 A federal appeals court has reversed an effort by the Federal Communications Commission to pre-empt state laws restricting municipal broadband expansion in Tennessee and North Carolina, ruling the FCC exceeded its authority by interfering with both states’ rights to define the boundaries where the community broadband networks can and cannot operate.
A federal appeals court has reversed an effort by the Federal Communications Commission to pre-empt state laws restricting municipal broadband expansion in Tennessee and North Carolina, ruling the FCC exceeded its authority by interfering with both states’ rights to define the boundaries where the community broadband networks can and cannot operate.
In a near-unanimous decision (with some minor dissent from one judge), judges from the Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals found the FCC exceeded their authority.
“The FCC order essentially serves to re-allocate decision-making power between the states and their municipalities,” the court ruled. “This is shown by the fact that no federal statute or FCC regulation requires the municipalities to expand or otherwise to act in contravention of the preempted state statutory provisions. This preemption by the FCC of the allocation of power between a state and its subdivisions requires at least a clear statement in the authorizing federal legislation. The FCC relies upon § 706 of the Telecommunications Act of 1996 for the authority to preempt in this case, but that statute falls far short of such a clear statement. The preemption order must accordingly be reversed.”
In other words, the court ruled that the FCC’s belief that Section 706 of the Telecommunications Act of 1996 allowed it to pre-empt state broadband laws goes too far. The judges opined Congress would have to rewrite the law to clearly state it was acceptable for the federal branch of government to overrule how a community or state decides to draw boundaries for public utilities.

EPB is the municipal utility in Chattanooga, Tenn.
The ruling will have an immediate impact on plans by municipal utility EPB in Chattanooga and city-owned provider Greenlight in Wilson, N.C., to expand service outside of their respective service areas. EPB has been working inside the Tennessee legislature to overturn or change the current broadband law but has been unsuccessful so far. Comcast and AT&T have lobbied the Tennessee legislature to keep municipal competitors from expanding, even where neither company offers service.
“Ultimately, Tennessee’s broadband gap is a problem for Tennesseans, and we need a Tennessee solution,” said David Wade, president of EPB. “We will continue to work with the growing number of state legislators and grassroots citizens interested in removing the barriers that prevent EPB and other municipal providers from serving our neighbors in surrounding areas who have little or no access to broadband. We are further encouraged by Commissioner Randy Boyd’s interest in addressing the lack of broadband in rural areas. As the head of the Tennessee Department of Economic and Community Development, he is especially well positioned to join with state lawmakers in addressing this challenge on behalf of Tennesseans.”

Greenlight announces gigabit service for Wilson, N.C.
North Carolina’s law was effectively drafted by Time Warner Cable, who shepherded the bill through the Republican-controlled state legislature, making huge political campaign contributions along the way, eventually winning enough votes to see the bill become law.
The ruling is a serious blow to FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler, who made municipal broadband expansion one of his active agenda items at the FCC. Wheeler believed the two state laws were not supposed to inhibit rural broadband expansion. Critics of the laws contend they were written and lobbied for by the same incumbent cable and phone companies that could eventually face competition from public broadband networks.
“Let’s be clear: industry-backed state laws to block municipal broadband only exist because pliant legislators are listening to their Big Cable and Big Telecom paymasters,” said Michael Copps, a former FCC commissioner. “This decision does not benefit our broadband nation.”

Wheeler
Wheeler tacitly agreed, saying today’s decision “appears to halt the promise of jobs, investment and opportunity that community broadband has provided in Tennessee and North Carolina.”
“[Since 2015], over 50 communities have taken steps to build their own bridges across the digital divide,” Wheeler said in written comments. “The efforts of communities wanting better broadband should not be thwarted by the political power of those who, by protecting their monopoly, have failed to deliver acceptable service at an acceptable price.”
The ruling can be appealed to the U.S. Supreme Court, and the FCC has an excellent chance of getting the high court to overturn today’s decision. Rulings issued by the Sixth Circuit were reversed by the Supreme Court 24 out of the 25 times they were reviewed in the five annual terms starting in October 2008 and ending in June 2013 — the highest number of any federal appellate court during that time period.
Broadband activists can also return to the two state legislatures and urge that the broadband laws be modified or repealed. Wheeler seems ready to join the fight.
“Should states seek to repeal their anti-competitive broadband statutes, I will be happy to testify on behalf of better broadband and consumer choice,” Wheeler said. “Should states seek to limit the right of people to act for better broadband, I will be happy to testify on behalf of consumer choice.”
 Thirty cities in Bosnia, Herzegovina, and the Serb-majority entity known as Republika Srpska will now have access to fiber to the home service with broadband, television, and telephone service — all equipment included — for $27.50US a month.
Thirty cities in Bosnia, Herzegovina, and the Serb-majority entity known as Republika Srpska will now have access to fiber to the home service with broadband, television, and telephone service — all equipment included — for $27.50US a month.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Further expansion of Google Fiber
Further expansion of Google Fiber 
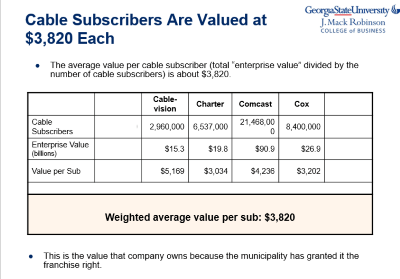 But like all publicly traded companies, Google must answer to Wall Street and their investors and some are not happy with what they see from Google Fiber. Craig Moffett from Wall Street research firm MoffettNathanson has rarely been a fan of any broadband provider other than cable operators and Google Fiber is no different.
But like all publicly traded companies, Google must answer to Wall Street and their investors and some are not happy with what they see from Google Fiber. Craig Moffett from Wall Street research firm MoffettNathanson has rarely been a fan of any broadband provider other than cable operators and Google Fiber is no different. A federal appeals court has reversed an effort by the Federal Communications Commission to pre-empt state laws restricting municipal broadband expansion in Tennessee and North Carolina, ruling the FCC exceeded its authority by interfering with both states’ rights to define the boundaries where the community broadband networks can and cannot operate.
A federal appeals court has reversed an effort by the Federal Communications Commission to pre-empt state laws restricting municipal broadband expansion in Tennessee and North Carolina, ruling the FCC exceeded its authority by interfering with both states’ rights to define the boundaries where the community broadband networks can and cannot operate.


 WOW! Internet, Cable & Phone will unveil gigabit speed broadband across five U.S. cities by the end of this year.
WOW! Internet, Cable & Phone will unveil gigabit speed broadband across five U.S. cities by the end of this year.

