 The Communications Workers of America today filed comments with the Federal Communications Commission opposing the proposed sale of Cablevision to Patrick Drahi’s Altice NV, arguing the claimed public interest benefits are illusory.
The Communications Workers of America today filed comments with the Federal Communications Commission opposing the proposed sale of Cablevision to Patrick Drahi’s Altice NV, arguing the claimed public interest benefits are illusory.
The CWA, which represents some of Cablevision’s workers in Brooklyn, took a hard look at Altice’s merger proposal and the $8.6 billion in debt Altice will take on to close the deal and called it dangerous, resulting in “considerable harm with no offsetting concrete, verifiable benefits for consumers, workers, and communities.”
“Altice’s track record in France and Portugal clearly shows the danger this deal poses to Cablevision’s customers and employees,” said Dennis Trainor, vice president of Communications Workers of America District 1. “Altice takes on too much debt, outsources as much work as possible and then downsizes its workforce. Customers get worse service and employees lose their job. Unless Altice makes commitments to protect customer service and Cablevision employees, the FCC should reject this deal.”
The CWA is also concerned about the disparity between what Altice is telling regulators and what the company is saying to Wall Street.
Altice’s Public Interest Statement, which outlines the benefits to the public of the proposed transaction, stands out for its lack of specificity. In fact, the application’s only concrete commitments are vague promises to bring Altice’s “expertise” and access to capital for Cablevision’s use. Altice also promises to upgrade Cablevision’s IT systems, including customer care, service, and billing systems, and alluded it would expand Cablevision’s fiber optics deeper into its network, but comes short of promising a direct fiber to the home connection. In fact, the only promised benefit of pushing fiber further out would be “the removal or reduction from the network of coaxial RF amplifiers, which consume substantial electricity and can be the cause of difficult-to-detect service outages (RF amplifier failures).”
“Deeper fiber deployment would enable Cablevision to reduce its power costs and to further improve network reliability, resulting, in turn, in a greater ability to invest further in the network and improved service delivery to subscribers,” Altice dubiously claimed.
 Many of Altice’s claims appeared “disingenuous and misleading” to the CWA. From the CWA’s filing:
Many of Altice’s claims appeared “disingenuous and misleading” to the CWA. From the CWA’s filing:
To finance its $17.7 billion acquisition of Cablevision, Altice is taking on $8.6 billion in new debt, which when added to Cablevision’s already heavy debt load of $5.9 billion, will leave the new Cablevision with a total net debt of $14.5 billion. Given the high cost of the new debt financing, the annual interest payments needed to finance the $8.6 billion in new debt amount to $654 million on top of Cablevision’s current interest payments of $559 million for a total of $1.2 billion in annual interest payments at the new Cablevision, representing a full 112 percent increase in Cablevision debt. The new interest payment ($654 million) plus Altice’s announced $ 1.05 billion in cuts means that the new Cablevision will have $1.7 billion less cash available to spend on the network and service.
“Altice’s business model, the one that it has used to fuel its explosive global growth, requires the acquired company – in this instance, Cablevision — to finance its own acquisition and to provide cash to the parent for future acquisitions,” the CWA argues. “Altice chief financial officer Dennis Okhuijsen explained the capital structure of post-transaction Cablevision: ‘[W]e’re not going to lever up the existing business. This is a stand-alone capital structure, so we’re levering up the target for Cablevision….’”
 Translation: Cablevision alone is responsible for the debt Altice raised to pay for Cablevision. Or, as Altice explained to investors in its third quarter 2015 earnings report, the parent company operates its various subsidiaries as “distinct credit silos in Europe and the U.S.”
Translation: Cablevision alone is responsible for the debt Altice raised to pay for Cablevision. Or, as Altice explained to investors in its third quarter 2015 earnings report, the parent company operates its various subsidiaries as “distinct credit silos in Europe and the U.S.”
Altice CEO Patrick Drahi’s business formula is always the same. To raise money to help offset the mountain of debt dumped on the acquired company, Altice’s designated managers helicopter in to the acquired company to begin slashing expenses and find money it can send to Altice headquarters to help fill its coffers to acquire even more companies. French telecom giant Numericable-SFR, while on the road to losing one million customers in just one year, was preoccupied borrowing nearly $2 billion, not to improve the company’s service, but rather to pay Altice a special dividend to help pay down the huge amount of debt Altice incurred when it bought the 60 percent stake in the French mobile and cable company it did not already own.
To keep Altice afloat, Drahi’s business strategy requires a steady supply of company acquisitions to deliver the increased cash flows Altice needs to finance its debt. The CWA warned regulators Altice may require Cablevision to spend its cash flow to help Drahi acquire other companies in the future, further reducing the amount of money Cablevision needs to attract and keep subscribers.
To make the deal a long term success, Altice-Cablevision will either have to cut its return to shareholders, raise its prices, and/or slash expenses and jobs. Past experience with Altice shows shareholders come first, which means company management will likely preside over a harvest of Cablevision’s assets to meet the expectations of Wall Street banks and investors. Customers will feel the cuts from the reduction in service and slowed investments and upgrades.
At the same time Altice was promising the FCC it would continue Cablevision’s “first in class” level of service, the company was telling Wall Street it was planning cuts to the bone. Among Altice’s already-proposed cuts for Cablevision:
- Capital expense: $150 million cut
- Network and Operations: $ 315 million cut
- Customer operations: $135 million cut
- Sales and marketing: $45 million cut
- Eliminate duplicative functions and “public company” costs: $135 million cut
- Other unspecified cuts: $135 million cuts.
The impact of these cuts shift costs onto others, argues the CWA, including making the acquired firm pay for its own demise, making the workforce pay through job loss and reduced compensation, making customers pay through deteriorating service, and making suppliers become Drahi’s bankers by delaying payments.
The CWA says customers will also pay for the privilege of getting declining service.
“In Israel, the cable provider Hot Telecommunications has raised prices multiple times since it was bought by Altice, including a cable rate increase of 20 percent in 2014 and the attempt to raise prices again this year,” the CWA argues. “The top Israeli cable regulator called the price hike ‘greed for its own sake’ which was not justified based on the company’s profit margins.”
In the United States, nobody oversees cable pricing.
“In summary, the experience in France, Portugal, Israel, and elsewhere provides concrete evidence that the Altice business model – one that it plans to replicate with its Cablevision acquisition – does not serve the public interest,” concludes the CWA. “Making an acquired company pay off massive debt load with service-impacting cost cutting has serious and negative consequences for customers, suppliers, communities, and workers. The lesson from France is clear: cutting to the bone leads to massive customer defection. It is not a business model that will benefit the people of New York, Connecticut, and New Jersey.”



 Subscribe
Subscribe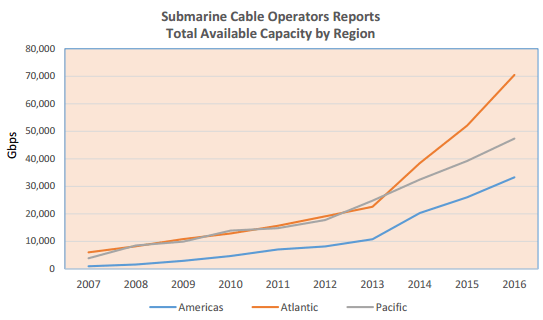 Overall submarine cable capacity, which supports a substantial amount of international Internet traffic, has grown around 36% per year for 2007-2014 and is expected to grow around 29% for 2014-2016. But traffic planners are confident the traffic growth will be easily accommodated over existing submarine cable circuits.
Overall submarine cable capacity, which supports a substantial amount of international Internet traffic, has grown around 36% per year for 2007-2014 and is expected to grow around 29% for 2014-2016. But traffic planners are confident the traffic growth will be easily accommodated over existing submarine cable circuits.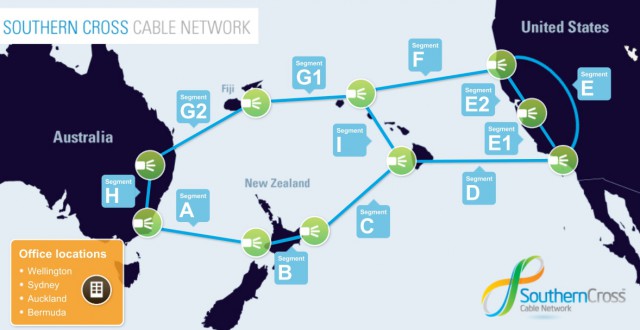
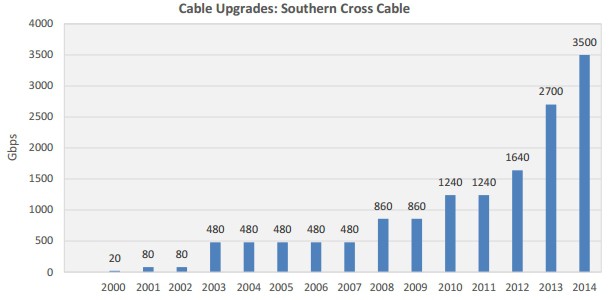 Southern Cross engineers are now deploying circuits capable of 40 and 100Gbps technology, bringing Southern Cross cable’s total available capacity to more than 12Tbps (12,000Gbps). Every upgrade was conducted at the cable station with zero new fiber pairs laid in the water. Other undersea cable operators are initiating similar upgrades, providing exponentially greater capacity at a minimal cost.
Southern Cross engineers are now deploying circuits capable of 40 and 100Gbps technology, bringing Southern Cross cable’s total available capacity to more than 12Tbps (12,000Gbps). Every upgrade was conducted at the cable station with zero new fiber pairs laid in the water. Other undersea cable operators are initiating similar upgrades, providing exponentially greater capacity at a minimal cost. The Communications Workers of America today
The Communications Workers of America today  Many of Altice’s claims appeared “disingenuous and misleading” to the CWA. From the CWA’s filing:
Many of Altice’s claims appeared “disingenuous and misleading” to the CWA. From the CWA’s filing: Translation: Cablevision alone is responsible for the debt Altice raised to pay for Cablevision. Or, as Altice explained to investors in its third quarter 2015 earnings report, the parent company operates its various subsidiaries as “distinct credit silos in Europe and the U.S.”
Translation: Cablevision alone is responsible for the debt Altice raised to pay for Cablevision. Or, as Altice explained to investors in its third quarter 2015 earnings report, the parent company operates its various subsidiaries as “distinct credit silos in Europe and the U.S.”
 House Republicans are hoping a back door legislative maneuver will successfully block the Federal Communications Commission from enforcing Net Neutrality and regulating or banning data caps.
House Republicans are hoping a back door legislative maneuver will successfully block the Federal Communications Commission from enforcing Net Neutrality and regulating or banning data caps. Comcast is inviting controversy launching a new live streaming TV service targeting cord-cutters while exempting it from its own data caps.
Comcast is inviting controversy launching a new live streaming TV service targeting cord-cutters while exempting it from its own data caps.
 Comcast claims it is reasonable to exempt Stream TV from its 300GB data cap being tested in a growing number of markets.
Comcast claims it is reasonable to exempt Stream TV from its 300GB data cap being tested in a growing number of markets.
