Verizon Communications is cutting investment in its landline and fiber optic networks, spending the money on improving the company’s more profitable wireless business, which now accounts for 67 percent of Verizon’s total revenue.
Verizon Communications is cutting investment in its landline and fiber optic networks, spending the money on improving the company’s more profitable wireless business, which now accounts for 67 percent of Verizon’s total revenue.
Verizon reported second-quarter results this morning, meeting most Wall Street analysts’ expectations. The company reported a minor increase in capital spending to bolster its wireless LTE 4G network which is seeing strong growth in data traffic.
Verizon Wireless added one million new wireless customers in the last quarter, many transferring from Sprint’s now-discontinued Nextel network shut down last month. Among the new customer additions, 941,000 signed two-year postpaid contracts.
A growing number of Verizon Wireless customers are also migrating to the company’s Share Everything plan. At least 36 percent of Verizon’s wireless customers are now on shared, usage-limited data plans. Verizon expects more customers to switch, especially when legacy plan customers discover they will not receive a subsidized phone upgrade unless they abandon the grandfathered, all-you-can-eat data plan. Verizon believes the Share Everything plan will keep the company in a strong place to accelerate earnings as customers find they must regularly upgrade to higher capacity data allowances to handle increasing data usage.

Verizon’s wired success story
The growing adoption of more expensive data plans means higher bills for Verizon Wireless’ 35 million contract customers. The average Verizon Wireless customer now pays $152.50 per month, an increase of 6.4 percent. In total, over 100 million Americans now use Verizon’s prepaid and postpaid wireless services.
In June, Verizon Wireless reported its nationwide upgrade to LTE 4G service was now essentially complete, with 99 percent of 3G service areas also covered by 4G. Verizon reports 59% of its total data traffic is carried on the 4G LTE network, which is five times more efficient than the 3G network.
Wireline: Success When Verizon Invests in Upgrades, Ongoing Customer Defections Where Verizon’s Copper Network Continues to Deteriorate
Verizon’s success story in wireless is not repeated on its wireline network. Verizon lost another 5.2 percent of its residential copper landline customers during the quarter, down from 6.6 percent at the same time last year. In contrast, where Verizon’s fiber optic network FiOS is in place, customer numbers are growing along with revenue.
In fact, 71 percent of the revenue Verizon now earns from its wired residential network now comes from FiOS. The fiber network helped Verizon boost revenues by another 4.7 percent in the second quarter. With an average Verizon FiOS bill now at over $150 a month, the company saw a 9.4 percent increase in the average revenue per wireline customer over last year.
Verizon added 161,000 new FiOS Internet customers and another 140,000 new video customers in the second quarter. FiOS Quantum, which offers a broadband speed upgrade to 50/25Mbps for $10 more a month, has continued to be a hit with customers. More than one-third of all FiOS Internet customers have upgraded to faster Quantum speeds.

Shammo
With continued growth possible in the wired network business, Verizon could increase investment in expanding FiOS fiber into more markets, but instead the company continues to divert its attention and money to Verizon Wireless.
Verizon’s legacy copper wire phone and FiOS businesses saw a further reduction of 5.9 percent in capital expenditures in the second quarter — just $1.5 billion spent in the quarter and $2.9 billion year to date. Verizon’s full-year capital spending outlook which includes wireless, in contrast, is on track to spend between $16.4-16.6 billion this year. The majority of Verizon’s capital investments are aimed at improving its wireless network. Verizon’s aging copper wire network will continue to see a declining percentage of investment, and the company continues to leave FiOS fiber expansion on hold.
Fran Shammo, Verizon’s chief financial officer, this morning told investors they should expect to see a continued decline in spending on Verizon’s wired networks and more cost savings wrung out from Verizon’s declining unionized workforce, which has been asked to make concessions in labor contracts and increase work rule flexibility.
Other highlights:
- 51 percent of new phone activations were Apple iPhones during the second quarter;
- Over 64 percent of all activated phones on Verizon Wireless’ network are now smartphones;
- Verizon’s 3G network will increasingly be used by prepaid and reseller (MVNO) customers not allowed on Verizon’s LTE network;
- Verizon’s proposed entry into the Canadian wireless market is primarily focused on serving southeastern Canada from roughly Montreal to Toronto;
- 60 percent of Verizon’s revenue declines in its enterprise division were due to the federal government’s sequestration — automatic spending cuts, and declining spending by state and local governments;
- Verizon has no interest in competing with AT&T to acquire Leap Wireless (Cricket);
- The impact of Verizon’s agreement with cable operators to sell each other’s products has underwhelmed, at least so far;
- Voice Over LTE service, which will dramatically improve sound quality on voice calls, will arrive in Verizon handsets later this year with an aim to introduce the service sometime in 2014. But Verizon Wireless wants to be certain 4G LTE coverage is robust, because if reception deteriorates, VoLTE calls are not backwards-compatible with its current CDMA network and the call will get dropped. Getting it right is more important for Verizon than getting the service out quickly.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Comcast has been a part of life in Muskegon, Mich. for decades, thanks in part to an unusually long 25-year franchise agreement signed when President Reagan was serving his last year in office. In 1988, the Berlin Wall was still in place, Mikhail Gorbachev formally implemented glasnost and perestroika, Snapple appeared on store shelves nationwide, and compact discs finally outsold vinyl records for the first time.
Comcast has been a part of life in Muskegon, Mich. for decades, thanks in part to an unusually long 25-year franchise agreement signed when President Reagan was serving his last year in office. In 1988, the Berlin Wall was still in place, Mikhail Gorbachev formally implemented glasnost and perestroika, Snapple appeared on store shelves nationwide, and compact discs finally outsold vinyl records for the first time. In December 2006, primarily at the behest of AT&T, the Michigan legislature passed a new statute that would create a uniform, statewide video franchise agreement template that providers could use to apply for or renew their franchises to operate.
In December 2006, primarily at the behest of AT&T, the Michigan legislature passed a new statute that would create a uniform, statewide video franchise agreement template that providers could use to apply for or renew their franchises to operate. 
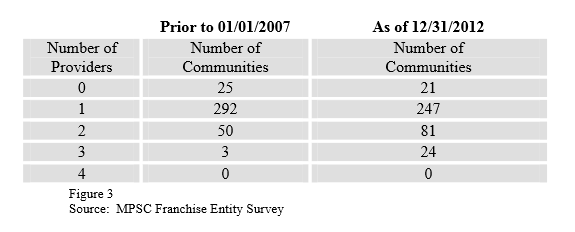
 Soon after the statewide franchise law was passed, Comcast notified the city of Detroit it could take the proposed renewal of its existing 1985 franchise agreement and go pound salt. The franchise agreement with the city expired in February 2007, just a month after the new law took effect. It was a new day, Comcast told city officials, and the company offered its own proposal for renewal — a 5% take-it-or-leave-it franchise fee and nothing else. Comcast even rejected the city’s counteroffer to include a 2% PEG fee, permitted under the new law.
Soon after the statewide franchise law was passed, Comcast notified the city of Detroit it could take the proposed renewal of its existing 1985 franchise agreement and go pound salt. The franchise agreement with the city expired in February 2007, just a month after the new law took effect. It was a new day, Comcast told city officials, and the company offered its own proposal for renewal — a 5% take-it-or-leave-it franchise fee and nothing else. Comcast even rejected the city’s counteroffer to include a 2% PEG fee, permitted under the new law.

 William Esbeck, WSTA’s executive director, has been on WiscNet’s case
William Esbeck, WSTA’s executive director, has been on WiscNet’s case 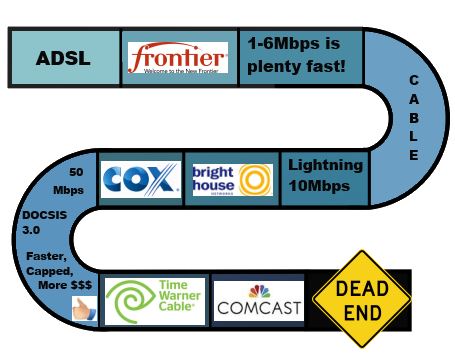 “We just don’t see the need of delivering [gigabit broadband] to consumers.” —
“We just don’t see the need of delivering [gigabit broadband] to consumers.” — 

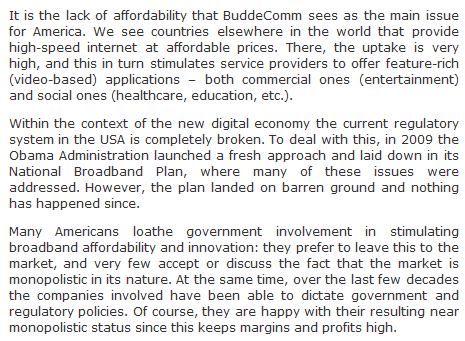
 Attention broadband planners: Although broadband deployment strategies differ around the world, a new report decisively concludes there is only one network technology proven to meet the demands of broadband users both today and tomorrow: a national fiber optic network.
Attention broadband planners: Although broadband deployment strategies differ around the world, a new report decisively concludes there is only one network technology proven to meet the demands of broadband users both today and tomorrow: a national fiber optic network.