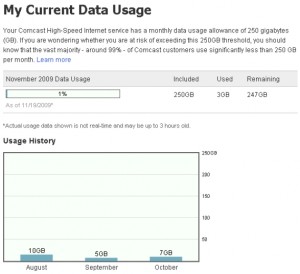
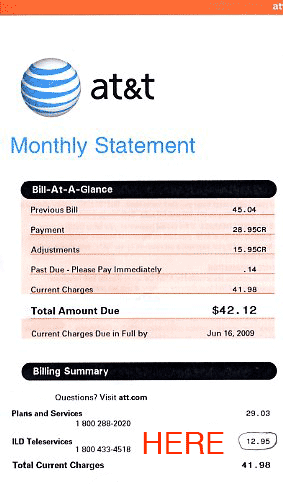
AT&T and Verizon are among the top recipients of ill-gotten gains from so-called “cramming” incidents — customers who find unauthorized charges on their phone bill placed there by third party companies that maintain a cozy billing relationship with the two phone companies.
Boston-area resident Mike Cunningham paid $567 in phone charges billed “conveniently” to his Verizon Wireless phone bill. Only he didn’t authorize them.
Cunningham recently sat down and reviewed nearly two years’ worth of dozen-page phone bills scrutinizing them for unauthorized charges. Speaking to the Boston Globe, Cunningham didn’t initially notice the “enhanced voice mail’’ charges of $14.95 and $13.22 buried on pages five and six. That’s not surprising, since many Verizon Wireless customers are now billed online and most customers don’t wade through multi-page online billing statements.
After Cunningham added several years of these monthly charges up, totaling $567, that got his attention.
Cunningham was billed by ILD Teleservices Inc., which said Cunningham’s grandson — then 10 years old — ordered its services while on a website that offers free video games. Cunningham said his grandson, who doesn’t have a cellphone, did not intentionally order voice mail — and knew nothing about it.
ILD generates an enormous number of complaints about unauthorized charges placed on consumer phone bills. The company describes itself as a leading payment processor of online transactions between merchants and consumers, processing more than 120 million billing transactions per year totaling $500 million of third party charges placed on telephone bills. Although the company claims to put its potential clients through a rigorous screening process, the avalanche of customer complaints, including the fact a 10-year old was able to be victimized by one of ILD’s clients, suggests otherwise.
Even worse, companies like AT&T and Verizon profit handsomely from fees paid by payment processors like ILD to gain the lucrative ability to charge customers’ phone bills for services, ordered or otherwise. With a profit incentive to protect, consumers are getting the short end of the stick when calling Verizon or AT&T to complain. More often than not they pass the buck (while keeping the change for themselves) back to the third party billing agency to try and secure refunds.
Only a staggering amount of potential earnings from such billing practices would seem enough to make risking the customer’s relationship with their phone company worthwhile. After customers spend hours dealing with unruly and hostile customer service representatives working for such billing agencies, there is little chance that customer will be endeared to the phone company that put them through the nightmare in the first place.
Susan from Ambler, Pennsylvania is an excellent example:
“ILD Teleservices placed a charge on my Verizon phone bill for a service that was not requested, authorized or that would even work (ringtones for a land line!) on Feb 22, 2010. When I called Verizon to question the bill, they informed me the charge was not a Verizon charge but from a third party company,” she told Consumer Affairs.
David in Galt, California was billed by ILD on his AT&T phone bill for ordering a service over his home computer, an amazing feat considering he doesn’t have one.
“I received a charge of 14.95 on my AT&T phone bill from ILD Teleservices. They claimed that someone in the household went online and ordered the service. We did not have the capability to do that with no computer at the house,” he writes.
More than 3,000 complaints have been logged against ILD by Consumer Affairs, with customers highly annoyed that their phone companies refuse to stand by them when illegitimate charges show up on their phone bills. John from Wisconsin got no help from AT&T when identify theft allowed someone to add unwanted services to his phone bill under his wife’s name.
It turns out someone signed him up for TotalContactSolutions, a Florida-based company that charges $14.95 a month to alert up to 10 people with text or voice messages “during catastrophic events such as terrorist attacks or natural disasters.” Perhaps the service will come in handy to contact those 10 friends and family members when you discover the charges on your phone bill and pass out on the floor.
John reports his credit rating is being terrorized by a company that refuses to refund the unauthorized charges unless he can prove, with an e-mail from AT&T no less, that nobody could have signed up for the service from John’s home. Unfortunately for John, AT&T’s surveillance of its customers doesn’t extend that far, and the company refused to forgive the charges, instead threatening him with collections.
Unfortunately, your tax dollars are hard at work paying for state utility commissions, the Federal Communications Commission, and consumer service agencies to assist consumers who are victimized twice by cramming charges — once by Verizon or AT&T for allowing them on their bills in the first place, and a second time trying to deal with a third party company to reverse them.
A Boston Globe review of more than 200 cramming-related complaints from consumers — filed with the Massachusetts Department of Telecommunications and Cable and the attorney general since 2007 — found that state workers reviewing complaints sometimes spent hours trying to resolve a single one.
The case of Soren Jensen, a retired engineer who lives in Duxbury, is typical. Jensen said he spotted four charges of $9.99 apiece for text messages on his wife and son’s cellphone bills starting in 2008. There was a common thread: Jensen’s wife and son said they had both taken IQ tests online, entering their cellphone numbers to receive the results. He suspected they mistakenly signed up for text messaging in the process.
After reviewing the fine print on his bill and doing some online sleuthing, he found Verizon Wireless had an agreement with Solow, a computer gaming website that contacts players using a text message service that charges $9.99 per message.
Jensen said he called Verizon Wireless to complain, and the company agreed to remove one of the $9.99 charges.
“I just don’t get why Verizon doesn’t want to protect us, as the customer,’’ Jensen said. “Verizon should not allow this kind of stuff. It raises a lot of questions.’’
The answers aren’t difficult to find when you follow the money. Both AT&T and Verizon collect plenty from fees charged to cramming companies and billing agencies for the right to bill their services directly on your phone bill. Neither company will disclose exactly how much they profit from such arrangements, but they are clear about who is responsible when mystery fees turn up on your phone bill: you are.
Both companies told the Boston Globe they “encourage customers to scrutinize their bills to make sure they are not improperly charged for services.”
And they make that very easy by labeling mystery fees with such helpful billing descriptions as “enhanced calling service” or “enhanced voicemail.” One of Stop the Cap!‘s readers was billed for services described as an “enhanced recovery fee” and another for “customer support and assistance.”
Verizon claims complaints about third-party charges are “infrequent” and says customers can contact the company and block all third-party charges from their bills, something we strongly recommend you consider doing before being victimized.
AT&T won’t go that far. It told the Globe:
AT&T, which also allows third-party billing, advises customers to direct their complaints to the company assessing the fee. Names of third-party vendors are disclosed on AT&T bills, the company said. “AT&T’s third-party billing contracts require service providers to address cramming complaints appropriately, including issuing credits if customers have been crammed,’’ an AT&T spokeswoman said in an e-mail.
But AT&T is still in the business of scaring its customers. TotalContactSolutions maintains a required AT&T customer disclaimer on their website, which includes several states where AT&T can disconnect your phone line over billing disputes:
You have the right to dispute the Employee Notification Services charges billed on your local telephone bill. You are not legally responsible for Employee Notification Services charges incurred by minors or vulnerable adults without your consent. Your local telephone service will not be disconnected because you fail to pay a charge by Employee Notification Services, except that nonpayment of certain regulated telecommunications charges may result in disconnection of service in AL, FL, GA, KY, LA, SC, and TN.
And we know what phone company lobbied their way into obtaining the right to cut your service off if you don’t pay, don’t we?
In the end, Cunningham got refunds for the unauthorized fees on his Verizon Wireless bill, after the companies discovered a minor child was involved.
ILD claims to have sent Cunningham $1,000 in coupons as part of a settlement, something Cunningham claims is a lie. Cunningham is better off without them. The $1,000 in coupons ILD offered is suspiciously similar to an offer from another ILD client that promises that amount in grocery coupons you can print on your computer… if you sign-up for enhanced voicemail service for $12.95 a month.

Was this the $1,000 in "free coupons" offered to Mike Cunningham? If so, it comes with some very expensive strings attached.
Cunningham is so disgusted with Verizon Wireless for putting him through this ordeal, he wanted to cancel his service and move on. But Verizon knows how to hold customers captive. Instead of sending him a refund check for $567, they applied it as a credit that can only be redeemed by remaining a Verizon Wireless customer until the credit is exhausted.
“It’s like salt in the wound,’’ he told the Globe. “I can’t leave. I’m a captive audience.’’
Stop the Cap! notes the Federal Communications Commission is overwhelmed with cramming complaints that number well into the thousands every year. Since telephone companies refuse to stand up for their customers, it is imperative that the FCC order phone companies to stop allowing all third-party billing unless and until a customer “opts-in” to such billing, in writing. No third party “opt-in” requests should be permitted, and customers should not have to chase their phone companies to opt-out of a service that has a built-in profit incentive for funny business, fraud, and costly scams that cost customers enormous time and money to resolve.
[flv width=”640″ height=”500″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CBS News Cramming Charges 2-23-08.flv[/flv]
The CBS Evening News ran this item about cramming charges and the problems they cause customers more than two years ago, interviewing a representative from Verizon Wireless. Very little has changed as the money, and complaints, keep pouring in. (3 minutes)
 One way around a court ruling unfavorable to Commission oversight powers would be to regulate broadband services under the existing rules governing phone service. The most controversial aspect of those rules are found in “common carrier” provisions — including those that could potentially force open the broadband networks offered by cable and telephone companies to third party competitors.
One way around a court ruling unfavorable to Commission oversight powers would be to regulate broadband services under the existing rules governing phone service. The most controversial aspect of those rules are found in “common carrier” provisions — including those that could potentially force open the broadband networks offered by cable and telephone companies to third party competitors.

 Subscribe
Subscribe