Phil Kerpen with Glenn Beck in 2009
A conservative pro-business group allied with the telecom industry run by a former top aide for the Koch Brothers is in the middle of a growing scandal over a flood of allegedly phony, identically worded messages opposing Net Neutrality sent to members of Congress.
Politico today reported Phil Kerpen’s group – American Commitment – claimed it had easily found a half-million Americans opposed to the Obama Administration’s support for Net Neutrality and helped funnel 1.6 million messages from them to members of the House and Senate.
But suspicious members of Congress quickly determined that many of the messages originated from constituents who had no memory of sending them and a firm hired to help process incoming e-mail for members of Congress warned many of the messages originated from questionable email addresses and “a vast majority of the emails do not appear to have a valid in-district address.”
The content of many of the emails was exactly the same, with a variant paragraph inserted in the middle opposing Net Neutrality for different reasons, all urging Congress to defund the Federal Communications Commission to prevent the agency from enforcing its new Net Neutrality policies.
When Rep. Jackie Speier (D-Calif.) noticed the majority of the anti Net Neutrality messages came from constituents that have never written her before, she quickly reached out to the senders to respond to their concerns. A few replied they had never signed up to send emails criticizing Net Neutrality. Lockheed Martin, which manages many of the email messages resulting from constituents clicking the “Contact Me” button on lawmakers’ websites, notified Congress they were suspicious about the authenticity of the emails as well, and had configured a filter to begin weeding them out.
American Commitment, which maintains close ties to the Koch Brothers, characterizes Net Neutrality as an “Obama Internet Takeover.”
“The idea that an outside group could use consumer data to impersonate constituents suggests an attempt to hijack the important feedback members of Congress need to truly represent their districts,” Speier said in a statement. “This is identity theft, but instead of impersonating for financial gain, the originators of this theft are striking at the heart of our representative democracy.”
Kerpen maintains close ties to several Koch Brother-funded, pro-corporate astroturf groups. His former work opposing Net Neutrality with Americans for Prosperity, almost entirely funded by Koch Industries, mirrors his continued opposition today.
As early as 2009, Stop the Cap! tangled with Kerpen and Americans for Prosperity after Kerpen appeared on Glenn Beck’s program attacking Net Neutrality. Kerpen nodded in agreement as Beck offered that Net Neutrality represented a joint Marxist and Maoist plot to take over the Internet on behalf of the Obama Administration. Stop the Cap! has repeatedly asked Americans for Prosperity to disclose their donor list, but Kerpen has consistently refused, even after the Sunlight Foundation detailed ties the group maintains with other Koch efforts.

Kerpen’s group pre-wrote most of the letters it sent to the FCC. A writer was offered a variant where an extra paragraph would appear at the point indicated expressing one of several views across the political spectrum. Those were pre-written as well.
In his new position at American Commitment, Kerpen’s group generated the majority of responses received during the FCC’s second round accepting comments about Net Neutrality. To evade Congress’ ability to sniff out a form letter writing campaign, American Commitment went over the top, designing its form letters with at least 30 different comment variants, many offering wildly different reasons why Net Neutrality was bad for America. When the final letter was created, it appeared original until groups like the Sunlight Foundation discovered nearly exact copies of the different variants ostensibly coming from different writers.
For example, Joe Smith could oppose Net Neutrality because it violates personal freedom — a common conservative view and Marsha Smith could oppose it because it would hurt small co-ops and municipal providers — likely a left-leaning view, but both letters were pre-written by Kerpen’s group. One telltale sign of Kerpen’s involvement is his relentless personal loathing of Robert McChesney, who helped found the consumer group Free Press. Kerpen can’t help himself routinely, almost reflexively accusing McChesney of being a Marxist, extreme leftist, or outright communist. His personal views show up in one of American Commitment’s letter variants:
The ideological leader of the angry liberals calling for you to reduce the Internet to a public utility is Robert McChesney, the avowed Marxist founder of the socialist group Free Press. In an interview with SocialistProject.ca, McChesney said: “What we want to have in the U.S. and in every society is an Internet that is not private property, but a public utility…At the moment, the battle over network neutrality is not to completely eliminate the telephone and cable companies. We are not at that point yet. But the ultimate goal is to get rid of the media capitalists in the phone and cable companies and to divest them from control.” In a country of over 300 million people, even an extremist like McChesney can find, perhaps, millions of followers. But you should know better than to listen to them.
Politico asked Kerpen about the matter and he denied impersonating the alleged letter writers and suggested some other group borrowed American Commitment’s idea and potentially ran too far with it.
“We’re aware that other groups used identical language in their campaigns and we cannot speak to those efforts,” Kerpen said. “We verified our data through postal address verification and follow up phone calls. We stand by our campaign and Congress should work to stop President [Barack] Obama’s plan to regulate the Internet at the request of these constituents.”
Kerpen also continued his refusal to disclose what corporations are paying to keep the lights on at American Commitment. No matter, the Sunlight Foundation triangulated donor data and discovered much of the money comes from Koch-affiliated political organizations. Another significant donor is the National Cable & Telecommunications Association, the nation’s biggest cable lobbyist and fierce Net Neutrality opponent.


 Subscribe
Subscribe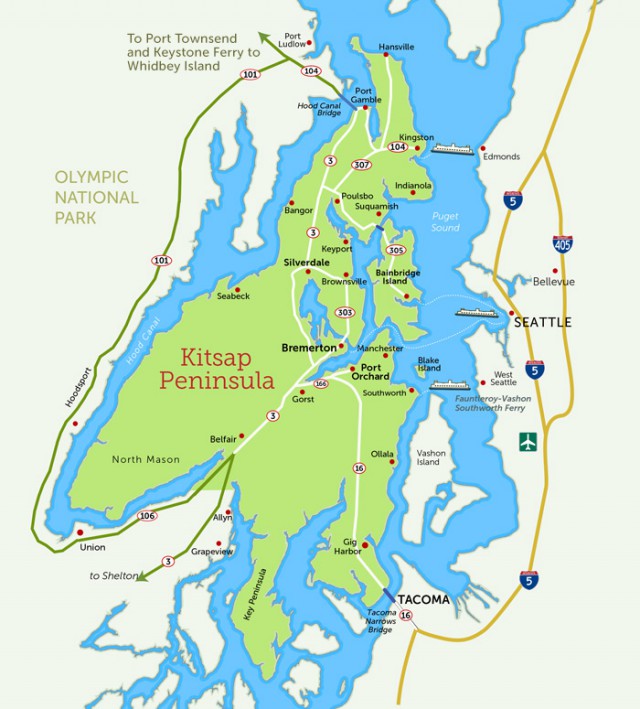 A Washington state man who just moved into his new home is now being forced to consider selling it to somebody else because Comcast repeatedly misled him about its ability to provide service.
A Washington state man who just moved into his new home is now being forced to consider selling it to somebody else because Comcast repeatedly misled him about its ability to provide service. Four of his options were wireless carriers that don’t provide a strong signal to his home or charge obscenely high prices for usage capped Internet access. ViaSat was on the list promising up to 25Mbps, but ViaSat satellite customers can testify the actual speeds received are much slower, and do not reliably support the VPN access Seth required.
Four of his options were wireless carriers that don’t provide a strong signal to his home or charge obscenely high prices for usage capped Internet access. ViaSat was on the list promising up to 25Mbps, but ViaSat satellite customers can testify the actual speeds received are much slower, and do not reliably support the VPN access Seth required.




 The Open Internet Order: Preserving and Protecting the Internet for All Americans
The Open Internet Order: Preserving and Protecting the Internet for All Americans