, how it affects customers, and what solutions are available to fix it. Because Lewis is speaking to an audience of mostly telecom professionals, we’ve provided a “cheat sheet” to explain some of the jargon. (11:43)
Telco Jargon Translated (in chronological order as it appears in the video)
Tier 1 Carriers – The biggest IP networks
CLEC’s – Competitive local phone companies (Time Warner, Comcast, MagicJack, Vonage, etc.)
ILEC’s – Incumbent local phone companies that have been around for decades
RBOC – A former regional Bell company (eg. Verizon, AT&T, SBC, Qwest, etc.)
Termination – When a call successfully reaches the called party’s phone number
PSTN – The network that powers your traditional landline
Enhanced 911 – 911 operators automatically get your calling location and other pertinent details
PSAPs – a 911 call center
Rate Deck – Essentially a price list showing the cost to complete calls to different areas
Bypassing Access – Getting around the traditional compensation system for calls made to rural telephone companies
Feature Group D – a type of telecommunication trunk used to provide “equal access” capability from telecommunication carriers and central offices (where the switching equipment is located and customer lines are connected and terminated) to the access tandem. The caller’s number is passed along to the next carrier in the call chain for Caller ID and 911.


 Subscribe
Subscribe AT&T does not expect to see much initial growth of FirstNet, the government-sponsored first responder wireless network built by AT&T with $6 billion in taxpayer dollars.
AT&T does not expect to see much initial growth of FirstNet, the government-sponsored first responder wireless network built by AT&T with $6 billion in taxpayer dollars.
 “Over the next five years, they have to have up to 99 percent rural coverage,” Lehr said. “There’s no reason why another carrier would do that. It just doesn’t make sense.”
“Over the next five years, they have to have up to 99 percent rural coverage,” Lehr said. “There’s no reason why another carrier would do that. It just doesn’t make sense.” It is rare for AT&T and Verizon to feud in public, even rarer for one company to accuse the other of being anti-competitive, but that is precisely what happened last week in California as the two companies sparred over building a next generation wireless network for first responders.
It is rare for AT&T and Verizon to feud in public, even rarer for one company to accuse the other of being anti-competitive, but that is precisely what happened last week in California as the two companies sparred over building a next generation wireless network for first responders. FirstNet is one of AT&T’s most lucrative contracts in years, and the phone company is doing everything possible to win over state officials in hopes they will embrace the FirstNet plan. It has been a successful effort with more than 30 states, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands purposely opting in, and more than a dozen still studying AT&T’s offer. To date, no state has opted out.
FirstNet is one of AT&T’s most lucrative contracts in years, and the phone company is doing everything possible to win over state officials in hopes they will embrace the FirstNet plan. It has been a successful effort with more than 30 states, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands purposely opting in, and more than a dozen still studying AT&T’s offer. To date, no state has opted out.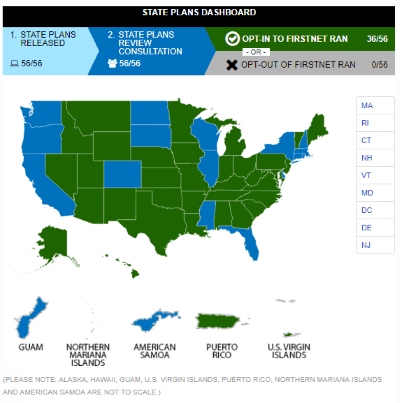 Verizon’s offer would seem to be a good deal for consumers and governments in states like New York and California that have yet to opt in to AT&T FirstNet, and in California, Verizon was invited to bid to create an alternative network in a potential “opt out” scenario. Verizon’s director of public-safety solutions group – David Wiederecht, promised the state Verizon would submit its bid by the state deadline, which was last Wednesday. By Friday, California officials leaked word Verizon had reneged on that commitment and did not participate, a fact Verizon later confirmed.
Verizon’s offer would seem to be a good deal for consumers and governments in states like New York and California that have yet to opt in to AT&T FirstNet, and in California, Verizon was invited to bid to create an alternative network in a potential “opt out” scenario. Verizon’s director of public-safety solutions group – David Wiederecht, promised the state Verizon would submit its bid by the state deadline, which was last Wednesday. By Friday, California officials leaked word Verizon had reneged on that commitment and did not participate, a fact Verizon later confirmed.


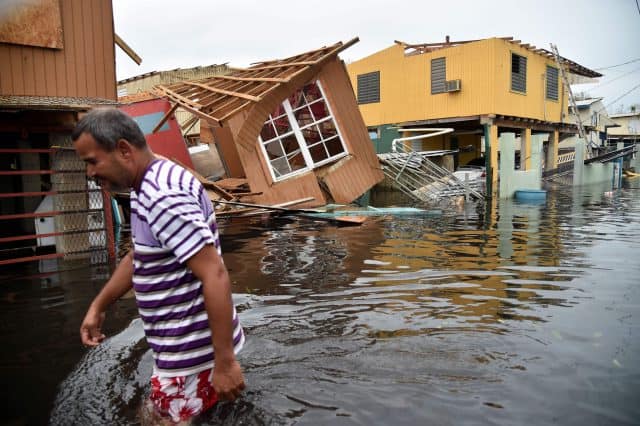
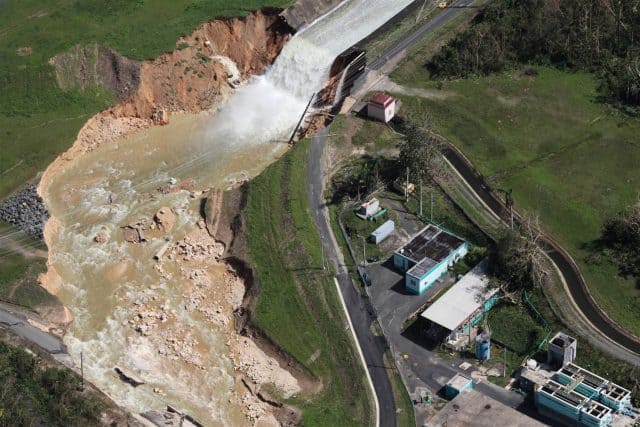
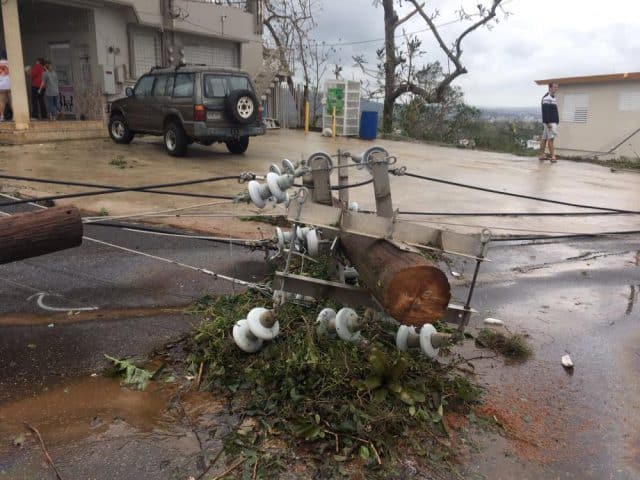
 Javier reports anyone moving between towns outside of the urban areas needs an all terrain vehicle with plenty of gas and a chainsaw to clear debris from the roads. Many are not passable because bridges have been washed out or collapsed. His job of late is utility infrastructure inspection and the news is not good.
Javier reports anyone moving between towns outside of the urban areas needs an all terrain vehicle with plenty of gas and a chainsaw to clear debris from the roads. Many are not passable because bridges have been washed out or collapsed. His job of late is utility infrastructure inspection and the news is not good.
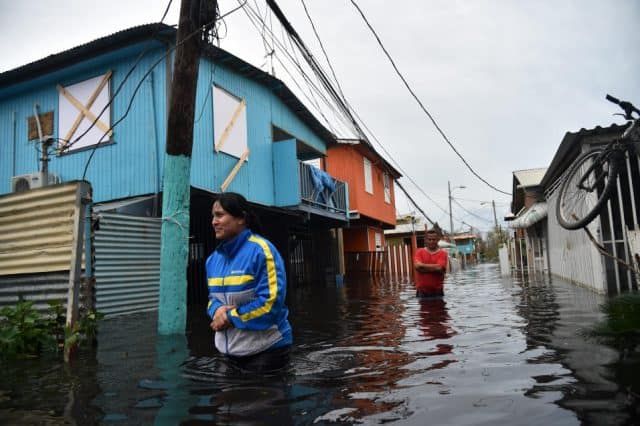




 COROZAL
COROZAL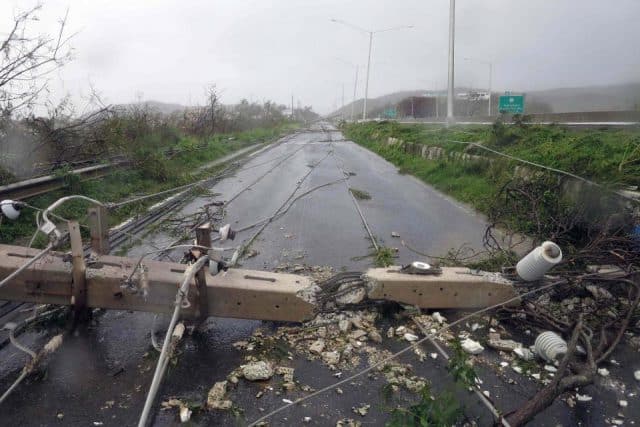




 NAGUABO
NAGUABO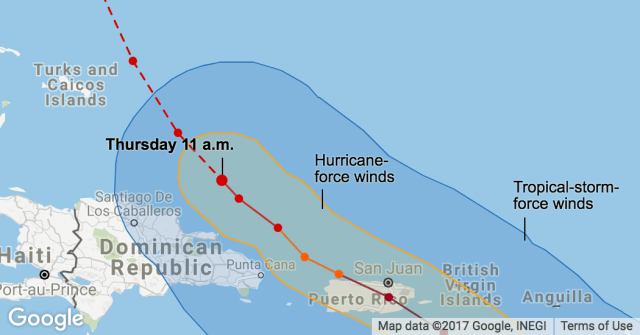 PATILLAS
PATILLAS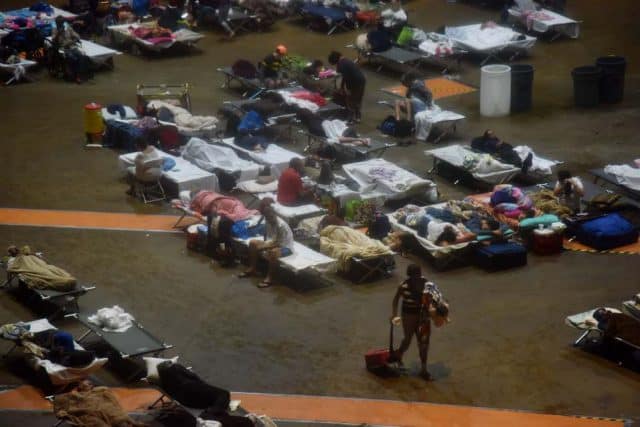
 SAN JUAN
SAN JUAN


 A residential burglar alarm in the city of Houston
A residential burglar alarm in the city of Houston 