 Stop the Cap! has hammered ISPs for a long time for promising “unlimited” broadband but sneaking in “traffic management speed throttles” they call a matter of fairness and we call deceptive marketing.
Stop the Cap! has hammered ISPs for a long time for promising “unlimited” broadband but sneaking in “traffic management speed throttles” they call a matter of fairness and we call deceptive marketing.
Virgin Media’s UK broadband customers have just been introduced to the extreme absurdity of selling “insanely fast” fiber broadband that comes with a sneaky spreadsheet guaranteed to confuse all but the most observant byte counters.
Some customers suspect Virgin Media is just retaliating for repeated findings from British regulators that the company runs dodgy advertising that promises one thing and delivers something entirely different in the fine print. More than two dozen of their TV commercials and print advertisements have been banned for deceptive ad claims, ranging from the “fastest broadband in Britain” (not exactly) to promotions promising “free service” that actually costs around £15 a month (what is a dozen quid or so among friends).
So why does Virgin Media need traffic management? They have oversold the service to too many customers and won’t invest enough in upgrades to keep up with demand.
Network overselling is more common that you might think. ISPs understand that all of their customers will not be online at the same time, so there is only a need to provision enough bandwidth to support their assumptions about anticipated usage. If your ISP serves a gated Luddite community, it won’t need the same data pipe required to provide access along University Row. The trick is to use real science and math to correctly anticipate user demand, but many ISPs answer first to their investors, who simply hate spending good money on upgrades. Expansion proposals are about as popular as North Korea’s Kim Jong-un. The result is “good enough” broadband service that is susceptible to overcrowding during prime usage times.
You already know what happens next. Once the kids are home from school and dinner is finished, your online experience quickly s l o w s t o (buffering).
In Britain, some ISPs are notorious for overselling broadband service that advertises speeds in the dozens of megabits, but can’t even break 1Mbps during peak usage times.
How can this be fixed? With investment in upgrades. What do ISPs do instead? They slap on usage caps and “network management” speed throttles that artificially slow browsing speeds for those considered “heavy users.”
Virgin Media was supposed to be a breath of fresh air from usage caps. Instead, the company promises a truly unlimited experience, with limitations.
Virgin’s latest iteration of its “peak time usage policy” resembles a tax table from the Internal Revenue Service. Can you understand it?
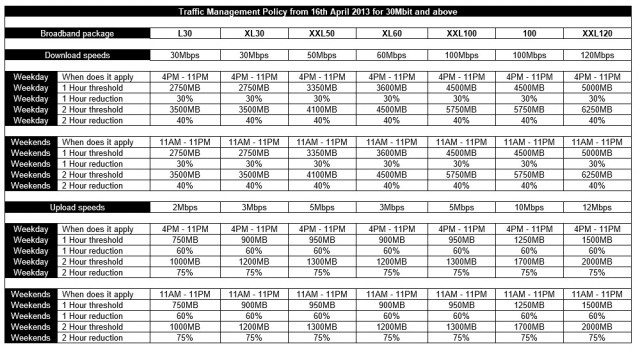
Despite this, Virgin calls its broadband service “to all intents and purposes, completely unlimited.”
Where is that British regulator, again?
The company claims less than 3% of its customers will ever be affected by these limits. They might be right if customers avoid online video, downloading large files or games, cloud storage, or allowing other family members to use their connection at the same time. If one is subjected to the speed throttles, Virgin will take away nearly half of the speed customers were sold.
Here is Virgin’s position on all this:
“Our 100Mb customers receive speeds up to 104.6Mb, proven by Ofcom, and even if you’re one of the 2.3 per cent of heavy users we sometimes, temporarily traffic manage you’ll be receiving speeds of around 60Mb — so you can download and stream as much as you like.Today’s update makes it more flexible and responsive to how people are using our services and is designed to reduce the time customers may spend in traffic management, it could be just one hour. We do not have caps, nor do we charge customers more.”
That is true, but Virgin is charging a premium for broadband service speeds they are prepared to automatically take away when a customer persists in using the service they paid to receive.
Virgin could pay their experts to conjure up speed management charts like the one above, or they could invest in network upgrades that make such network management techniques unnecessary.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Japan has leapfrogged over Google’s revolutionary 1Gbps broadband service with twice the speed for roughly $20 less a month.
Japan has leapfrogged over Google’s revolutionary 1Gbps broadband service with twice the speed for roughly $20 less a month.
 Shaw Communications has acquired Calgary’s largest fiber optic cable network in a $225 million deal with ENMAX Corp. in a bid to strengthen its ability to serve large corporate customers who need more bandwidth than Shaw is now positioned to offer.
Shaw Communications has acquired Calgary’s largest fiber optic cable network in a $225 million deal with ENMAX Corp. in a bid to strengthen its ability to serve large corporate customers who need more bandwidth than Shaw is now positioned to offer.

 On the heels of today’s announcement from Google that it intends to make Austin, Tex. the next home for Google Fiber, AT&T
On the heels of today’s announcement from Google that it intends to make Austin, Tex. the next home for Google Fiber, AT&T 