Goei
The CEO of Altice USA took time away from his luxurious homes in Switzerland and New York this week to sit down with concerned middle and working-class Cablevision employees at a meeting held at an unassuming company garage in the Bronx.
Dexter Goei has worries of an organized workforce on his mind. A recording of the meeting provided to Stop the Cap!, showed Goei spent most of his time trying to convince employees they could trust him to protect their future employment at the cable operator.
Since Altice acquired Cablevision in the U.S., the French media have criticized the ‘naiveté of American regulators’ that largely accepted the promises and commitments of the rapidly growing international cable and wireless company at the same time Altice was regularly accused of reneging on the promises it made to regulators in Europe, especially in France. The company has been fined at least twice for breaking those commitments.
Altice’s entrance into the United States began with the acquisitions of Suddenlink, a relatively small cable company serving forgotten small cities in states like Texas and West Virginia and the should-have-been-acquired-by-Comcast-or-Time-Warner-Cable-years-ago oddity Cablevision, which made money for its founding family the Dolans for decades, selling cable mostly in suburban downstate New York.
In America, those acquiring a rival operator are usually asked to show how a deal is “in the public interest” while also submitting to a review to ensure the transaction does not irreparably harm competition. For Suddenlink customers, almost anything Altice could do would be an improvement for a cable company run by a guy who admitted on national television that the days of big investments by cable companies in service improvements were over. It was time to reap the profits, to paraphrase then-CEO Jerry Kent. And so they did, coming up with innovative usage caps and overlimit penalties for customers who dared to use the cable company’s internet service to circumvent a costly cable television package.
 Cablevision, in contrast, was usually better regarded than the cable giants that surrounded it. Although technologically aggressive, Comcast canceled most of the goodwill earned for its service improvements by treating customers like patrons of an S&M club. Time Warner Cable was also loathed for its “last to do anything” upgrades, disengaged customer service, and reliable rate hikes, but at least they learned from earlier customer service mishaps and generally relied on a policy of being nicer to customers that threatened to leave.
Cablevision, in contrast, was usually better regarded than the cable giants that surrounded it. Although technologically aggressive, Comcast canceled most of the goodwill earned for its service improvements by treating customers like patrons of an S&M club. Time Warner Cable was also loathed for its “last to do anything” upgrades, disengaged customer service, and reliable rate hikes, but at least they learned from earlier customer service mishaps and generally relied on a policy of being nicer to customers that threatened to leave.
Cablevision innovated on ways to keep customer loyalty after Verizon FiOS arrived to compete in large sections of its service area. The company spent millions on a major Wi-Fi network for the benefit of its commuting customers, launched broadband speed upgrades earlier than most, and after one embarrassing episode with the FCC showing their speed claims were not met by reality, they have usually overachieved ever since.
Drahi
In 2016, almost everything except Comcast changed. Time Warner Cable was successfully sold to Charter Communications and a self-styled ‘Baron of the Stock Exchange‘ — Patrick Drahi, managed to invade the United States and successfully acquire the two cable operators, despite admitting he would gut spending and wring hundreds of millions in savings out of the transactions for the benefit of his investors.
Mr. Drahi’s penchant for ruthless cost-cutting isn’t new, and he’s been dubbed “The Slasher” in Europe since decimating the budget at his French wireless and broadband company SFR-Numericable. French unions hate him, and not just those representing workers at his telecom businesses. Since the Altice Media Group took control of several major print publications in France, independent photographers have complained Altice slowed payments to a crawl, leading to an open letter to the French government from several press photography agencies demanding action. To date, Altice owes more than a half million dollars in outstanding licensing payments.
Critics contend this is nothing new for Altice, often denounced for not paying vendors (or paying them only after they agree to provide discounts) or alienating employees with radical cost cutting and cutbacks. Customers don’t like what they see either, with more than a million dropping SFR for other providers.
But that was not a story Goei was prepared to share with Cablevision workers in the Bronx.
Instead, Mr. Goei told employees he turned his back on a lucrative career on Wall Street after the great financial meltdown of 2008 and saw more potential running cable companies in Europe and the United States. Goei told the workers Altice’s business plan is to acquire cable and telecom companies and reinvest the profits in improved customer service and better technology for customers. Actual customers of Altice’s cable companies in Europe are still waiting for those improvements.

The French loathe SFR-Numericable, giving it one out of five stars in reviews.
SFR-Numericable, which Goei claimed this week won acclaim from French regulators for being the most reliable in the country, gets scathing reviews criticizing the company for its very frequent service outages, tricky marketing, and incoherent customer service. “Legalized banditry,” claimed one customer. Another described the offshore customer care center as “the Moroccan nightmare,” with more than a few call center workers demonstrating less-than-capable comprehension of French. Service outages are rampant and represent the single biggest reason customers have canceled service.
Goei complained that acquisitions and upgrades have been complicated in Europe by former managers grabbing their golden parachutes and abandoning the acquired companies (without mentioning Altice’s well-known reputation for draconian salary cuts and downsizing) and slowdowns from underperforming suppliers (despite the fact some vendors in France complained their invoices went unpaid for weeks or months, leading to complaints to government regulators).
Forthcoming upgrades are one of the reasons Goei was in the Bronx to sell employees on the merits of Altice Technical Services (ATS), a spinoff entity expected to eventually manage all of Altice’s technical infrastructure and the technicians that will care for it.
“We don’t want to contract out,” explained Goei, who aspires to manage Altice’s forthcoming upgrades effectively in-house through ATS instead of going to outside contractors. To manage this, Goei needs to convince Altice USA’s technical employees to leave Altice and join ATS.

Will ATS protect workers and customers or simply help Altice rid itself of regulator-imposed conditions for its acquisitions?
Goei’s statements seemed to suggest that most will need to make that transition if they want to remain a part of Altice for more than five years, hinting ATS will increasingly manage more and more of Altice’s technical needs, eventually making Altice USA employees potentially redundant.
Goei also hinted ATS might perform work for more than just Altice, which underlined concerns for union organizers that ATS is being established as an independent contracting entity that would not be subject to any regulatory job protection conditions that came with the approval of Altice’s acquisition of Cablevision.
Altice’s plans to rip out and replace coaxial cable with an all-fiber network will likely provide work for the next 7-10 years, notwithstanding the ambitious five-year timeline Altice gave for the fiber upgrade. But employees peppered Goei with questions about job security, benefits like vacation pay, and exactly who will be running ATS and what their opportunities for advancement are.
The transition to ATS might effectively be in name only, because Goei claimed ATS will have full access to employees’ files and work history with Altice and Cablevision, and if managers make the transition to ATS, employees could report to the same manager or supervisor they did under Altice.
“We’re not bringing in some Mexican guy” to run things Goei said to nervous laughter and raised eyebrows from the almost all-minority audience.
Goei’s question and answer session is unlikely to assuage concerns ATS could evolve into little more than Altice’s version of an independent subcontractor with enhanced loyalty to Altice USA. Despite assurances Altice is not looking for excuses to radically trim its workforce, Altice’s history shows job cuts are an integral part of what the French business press calls “The Drahi Method.”
 At France’s SFR, Drahi made clear he is looking to cut at least 5,000 paid positions, reducing the workforce from 14,700 to 9,000, starting in July. Observers suspect Altice’s reliance on ATS to act as an umbrella technical department for all of Altice’s North American acquisitions guarantees workforce reductions, if only to eliminate redundancy. Altice has already shown a willingness to lay off employees at its Cablevision and Suddenlink call centers.
At France’s SFR, Drahi made clear he is looking to cut at least 5,000 paid positions, reducing the workforce from 14,700 to 9,000, starting in July. Observers suspect Altice’s reliance on ATS to act as an umbrella technical department for all of Altice’s North American acquisitions guarantees workforce reductions, if only to eliminate redundancy. Altice has already shown a willingness to lay off employees at its Cablevision and Suddenlink call centers.
But there is one area where Altice is willing to spend.
Le Temps reports Drahi is opening the checkbook to beef up its Geneva executive headquarters in Switzerland, increasing the workforce tenfold and centralizing business operations for the Altice empire. The office is packed with ex-Wall Street bankers and businessmen with a reputation for ruthlessness. Goei’s office is in the building, as is the company’s director — Michel Combes. Combes was notoriously hired away from Alcatel right after demonstrating a talent for swinging the job cutting ax. They are joined by Burkhard Koep, a former Morgan Stanley investment banker in charge of mergers and acquisitions.
The top shelf executives have moved themselves and their families from London, New York, Paris, Tel Aviv and Lisbon to the posh neighborhoods around suburban Geneva, where homes are more likely to be called estates.
The Geneva office conducts business through heavy reliance on videoconferencing and racking up frequent flier miles traveling abroad. Often absent is Drahi himself, who prefers to conduct business from his Zermatt-based luxury cottages. As much as executives spend their time pondering the next acquisition, Le Temps reports they also spend their weekends trying to renegotiate the company’s enormous debt load by seeking refinancing at lower interest rates.
“They play a bank against each other by saying: we will refinance to 6% the debt you loaned us at 7%,” reported the news outlet.
But Altice’s Geneva headquarters did not come for free. Drahi recently introduced a new franchise fee obligating each cable or telecom unit to pay 2-3% of their revenue to Mr. Drahi’s Switzerland office. In the first year that is expected to raise at least $550 million dollars. While popular with Swiss tax authorities, the substantial royalty payments are expected to reduce available cash for upgrades and debt service. Nobody is sure where the money will ultimately end up.


 Subscribe
Subscribe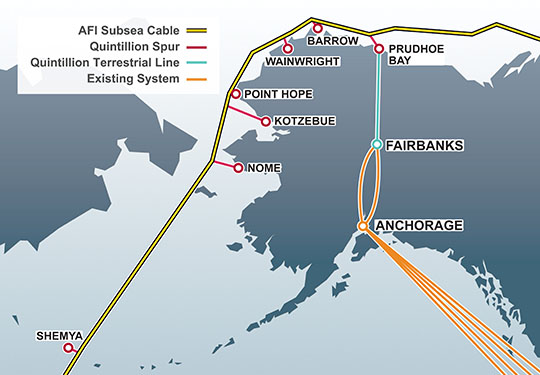
 The biggest weakness of the plan, according to its critics, is its lack of support for middle-mile networks — wired infrastructure that connects providers to a statewide broadband backbone that can manage traffic needs without having to turn to slow-speed satellite connectivity. One of Alaska’s biggest challenges is finding low-cost connectivity with Canada and the lower-48 states. Much of the state relies heavily on GCI’s still-expanding TERRA network, which provides fiber as well as microwave connectivity to 72 towns and villages in rural Alaska. Quintillion, a new player, is working on stretching fiber connectivity through the Northwest Passage. Its forthcoming 30 terabit capacity fiber network offers the possibility of dramatically lower broadband rates and no more data caps, assuming providers have the network capacity to connect their service areas and the nearest fiber access point.
The biggest weakness of the plan, according to its critics, is its lack of support for middle-mile networks — wired infrastructure that connects providers to a statewide broadband backbone that can manage traffic needs without having to turn to slow-speed satellite connectivity. One of Alaska’s biggest challenges is finding low-cost connectivity with Canada and the lower-48 states. Much of the state relies heavily on GCI’s still-expanding TERRA network, which provides fiber as well as microwave connectivity to 72 towns and villages in rural Alaska. Quintillion, a new player, is working on stretching fiber connectivity through the Northwest Passage. Its forthcoming 30 terabit capacity fiber network offers the possibility of dramatically lower broadband rates and no more data caps, assuming providers have the network capacity to connect their service areas and the nearest fiber access point. Instead, the ATA managed to convince regulators that 10/1Mbps service was good enough — speed that can be achieved by the DSL service phone companies favor. This is well below Alaska’s Broadband Task Force goal of 100Mbps for every state resident by 2020. Another free pass built into the plan is allowing providers to collect subsidies even when they do not offer 10Mbps because of network limitations, including lack of suitable middle mile networks. In those cases, the only speed requirement is 1Mbps download speeds and 256kbps uploads, the same as satellite broadband providers.
Instead, the ATA managed to convince regulators that 10/1Mbps service was good enough — speed that can be achieved by the DSL service phone companies favor. This is well below Alaska’s Broadband Task Force goal of 100Mbps for every state resident by 2020. Another free pass built into the plan is allowing providers to collect subsidies even when they do not offer 10Mbps because of network limitations, including lack of suitable middle mile networks. In those cases, the only speed requirement is 1Mbps download speeds and 256kbps uploads, the same as satellite broadband providers.




 But despite Webpass’ claim its performance is comparable to fiber, its inability to guarantee customers a certain speed level and its tremendous performance variability from 100 to 1,000Mbps exposes one of the weaknesses of fixed wireless networks. At a time when capacity is king, only fiber optic networks have shown a consistent ability to deliver synchronous broadband speeds that do not suffer the variability of shared networks, poor antenna placement/signal levels, or harmful interference.
But despite Webpass’ claim its performance is comparable to fiber, its inability to guarantee customers a certain speed level and its tremendous performance variability from 100 to 1,000Mbps exposes one of the weaknesses of fixed wireless networks. At a time when capacity is king, only fiber optic networks have shown a consistent ability to deliver synchronous broadband speeds that do not suffer the variability of shared networks, poor antenna placement/signal levels, or harmful interference. At Stop the Cap!, we believe these developments further the argument broadband is an essential utility best administered for the public good and not solely as a profit-motivated venture. The path to fiber to the home service in rural, suburban, and urban communities has and will continue to come from a mix of private and public utilities, just as local public and private gas and electric companies have served this country for the last century. Where there is a business model for fiber to the home service that investors support, there is a for-profit fiber provider. Where there isn’t, now there is often no service at all. So far, the FCC in conjunction with Congress has seen fit to solve broadband availability problems by bribing private providers into offering service (usually low-speed DSL that does not even meet the FCC’s definition of broadband) with cash subsidies, tax write-offs, or occasional tax abatement schemes. Imagine if we followed that model with the nation’s public roads and highways. We would today be paying tolls or a subscription to travel down roads built and owned by a private company often financed by tax dollars.
At Stop the Cap!, we believe these developments further the argument broadband is an essential utility best administered for the public good and not solely as a profit-motivated venture. The path to fiber to the home service in rural, suburban, and urban communities has and will continue to come from a mix of private and public utilities, just as local public and private gas and electric companies have served this country for the last century. Where there is a business model for fiber to the home service that investors support, there is a for-profit fiber provider. Where there isn’t, now there is often no service at all. So far, the FCC in conjunction with Congress has seen fit to solve broadband availability problems by bribing private providers into offering service (usually low-speed DSL that does not even meet the FCC’s definition of broadband) with cash subsidies, tax write-offs, or occasional tax abatement schemes. Imagine if we followed that model with the nation’s public roads and highways. We would today be paying tolls or a subscription to travel down roads built and owned by a private company often financed by tax dollars.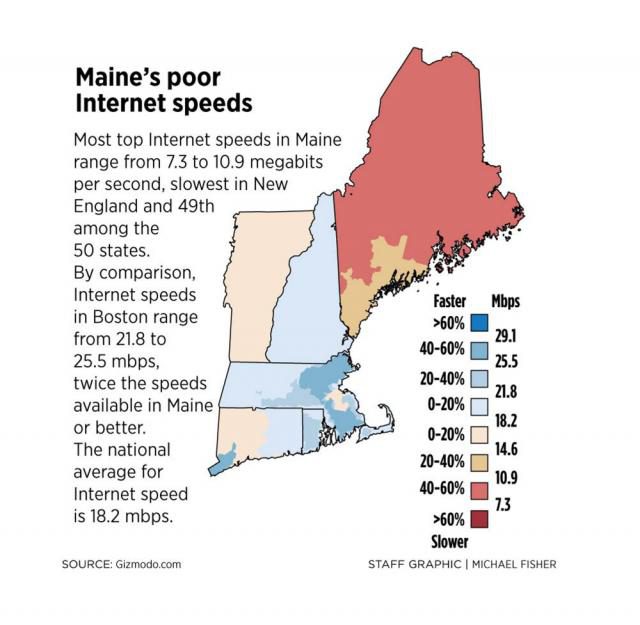
 Only half of CenturyLink’s customers in well-populated areas formerly served by Qwest can buy broadband service at 40Mbps or higher, while rural customers fare considerably worse with less than 25% able to get High Speed Internet at those speeds.
Only half of CenturyLink’s customers in well-populated areas formerly served by Qwest can buy broadband service at 40Mbps or higher, while rural customers fare considerably worse with less than 25% able to get High Speed Internet at those speeds. CenturyLink attempts to cover their claims with fine print attached to their FCC submission: “The numbers shown in this chart reflect the percentages of households served by DSLAMs that are capable of providing the specified broadband speeds.” (A DSLAM is a network device typically used to extend faster DSL speeds to customers by reducing the amount of copper wiring between the telephone company’s central office and the customer’s home. Customers in a neighborhood typically share space on a DSLAM, in effect sharing a single connection back to the phone company.)
CenturyLink attempts to cover their claims with fine print attached to their FCC submission: “The numbers shown in this chart reflect the percentages of households served by DSLAMs that are capable of providing the specified broadband speeds.” (A DSLAM is a network device typically used to extend faster DSL speeds to customers by reducing the amount of copper wiring between the telephone company’s central office and the customer’s home. Customers in a neighborhood typically share space on a DSLAM, in effect sharing a single connection back to the phone company.)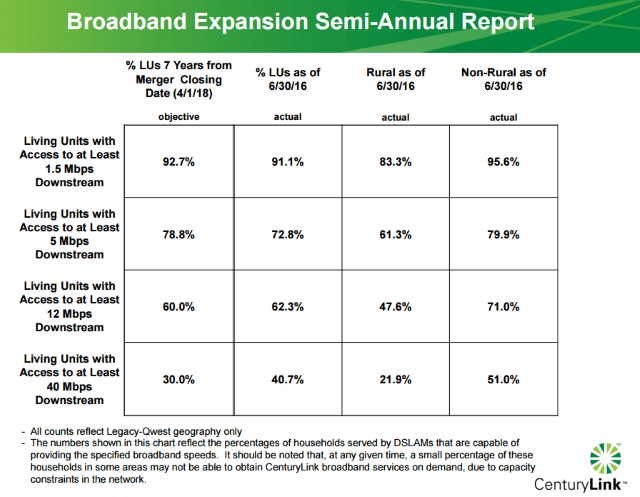
 Further expansion of Google Fiber
Further expansion of Google Fiber 
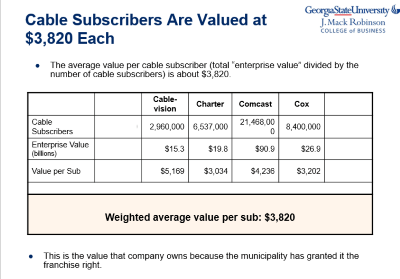 But like all publicly traded companies, Google must answer to Wall Street and their investors and some are not happy with what they see from Google Fiber. Craig Moffett from Wall Street research firm MoffettNathanson has rarely been a fan of any broadband provider other than cable operators and Google Fiber is no different.
But like all publicly traded companies, Google must answer to Wall Street and their investors and some are not happy with what they see from Google Fiber. Craig Moffett from Wall Street research firm MoffettNathanson has rarely been a fan of any broadband provider other than cable operators and Google Fiber is no different.