West Virginia has spent nearly three times more than it anticipated for each mile of fiber optics being laid by Frontier Communications as part of the state’s taxpayer-funded broadband expansion project, according to a new report.
West Virginia has spent nearly three times more than it anticipated for each mile of fiber optics being laid by Frontier Communications as part of the state’s taxpayer-funded broadband expansion project, according to a new report.
The Saturday Gazette-Mail reports that state officials originally planned to spend $17,000 for each mile of fiber cable laid to community institutions including schools and libraries. Instead, it is paying $47,500 per fiber mile, more than double the industry average of $20,000.
Frontier Communications is getting at least $45 million in taxpayer dollars towards construction costs and will end up owning the completed fiber network that won’t directly deliver broadband service to a single home or business in the state.
West Virginia will make use of a 675-mile institutional fiber network when the project is finished, 25 percent smaller than the 900-mile network originally proposed.
State officials including Homeland Security director Jimmy Gianato have come up with some novel defenses for the cost overruns, blaming:
- The 2011 Japanese earthquake/tsunami that allegedly spiked fiber prices to as much as $50,000 per mile;
- Superstorm Sandy which delayed the project and caused $14 million in damage;
- The cost of environmental impact studies.
The state is in a hurry to spend down the remaining funds left over from the $126.3 million taxpayer grant before they expire September 30. The broadband project has been mired in controversy from almost the beginning, including allegations that major telecom company employees serving as consultants steered project managers to invest in expensive, oversized routers intended to serve college campuses that ended up installed in tiny community libraries.
State officials also found many of the institutions slated to receive fiber upgrades already had fiber service. That left officials scrambling to find any schools, libraries, hospitals — even prisons where taxpayer-funded fiber broadband would prove useful.
In the end, Frontier will be the biggest beneficiary of the project and state officials predict $4-8 million will remain in unspent funds when the project is complete.
“If people step back, they can see this monstrosity in all its true glory,” says Jan Huntser. “Private companies like Frontier don’t want taxpayer money building public fiber networks for homes and businesses because that represents unfair competition. Instead, Frontier pockets taxpayer money to build a private fiber network they will end up owning that taxpayers cannot access. Instead, we’ll keep using their slow DSL service.”
Huntser says if taxpayer money is spent to build fiber networks, taxpayers ought to be able to use them.
“None of this makes any sense,” Huntser adds. “Frontier tells friends to buy a satellite dish for broadband because they will never offer it while a library in that town has four terminals and enough broadband equipment to support a business with hundreds of employees. They can’t even understand how to make it work, so they still rely on their DSL service to run the Wi-Fi connection instead.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe Israel has decided its broadband future can no longer lie in the hands of one phone and one cable company, so the country is commissioning a nationwide fiber to the home broadband network that will be run as a public-private partnership, eventually reaching every home and business in the country.
Israel has decided its broadband future can no longer lie in the hands of one phone and one cable company, so the country is commissioning a nationwide fiber to the home broadband network that will be run as a public-private partnership, eventually reaching every home and business in the country. Current consumer broadband speeds in Israel top out at around 100Mbps, but at a price. Broadband is still costly in Israel and most customers choose packages comparable to what Americans receive — 10-15Mbps service.
Current consumer broadband speeds in Israel top out at around 100Mbps, but at a price. Broadband is still costly in Israel and most customers choose packages comparable to what Americans receive — 10-15Mbps service. Only 12% of Dutch consumers do not already receive 50Mbps broadband service. They will have it within two years according to Dutch telecom observers.
Only 12% of Dutch consumers do not already receive 50Mbps broadband service. They will have it within two years according to Dutch telecom observers.
 CenturyLink now sells up to 40Mbps speeds in Omaha, with a 300GB monthly usage cap. The company has not said if it intends to apply a usage limit on its fiber customers.
CenturyLink now sells up to 40Mbps speeds in Omaha, with a 300GB monthly usage cap. The company has not said if it intends to apply a usage limit on its fiber customers.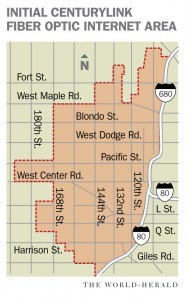 Only around 12% of metropolitan Omaha will have access to the experimental fiber service, primarily those living in West Omaha. The network will bypass residents that live further east. The boundaries of the forthcoming fiber network are notable: West Omaha comprises mostly affluent middle and upper class professionals and is one of the wealthiest areas in the metropolitan region. Winning a right to offer service on a limited basis within Omaha is an important consideration for telecom companies like CenturyLink.
Only around 12% of metropolitan Omaha will have access to the experimental fiber service, primarily those living in West Omaha. The network will bypass residents that live further east. The boundaries of the forthcoming fiber network are notable: West Omaha comprises mostly affluent middle and upper class professionals and is one of the wealthiest areas in the metropolitan region. Winning a right to offer service on a limited basis within Omaha is an important consideration for telecom companies like CenturyLink.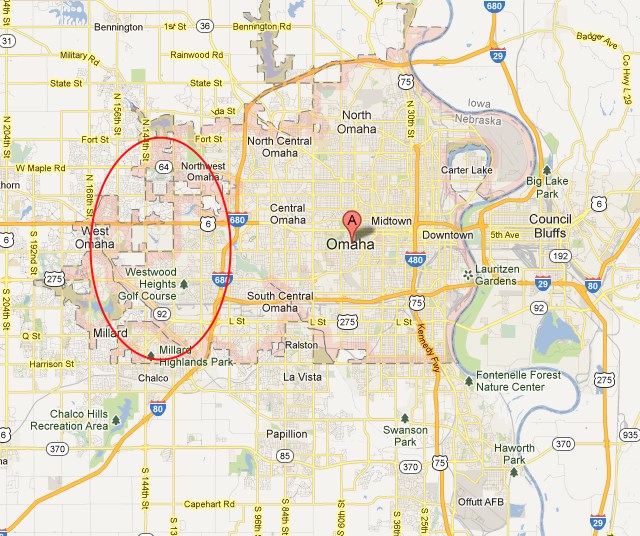
 Japan has leapfrogged over Google’s revolutionary 1Gbps broadband service with twice the speed for roughly $20 less a month.
Japan has leapfrogged over Google’s revolutionary 1Gbps broadband service with twice the speed for roughly $20 less a month.