 Wall Street analysts are warning investors that mobile providers like AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile and Sprint will have to spend $130-150 billion on fiber optic cables alone to make 5G wireless broadband a reality in the next 5-7 years.
Wall Street analysts are warning investors that mobile providers like AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile and Sprint will have to spend $130-150 billion on fiber optic cables alone to make 5G wireless broadband a reality in the next 5-7 years.
A new Deloitte study found providers will have to spend a lot of money to deploy next generation wireless service across the United States, money that many may be unwilling to spend.
“5G relies heavily on fiber and will likely fall far short of its potential unless the United States significantly increases its deep fiber investments,” the study notes. “Increased speed and capacity from 5G will rely on higher radio frequencies and greater network densification (i.e., increasing the number and concentration of cell sites and access points).”
Unlike earlier cellular technology, which worked from centralized cell towers that covered several miles in all directions, 5G technology is expected to be deployed through “small cell” antennas attached to utility and light poles with coverage limited to just 300-500 feet. To reach city residents, providers will need countless thousands of new antenna installations and a massive fiber network to connect each antenna to the provider.
Telecom providers seeking financing for such networks will face the same criticism Verizon Communications took from Wall Street over the expense of its FiOS fiber-to-the-home upgrade as well as doubts about the viability of other fiber projects like Google Fiber.
Goldman Sachs told its investors back in 2012 that throwing money at Google Fiber or Verizon FiOS was not going to give them a good return on their investment. That year, Goldman was “Still Bullish on Cable, But Not Blind to the Risks.” That report, written by analyst Jason Armstrong, noted Google’s fiber upgrades would cost billions and only further dilute industry profits from increasing competition.
 Goldman Sachs steered investors back to the cable industry, which gets significant praise from Wall Street for its ability to repurpose 20-year-old wired infrastructure for enhanced broadband without having to spend huge sums on a complete system rebuild.
Goldman Sachs steered investors back to the cable industry, which gets significant praise from Wall Street for its ability to repurpose 20-year-old wired infrastructure for enhanced broadband without having to spend huge sums on a complete system rebuild.
In 2013, Alliance Bernstein continued to slam Google Fiber’s buildout as an unwise business investment:
We remain skeptical that Google will find a scalable and economically feasible model to extend its build out to a large portion of the US, as costs would be substantial, regulatory and competitive barriers material, and in the end the effort would have limited impact on the global trajectory of the business.
For example, making the far from trivial assumption that Google can identify 20 million homes in relatively contiguous areas with (on average) similar characteristics as Kansas City when it comes to the most important drivers of network deployment cost, homes per mile of plant and the mix of aerial, buried and underground infrastructure, and that Google decides to build out a fiber network to serve them over a period of five years, we estimate the [total capital expenditure] investment required to be in the order of $11 billion to pass the homes, before acquiring or connecting a single customer.
Some analysts are even questioning the relevance of 5G when providers investing in the massive fiber expansion required for 5G wireless could simply extend fiber cables directly into homes, assuring customers of more bandwidth and reliability. In many cases, fiber to the home technology is actually cheaper than 5G deployment will be.

VantagePoint released a report in February that called a lot of the excitement surrounding 5G “hype” and cautioned it will not be the ultimate broadband solution:
Undoubtedly, 5G wireless technologies will result in better broadband performance than 4G wireless technologies and will offer much promise as a mobile complement to fixed services, but they still will not be the right choice for delivering the rapidly increasing broadband demanded by thousands or millions of households and businesses across America.
Previous analysis of 4th generation (4G) wireless networks clearly demonstrated how these networks, even with generous capacity assumptions for the future, will have limited broadband capabilities, and inevitably will fail to carry the fixed broadband experience that has been and will be demanded by subscribers accustomed to their wireline counterparts. Although there is understandably much anticipation today about phenomenal possible speeds for 5G wireless networks tomorrow, they will continue to have technical shortcomings that will, like their predecessor wireless networks, render them very useful complements but poor substitutes for wireline broadband. These technical challenges include:
- Spectral limitations: 5G networks will require massive amounts of spectrum to accomplish their target speeds. At the lower frequencies traditionally used for wide area coverage, there is not enough spectrum. At the very high frequencies proposed for 5G where there may be enough spectrum, the RF signal does not propagate far enough to be practical for any wide area coverage. This is particularly important in rural areas where customer concentration is far, far less than what can be expected in densely populated urban areas where 5G may offer greater promise.
- Access Network Sharing: This is not a good solution for continuous-bit-rate traffic such as video, which will make up 82% of Internet traffic by 2020.
- Economics: When compared to a 5G network that can deliver significant bandwidth using very high, very short-haul frequencies, FTTP is often less expensive and will have lower operational costs. This is particularly true when one consider how much fiber deployment will be needed very close to each user even just to enable 5G.
- Reliability: Wireless inherently is less reliable than wireline, with significantly increased potential for impairments with the very high frequencies required by 5G.
 In 2014, PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP released a report urging telecom executives to shift their thinking about telecom capital spending away from one that focuses on upgrades to deal with increasing traffic and demand and move instead to a hardline view of only spending on projects that meet Return On Investment (ROI) objectives for investors.
In 2014, PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP released a report urging telecom executives to shift their thinking about telecom capital spending away from one that focuses on upgrades to deal with increasing traffic and demand and move instead to a hardline view of only spending on projects that meet Return On Investment (ROI) objectives for investors.
“The predominant task of management is to take a considered view of the future, allocate capital towards strategies that maximize value for the providers of that capital, and manage the execution of those strategies through to the delivery of returns for those investors,” wrote PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP. “For too long, telecoms have been on auto-drive for much of their capex. Departments assume if they had the money last year, they are going to get it again this year, under the premise of increasing traffic. But rarely do telecoms truly analyze that spending for its ROI or ask whether the investment should be made at all.”
In short, if a project is not certain to quickly deliver significant ROI, serious questions should be asked about whether that investment is appropriate to undertake. That reluctance is at the heart of Deloitte’s new study.
Deloitte notes if providers cannot overcome Wall Street’s reluctance to support major spending on fiber infrastructure, lack of investment will be even more costly.
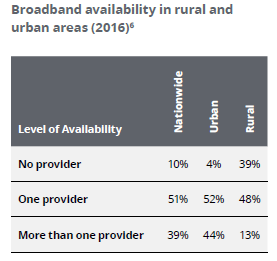
 It predicts falling short on fiber deployment will cause a dwindling number of broadband provider choices for consumers. Today, fewer than 33% of U.S. homes have access to fiber broadband and only 39% have the option of choosing more than one provider capable of meeting the FCC’s minimal definition of broadband – 25Mbps. As competition declines, the need to further expand is reduced while prices can freely rise.
It predicts falling short on fiber deployment will cause a dwindling number of broadband provider choices for consumers. Today, fewer than 33% of U.S. homes have access to fiber broadband and only 39% have the option of choosing more than one provider capable of meeting the FCC’s minimal definition of broadband – 25Mbps. As competition declines, the need to further expand is reduced while prices can freely rise.
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP also recommends cable and phone companies partner with content providers like Netflix or Google, and let those companies take an ownership interest in return for capital investments for fiber upgrades. Those type of solutions also protect Wall Street from a feared price war should alternative providers launch in markets that are barely competitive, if at all.
 Verizon Communications will decommission its existing copper wire facilities in multiple markets in Delaware, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Virginia starting in 2018.
Verizon Communications will decommission its existing copper wire facilities in multiple markets in Delaware, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Virginia starting in 2018.

 Subscribe
Subscribe





 Two years after Verizon promised its FiOS fiber to the home service would be available to every resident of New York City, the city sued Verizon Communications on Monday, alleging Verizon failed to meet its commitment.
Two years after Verizon promised its FiOS fiber to the home service would be available to every resident of New York City, the city sued Verizon Communications on Monday, alleging Verizon failed to meet its commitment. Some landlords claimed no tenants in their building wanted Verizon FiOS and the telephone company wasn’t welcome. Others accused Verizon installers of damaging buildings or performing shoddy work and sought assurances Verizon will meet the building owner’s installation standards. Some live-in building managers have even demanded kickbacks or free service in return for entry. New York State law gives Verizon a right of entry and the company has followed legal channels to eventually gain admittance.
Some landlords claimed no tenants in their building wanted Verizon FiOS and the telephone company wasn’t welcome. Others accused Verizon installers of damaging buildings or performing shoddy work and sought assurances Verizon will meet the building owner’s installation standards. Some live-in building managers have even demanded kickbacks or free service in return for entry. New York State law gives Verizon a right of entry and the company has followed legal channels to eventually gain admittance.


