 In the last three years, several Wall Street analysts have called on cable and telephone companies to raise the price of broadband service to make up for declining profits selling cable TV. As shareholders pressure executives to keep profits high and costs low, dramatic price changes may be coming for broadband and television service that will boost profits and likely eliminate one of their biggest potential competitors — Sling TV.
In the last three years, several Wall Street analysts have called on cable and telephone companies to raise the price of broadband service to make up for declining profits selling cable TV. As shareholders pressure executives to keep profits high and costs low, dramatic price changes may be coming for broadband and television service that will boost profits and likely eliminate one of their biggest potential competitors — Sling TV.
For more than 20 years, the most expensive part of the cable package has been television service. Cable One CEO Thomas Might acknowledged that in 2005, despite growing revenue from broadband, cable television still provided most the profits. That year, 64% of Cable One’s profits came from video. Three years from now, only 30% will come from selling cable TV.
While broadband prices remained generally stable from the late 1990’s into the early 2000’s, cable companies were still raising cable television prices once, sometimes twice annually to support very healthy profit margins on a service found in most American homes no matter its cost. Despite customer complaints about rate hikes, as long as they stayed connected, few providers cared to listen. With little competition, pricing power was tightly held in the industry’s hands. The only significant challenge to that power came from programmers demanding (and consistently winning) a bigger share of cable’s profit pie.
The retransmission consent wars had begun. Local broadcast stations, popular cable networks, and even the major networks all had hands out for increased subscriber fees.

Rogers
In the past, cable companies simply passed those costs along, blaming “increased programming costs” in rate hike notifications without mentioning the amount was also designed to keep their healthy margins intact. Only the arrival of The Great Recession changed that. New housing numbers headed downwards as children delayed leaving to rent their own apartment or buy a house. Many income-challenged families decided their budgets no longer allowed for the luxury of cable television and TV service was dropped. Even companies that managed to hang on to subscribers recognized there was now a limit on the amount customers would tolerate and the pace of cable TV rate hikes has slowed.
For a company like Cable One, the impact of de facto profit-sharing on cable television service was easy to see. Ten years ago, only about $30 of a $70 video subscription was handed over to programmers. This year, a record $45.85 of each $81 cable TV subscription is paid to programmers. The $35.50 or so remaining does not count as profit. Cable One reported only $10.61 was left after indirect costs per customer were managed, and after paying for system upgrades and other expenses, it got to keep just $0.96 a month in profit.
To combat the attack on the traditional video subscription model, Cable One raised prices in lesser amounts and began playing hardball with programmers. It permanently dropped Viacom-owned cable networks to show programmers it meant business. Subscribers were livid. More than 103,000 of Cable One’s customers across the country canceled TV service, leaving the cable company with just over 421,000 video customers nationwide.
Some on Wall Street believe conducting a war to preserve video profits need not be fought.
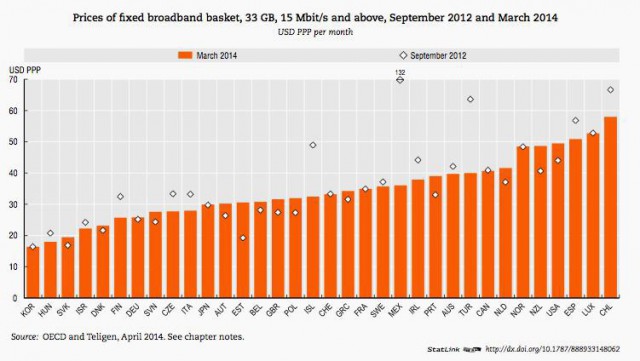
U.S. broadband providers already deliver some of the world’s most expensive Internet access.
Analysts told cable companies that the era of fat profits selling bloated TV packages is over, but the days of selling overpriced broadband service to customers that will not cancel regardless of the price are just beginning.
Cablevision CEO James Dolan admitted the real money was already in broadband, telling investors Cablevision’s broadband profit margins now exceed its video margins by at least seven to one.
The time to raise broadband prices even higher has apparently arrived.
 “Our work suggests that cable companies have room to take up broadband pricing significantly and we believe regulators should not oppose the re-pricing (it is good for competition & investment),” wrote New Street Research’s Jonathan Chaplin in a recent note to investors. The Wall Street firm sells its advice to telecom companies. “The companies will undoubtedly have to take pay-TV pricing down to help ‘fund’ the price increase for broadband, but this is a good thing for the business. Post re-pricing, [online video] competition would cease to be a threat and the companies would grow revenue and free cash flow at a far faster rate than they would otherwise.”
“Our work suggests that cable companies have room to take up broadband pricing significantly and we believe regulators should not oppose the re-pricing (it is good for competition & investment),” wrote New Street Research’s Jonathan Chaplin in a recent note to investors. The Wall Street firm sells its advice to telecom companies. “The companies will undoubtedly have to take pay-TV pricing down to help ‘fund’ the price increase for broadband, but this is a good thing for the business. Post re-pricing, [online video] competition would cease to be a threat and the companies would grow revenue and free cash flow at a far faster rate than they would otherwise.”
If you are already a triple play cable television, broadband, and phone customer, you may not notice much change if this comes to pass, at least not at first. To combat cord-cutting and other threats to video revenue, some advisers are calling on cable companies like Comcast, Time Warner Cable and Charter to re-price the components of their package. Under one scenario, the cost of cable television would be cut up to $30 a month while the price of Internet access would increase by $30 or more a month above current prices. Only customers who subscribe to one service or the other, but not both, would see a major change. A cable TV-only subscriber would happily welcome a $50 monthly bill. A broadband-only customer charged $80, 90, or even 100 for basic broadband service would not.
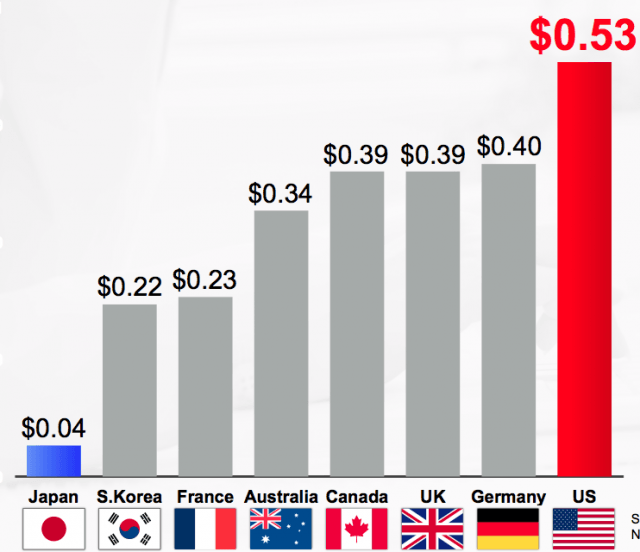 Neither would Sling CEO Roger Lynch, who has a package of 23 cable channels to sell broadband-only customers for $20 a month.
Neither would Sling CEO Roger Lynch, who has a package of 23 cable channels to sell broadband-only customers for $20 a month.
“They have their dominant — in many cases monopolies — in their market for broadband, especially high-speed broadband,” Sling CEO Roger Lynch told Business Insider in an interview, adding that some cable companies already make it cheaper for people to subscribe to TV and broadband from a cable company than just subscribe to broadband.
A typical Sling customers would be confronted with paying up to $100 a month just for broadband service before paying Sling its $20 a month. Coincidentally, that customer’s broadband provider is likely already selling cable TV and will target promotions at Sling’s customers offering ten times the number of channels for as little as a few dollars more a month on top of what they currently pay for Internet access.
Such a pricing change would damage, if not destroy, Sling TV’s business model. Lynch is convinced providers are seriously contemplating it to use “their dominant position to try to thwart over the top services.”
At least 75% of the country would be held captive by any cable re-pricing tactic, because those Americans have just one choice in providers capable of meeting the FCC’s minimum definition of broadband.
Even more worrying, FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler may be responsible for leading the industry to the re-pricing road map by repeatedly reassuring providers the FCC will have nothing to do with price regulation, which opens the door to broadband pricing abuses that cannot be easily countered by market forces.
Lynch has called on the FCC to “protect consumers” and “make sure there’s innovation and competition in video.”
Unfortunately, Wheeler may have something else to prove to his critics who argued Net Neutrality and Title II oversight of broadband would lead to rampant price regulation. Wheeler has hinted repeatedly he is waiting to prove what he says — an allusion to hoping for a formal rate complaint to arrive at the FCC just so he can shoot it down.



 Subscribe
Subscribe Two cable industry trade associations have asked the Federal Communications Commission to start collecting more fees from satellite television operators to cover the FCC’s regulatory expenses — a move satellite providers argue will cause consumers to suffer bill shock from increased prices.
Two cable industry trade associations have asked the Federal Communications Commission to start collecting more fees from satellite television operators to cover the FCC’s regulatory expenses — a move satellite providers argue will cause consumers to suffer bill shock from increased prices. “The FCC is off to a good start by declaring that Dish and DirecTV should pay regulatory fees to support the work of the agency’s Media Bureau for the first time and proposing setting the initial per subscriber fee at one cent per month in 2015,” said Matthew Polka, president and CEO of the ACA. “But given the FCC proposes that cable operators pay nearly 8 cents per month, per customer, it must do more, including requiring these two multibillion dollar companies with national reach to shoulder more of the fee burden next year that is now disproportionately borne by smaller, locally based cable operators.”
“The FCC is off to a good start by declaring that Dish and DirecTV should pay regulatory fees to support the work of the agency’s Media Bureau for the first time and proposing setting the initial per subscriber fee at one cent per month in 2015,” said Matthew Polka, president and CEO of the ACA. “But given the FCC proposes that cable operators pay nearly 8 cents per month, per customer, it must do more, including requiring these two multibillion dollar companies with national reach to shoulder more of the fee burden next year that is now disproportionately borne by smaller, locally based cable operators.” The ACA reminded the FCC it did not seem too concerned about rate shock when it imposed a 99 cent fee on IPTV providers like AT&T U-verse in 2014 without a phase-in.
The ACA reminded the FCC it did not seem too concerned about rate shock when it imposed a 99 cent fee on IPTV providers like AT&T U-verse in 2014 without a phase-in.

 Bahrami responds Time Warner’s attitude is based on a distinction without much difference because he is effectively being told CNS must pay extra for a suitable connection with Time Warner to guarantee his web visitors will have a good experience.
Bahrami responds Time Warner’s attitude is based on a distinction without much difference because he is effectively being told CNS must pay extra for a suitable connection with Time Warner to guarantee his web visitors will have a good experience. In the last three years, several Wall Street analysts have called on cable and telephone companies to raise the price of broadband service to make up for declining profits selling cable TV. As shareholders pressure executives to keep profits high and costs low, dramatic price changes may be coming for broadband and television service that will boost profits and likely eliminate one of their biggest potential competitors — Sling TV.
In the last three years, several Wall Street analysts have called on cable and telephone companies to raise the price of broadband service to make up for declining profits selling cable TV. As shareholders pressure executives to keep profits high and costs low, dramatic price changes may be coming for broadband and television service that will boost profits and likely eliminate one of their biggest potential competitors — Sling TV.

 “Our work suggests that cable companies have room to take up broadband pricing significantly and we believe regulators should not oppose the re-pricing (it is good for competition & investment),”
“Our work suggests that cable companies have room to take up broadband pricing significantly and we believe regulators should not oppose the re-pricing (it is good for competition & investment),”  Neither would Sling CEO Roger Lynch, who has a package of 23 cable channels to sell broadband-only customers for $20 a month.
Neither would Sling CEO Roger Lynch, who has a package of 23 cable channels to sell broadband-only customers for $20 a month.
 Commissioner Michael O’Rielly
Commissioner Michael O’Rielly 