 CenturyLink does not believe it will face much of a competitive threat from AT&T and Verizon’s plans to decommission rural landline service in favor of fixed wireless broadband because the two companies’ offers are too expensive, overly usage-capped and too slow.
CenturyLink does not believe it will face much of a competitive threat from AT&T and Verizon’s plans to decommission rural landline service in favor of fixed wireless broadband because the two companies’ offers are too expensive, overly usage-capped and too slow.
Both AT&T and Verizon have proposed mothballing traditional landline service in rural areas because both companies claim wireline financial returns are too low and ongoing maintenance costs are too high. In its place, both companies are developing rural fixed wireless solutions for voice and broadband service that will rely on 4G LTE networks.
CenturyLink does not traditionally compete against either AT&T or Verizon because their landline service areas do not overlap. But as both AT&T and Verizon Wireless continue to emphasize their nationwide wireless networks, independent phone companies are likely to face increased competition from wireless phone and broadband services.
CenturyLink isn’t worried.
“About two-thirds of our customers can get access to 10Mbps or higher [from us and] that continues to increase year by year,” CenturyLink chief financial officer Stewart Ewing told attendees at Bank of America Merrill Lynch’s 2014 Global Telecom & Media Conference. “Our belief is that with the increasing demands customers have for bandwidth — the Netflix bandwidth requirement — just the increasing amount of video that customers are watching and downloading over their Internet pipes, we believe will drive customers to using a provider that basically has a wire in their home because we believe you will get generally higher bandwidth and a much better experience at lower cost.”

Ewing
CenturyLink customers consume an average of slightly less than 50GB of Internet usage per month, and that number is growing. Ewing said that CenturyLink has long believed that as bandwidth demand increases, wireless becomes less and less capable of providing a good customer experience.
“At this point, we don’t really have any concerns because people on the margin — the folks that don’t use much bandwidth — probably use a wireless connection today to download,” Ewing said. “But as the bandwidth demands grow, the wireless connection becomes more and more expensive and that could tend to drive people our way. So as long as we have 10Mbps or better to the customers, we don’t really think there is that much exposure.”
CenturyLink does not measure the difference in Internet usage between urban and rural residential customers, but the company suspects rural customers might naturally use more because alternative outlets are fewer in number outside of urban America.
“Folks in rural areas might actually can use Internet more for buying things that they can’t source [easily], but it’s hard to really count,” said Ewing. “I think our customers in the rural areas probably are not that much different from folks in urban areas.”

Prism is CenturyLink’s fiber to the neighborhood service, similar to AT&T U-verse. It is getting only a modest expansion in 2014.
CenturyLink’s largest competitor remains Comcast, which co-exists in about 40% of CenturyLink’s markets. The merger with Time Warner Cable won’t have much impact on CenturyLink, increasing Comcast’s footprint in CenturyLink territory by only about only 6-7%. CenturyLink believes most of any new competition will come in the small business market segment. Comcast’s residential pricing is unlikely to attract current CenturyLink customers in Time Warner Cable territory to consider a switch to Comcast if the merger is approved.
Ewing also shared his thinking about several other CenturyLink initiatives that customers might see sometime this year:
- Don’t expect CenturyLink to expand Wi-Fi hotspot networks. The company found they are difficult to monetize and is unlikely to expand them further;
- Any change in the FCC’s definition of minimum broadband speed to qualify for federal broadband expansion funds would slow rural broadband expansion. Ewing admitted a 10Mbps speed minimum is considerably more difficult to achieve over DSL than a 4 or 6Mbps minimum;
- Don’t expect any more merger/acquisition activity from CenturyLink in the Competitive Local Exchange Carrier business. CenturyLink shows no sign of pursuing Frontier, Windstream, FairPoint, or other independent phone companies. It is focused on expanding business services, where 60% of CenturyLink’s revenue now comes;
- CenturyLink fiber expansion will primarily be focused on reaching business offices and commercial customers in 2014;
- CenturyLink will only modestly expand PrismTV, its fiber-to-the-neighborhood service, to an additional 300,000 homes this year. The company now offers the service to two million of its customers, with 200,000 signed up nationwide. Last year, CenturyLink expanded PrismTV availability to 800,000 homes.


 Subscribe
Subscribe The town of Hollis, N.H., population 7.600, is the first community in New Hampshire to receive gigabit broadband, courtesy of the local telephone company.
The town of Hollis, N.H., population 7.600, is the first community in New Hampshire to receive gigabit broadband, courtesy of the local telephone company.
 While the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities was able to quickly settle its differences with Verizon by granting the phone company’s wish to walk away from its commitment to offer 45Mbps broadband across the state, New Jersey ratepayers are out $15 billion in excess phone charges levied since 1993 for promised upgrades many will never get.
While the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities was able to quickly settle its differences with Verizon by granting the phone company’s wish to walk away from its commitment to offer 45Mbps broadband across the state, New Jersey ratepayers are out $15 billion in excess phone charges levied since 1993 for promised upgrades many will never get.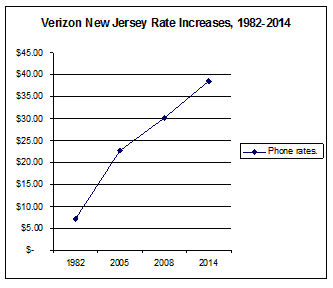 After adding up various other surcharges, Kushnick’s bill increased a lot.
After adding up various other surcharges, Kushnick’s bill increased a lot.
 The United Arab Emirates leads the world with the highest penetration of fiber-to-the-home broadband service.
The United Arab Emirates leads the world with the highest penetration of fiber-to-the-home broadband service. Subscription rates in the next-biggest markets — South Korea, Hong Kong, Japan, Singapore, and Taiwan — range from 63 percent to 37 percent, the council notes. In comparison, the United States
Subscription rates in the next-biggest markets — South Korea, Hong Kong, Japan, Singapore, and Taiwan — range from 63 percent to 37 percent, the council notes. In comparison, the United States 
