 [Editor’s Note: Federal Communications Commission chairman Thomas Wheeler today released a compromise proposal hoping to get the cost of set-top box equipment down for millions of Americans forced to lease equipment to watch cable television.
[Editor’s Note: Federal Communications Commission chairman Thomas Wheeler today released a compromise proposal hoping to get the cost of set-top box equipment down for millions of Americans forced to lease equipment to watch cable television.
Wheeler originally proposed requiring an open standard for set-top box equipment that would open the market to competition by allowing manufacturers to directly sell equipment to consumers and compete for their business. Cable operators, programmers, and various special interest groups that depend on financial contributions from those operators immediately launched an unprecedented pushback claiming set-top box reform was racist, anti-minority, promoted copyright theft, and was illegal and unconstitutional. Small cable operators claimed they might be driven out of business, and programmers claimed companies like Google might fundamentally change the channel lineup on new equipment that would leave them in a disadvantaged position.
In fact, the hundreds of millions of dollars in annual revenue earned by cable operators charging the same price for equipment fresh out of the box or handed down in beat up condition to the fifth customer in eight years was more likely the driving factor.
Mr. Wheeler capitulated and released a more modest proposal promising cable operators would be forced to offer free “apps” for devices like Roku and Apple TV. But cable operators will likely own and manage those apps and have direct control of authentication methods and anti-piracy measures that are likely to be proprietary. Still, apps like TWC TV which covers Time Warner Cable’s lineup on devices like Roku have allowed consumers to ditch expensive set-top equipment and irritating Digital Adapters that don’t function well and have almost tripled in price since their introduction. Making sure these apps provide comparable functionality with set-top boxes and are released to a variety of devices will be key to whether Wheeler’s proposal, delivered in full below courtesy of the Los Angeles Times, has a measurable impact on cable bills.]
FCC chairman: Here are the new proposed rules for set-top boxes
There’s never been a better time to watch television in America. We have more options than ever, and, with so much competition for eyeballs, studios and artists keep raising the bar for quality content. But when it comes to the set-top-box that delivers our pay-TV subscriptions, we have essentially no options, creating headaches and costing us serious money in rental fees. That makes no sense, which is why I’m sharing a proposal with my fellow commissioners at the Federal Communications Commission to change the system.

Wheeler’s compromise
Ninety-nine percent of pay-TV subscribers currently lease set-top boxes from their cable, satellite or telecommunications provider, paying an average of $231 a year for the privilege, according to a recent analysis. The collective tab is $20 billion annually in rental fees. In a recent study, 84% of consumers felt their cable bill was too high. What they may not realize is that every bill includes an add-on fee for their set-top boxes. We keep paying these charges even after the cost of the box has been recovered because we have no meaningful alternative.
Pay-TV providers will be required to provide apps — free of charge — that consumers can download to the device of their choosing.
Earlier this year, the FCC launched a process to unlock the set-top-box marketplace. We were motivated by the desire to give consumers relief, but we were also mandated to take action by Congress and the law, which says that consumers should be able to choose their preferred device to access pay-TV programming.
Over the past seven months, the Commission conducted an open proceeding where we heard from pay-TV providers, programmers, device and software manufacturers, consumers groups, and, most important, the American people. We listened.
Now, I am proposing rules that would end the set-top-box stranglehold. If adopted, consumers will no longer have to rent a set-top box, month after month. Instead, pay-TV providers will be required to provide apps – free of charge– that consumers can download to the device of their choosing to access all the programming and features they already paid for.
 If you want to watch Comcast’s content through your Apple TV or Roku, you can. If you want to watch DirectTV’s offerings through your Xbox, you can. If you want to pipe Verizon’s service directly to your smart TV, you can. And if you want to watch your current pay-TV package on your current set-top box, you can do that, too. The choice is yours. No longer will you be forced to rent set-top boxes from your pay-TV provider.
If you want to watch Comcast’s content through your Apple TV or Roku, you can. If you want to watch DirectTV’s offerings through your Xbox, you can. If you want to pipe Verizon’s service directly to your smart TV, you can. And if you want to watch your current pay-TV package on your current set-top box, you can do that, too. The choice is yours. No longer will you be forced to rent set-top boxes from your pay-TV provider.
One of the biggest benefits consumers will see is integrated search. The rules would require all pay-TV providers to enable the ability for consumers to search for pay-TV content alongside other sources of content. Just type in the name of a movie, and a list will come up with all the places it is scheduled for broadcast and where it can be streamed (like Amazon Prime or Hulu).
Integrated search also means expanded access to programming created by independent and diverse voices on the same platform as your pay-TV providers. Consumers will more easily find content even if it’s not on the pay-TV service to which they subscribe.
These rules will open the door for innovation, spurring new apps and devices, giving consumers even more choice and user control.
While our primary focus during this proceeding was to promote consumer choice and fulfill our congressional mandate, we recognize that protecting the legitimate copyright interests of content creators is also key to serving the public interest. To ensure that all copyright and licensing agreements will remain intact, the delivery of pay-TV programming will continue to be overseen by pay-TV providers from end-to-end. The proposed rules also maintain important protections regarding emergency alerting, accessibility and privacy.
Large pay-TV providers, which serve more than 90% of subscribers, will have two years to fully implement the new requirements. Medium-sized providers will have an additional two years to comply, and the smallest providers would be exempt.
This is a golden era for watching television and video. By empowering consumers to access their content on their terms, it’s about to get cheaper — and even better.

 “Enabling consumers to use apps instead of set-top boxes may be a valid goal, but the marketplace is already delivering on the goal without overreaching government intervention. The FCC’s mandate threatens to bog down with regulations and bureaucracy the entire TV app market that consumers are increasingly looking to for innovation, choice and competition.”
“Enabling consumers to use apps instead of set-top boxes may be a valid goal, but the marketplace is already delivering on the goal without overreaching government intervention. The FCC’s mandate threatens to bog down with regulations and bureaucracy the entire TV app market that consumers are increasingly looking to for innovation, choice and competition.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe [Editor’s Note: Federal Communications Commission chairman Thomas Wheeler today released a compromise proposal hoping to get the cost of set-top box equipment down for millions of Americans forced to lease equipment to watch cable television.
[Editor’s Note: Federal Communications Commission chairman Thomas Wheeler today released a compromise proposal hoping to get the cost of set-top box equipment down for millions of Americans forced to lease equipment to watch cable television.
 If you want to watch Comcast’s content through your Apple TV or Roku, you can. If you want to watch DirectTV’s offerings through your Xbox, you can. If you want to pipe Verizon’s service directly to your smart TV, you can. And if you want to watch your current pay-TV package on your current set-top box, you can do that, too. The choice is yours. No longer will you be forced to rent set-top boxes from your pay-TV provider.
If you want to watch Comcast’s content through your Apple TV or Roku, you can. If you want to watch DirectTV’s offerings through your Xbox, you can. If you want to pipe Verizon’s service directly to your smart TV, you can. And if you want to watch your current pay-TV package on your current set-top box, you can do that, too. The choice is yours. No longer will you be forced to rent set-top boxes from your pay-TV provider. Only half of CenturyLink’s customers in well-populated areas formerly served by Qwest can buy broadband service at 40Mbps or higher, while rural customers fare considerably worse with less than 25% able to get High Speed Internet at those speeds.
Only half of CenturyLink’s customers in well-populated areas formerly served by Qwest can buy broadband service at 40Mbps or higher, while rural customers fare considerably worse with less than 25% able to get High Speed Internet at those speeds. CenturyLink attempts to cover their claims with fine print attached to their FCC submission: “The numbers shown in this chart reflect the percentages of households served by DSLAMs that are capable of providing the specified broadband speeds.” (A DSLAM is a network device typically used to extend faster DSL speeds to customers by reducing the amount of copper wiring between the telephone company’s central office and the customer’s home. Customers in a neighborhood typically share space on a DSLAM, in effect sharing a single connection back to the phone company.)
CenturyLink attempts to cover their claims with fine print attached to their FCC submission: “The numbers shown in this chart reflect the percentages of households served by DSLAMs that are capable of providing the specified broadband speeds.” (A DSLAM is a network device typically used to extend faster DSL speeds to customers by reducing the amount of copper wiring between the telephone company’s central office and the customer’s home. Customers in a neighborhood typically share space on a DSLAM, in effect sharing a single connection back to the phone company.)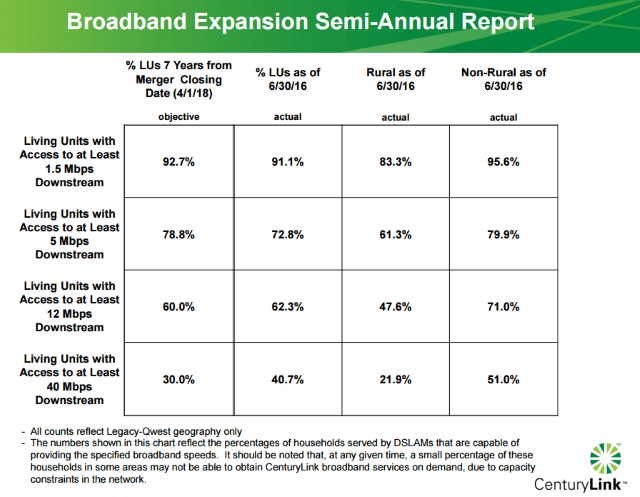
 Community broadband advocates will have to redouble their efforts to overturn state laws that restrict or prohibit municipal broadband, because the Federal Communications Commission today signaled it will no longer be a part of that fight.
Community broadband advocates will have to redouble their efforts to overturn state laws that restrict or prohibit municipal broadband, because the Federal Communications Commission today signaled it will no longer be a part of that fight.
