Patrick Drahi, Altice, and his friends at Goldman Sachs are depicted as working together to make Altice’s acquisition dreams come true.
Patrick Drahi rarely gives up on his dreams. His latest is to be America’s biggest cable magnate, and there are signs he is laying the groundwork to make that dream come true.
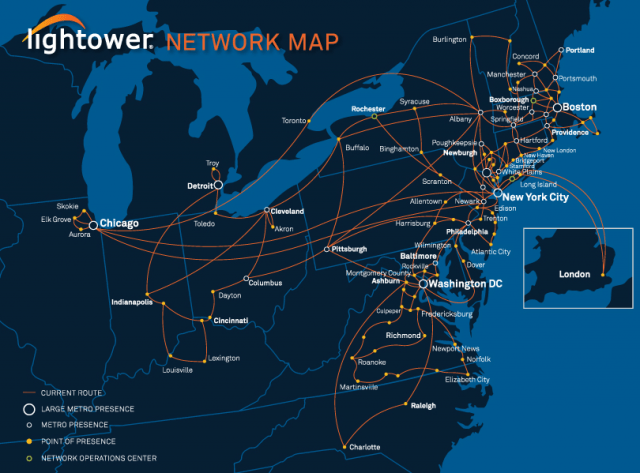
CNBC and some French media outlets report Drahi’s Altice NV and Altice USA are assembling their European and North American financiers, attorneys, and dealmakers to potentially make an offer to acquire Charter Communications. If successful, Altice would leapfrog to the largest cable operator in the United States after combining its Cablevision and Suddenlink systems with Charter’s own legacy systems and those it acquired from Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks.
Any succcessful deal would likely require an offer of $500 a share for Charter stock, which would make the company worth about $200 billion. Because Altice is dwarfed by Charter, it is unlikely Drahi will be able to raise enough cash on his own to make a deal, and Altice is already mired in debt from its ongoing aggressive acquisitions. Drahi’s biggest competitor for Charter is expected to be Japan’s SoftBank, which has shown an interest in acquiring the cable operator to combine with its wireless carrier Sprint.
Altice isn’t likely to encounter the regulatory hurdles that have caused other colossal cable deals like Comcast’s attempt to buy Time Warner Cable to collapse over regulator opposition. Drahi’s involvement in U.S. cable has been limited to acquisitions of two smaller players – Cablevision and Suddenlink.
 Drahi’s strongest arguments to sell investors on the deal are likely to surround his well-known obsession with draconian cost-cutting at his acquired companies. Drahi would certainly offer investors billions in deal synergies and savings, accomplished through dramatic layoffs, scrutinizing costs right down to replacement coffee makers for the break room and copy paper for the office, and sweeping cutbacks on employee and vendor perks. Drahi has also taken a strong stand against Hollywood studios and cable programmers that seek double-digit rate increases for cable programming. In Europe, Drahi is known for terminating costly contracts with programmers and launching alternative channels Altice owns and operates to replace them.
Drahi’s strongest arguments to sell investors on the deal are likely to surround his well-known obsession with draconian cost-cutting at his acquired companies. Drahi would certainly offer investors billions in deal synergies and savings, accomplished through dramatic layoffs, scrutinizing costs right down to replacement coffee makers for the break room and copy paper for the office, and sweeping cutbacks on employee and vendor perks. Drahi has also taken a strong stand against Hollywood studios and cable programmers that seek double-digit rate increases for cable programming. In Europe, Drahi is known for terminating costly contracts with programmers and launching alternative channels Altice owns and operates to replace them.
 Drahi is also likely to sell regulators on his current plans to transform cable in the United States away from coaxial cable and towards fiber optics straight through to the home. Drahi has already offered to wire all of France with fiber optics and is presently embarking on a fiber upgrade for his Cablevision systems in New Jersey, New York, and Connecticut. But Drahi’s ambitious fiber plans have been met with suspicion in France where some believe Drahi is all talk and no spending.
Drahi is also likely to sell regulators on his current plans to transform cable in the United States away from coaxial cable and towards fiber optics straight through to the home. Drahi has already offered to wire all of France with fiber optics and is presently embarking on a fiber upgrade for his Cablevision systems in New Jersey, New York, and Connecticut. But Drahi’s ambitious fiber plans have been met with suspicion in France where some believe Drahi is all talk and no spending.
He has promised the Macron government he will spend $17.6 billion on building an Altice-owned fiber broadband network in France by 2025 without any taxpayer subsidies. While that sounds laudable, it would mean Altice’s SFR would pull out of the government’s national fiber strategy that depends on different telecom companies building out fiber in different regions of the country.
Drahi is threatening to become a spoiler because before he acquired SFR, the former management cut a deal with Orange – France’s largest telecom company, to jointly build a fiber network for 14 million French households in smaller towns and suburbs. Orange would build and own 80% of the territory, SFR 20%. But because SFR needs access to that fiber network for its own wired and wireless broadband and television services, it will have to pay rental fees to Orange to use the network in most of the territory. Drahi instead wants a 50-50 ownership split to cut costs and Orange has said no. Altice’s plans for its own alternative fiber network would allow it to bypass the Orange-owned network and deliver traffic over its own fiber system. That could mean parts of less-populated France will have two fiber networks to choose from instead of just one.
It is an expensive gamble, but investors seem largely unfazed so far, perhaps suspecting Drahi has no intention of actually following through on spending billions on a potentially redundant fiber network in the suburbs and farm country, preferring to believe the threat of doing so will drive Orange back to the negotiating table.
Some American analysts are uncertain whether Drahi can pull off an acquisition deal that would combine Charter, a company many times larger than Altice, with Altice’s much smaller earlier cable acquisitions. Some also suspect he won’t find enough money to attract interest from Charter’s biggest shareholder — John Malone’s Liberty Media and Charter’s current CEO Thomas Rutledge.
But French media has little doubt Drahi can pull it off, especially when he is motivated.
“Patrick Drahi, founder of Altice, has set his limits: he has none,” notes Le Figaro, adding Drahi is a classic industry spoiler, completely happy to blow up cable’s comfortable status quo, even when at risk of attracting the wrath of his competitors.
CNBC reports Altice is preparing a serious offer to acquire Charter Communications. (5:54)


 Subscribe
Subscribe