
Wheeler
FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler today told an audience at the National Press Club that 5G — the next generation of wireless networks — “is a national priority, and why, this Thursday, I am circulating to my colleagues proposed new rules that will identify and open up vast amounts of spectrum for 5G applications.”
Wheeler’s proposal, dubbed “Spectrum Frontiers,” is supposed to deliver wireless connectivity as fast as fiber optic broadband, and in Wheeler’s view, will deliver competitive high-speed access for consumers.
“If the Commission approves my proposal next month, the United States will be the first country in the world to open up high-band spectrum for 5G networks and applications,” said Wheeler. “And that’s damn important because it means U.S. companies will be first out of the gate.”
Central to Wheeler’s 5G proposal is opening up very high frequency millimeter wave spectrum — for unlicensed and licensed data communications. Wheeler named two in his speech: a “massive” 14GHz unlicensed band and a 28GHz “shared band” that will allow mobile and satellite operators to co-exist.
“Consider that – 14,000 megahertz of unlicensed spectrum, with the same flexible-use rules that has allowed unlicensed to become a breeding ground for innovation,” Wheeler said.
 “Sharing is essential for the future of spectrum utilization. Many of the high-frequency bands we will make available for 5G currently have some satellite users, and some federal users, or at least the possibility of future satellite and federal users,” Wheeler noted. “This means sharing will be required between satellite and terrestrial wireless; an issue that is especially relevant in the 28GHz band. It is also a consideration in the additional bands we will identify for future exploration. We will strike a balance that offers flexibility for satellite users to expand, while providing terrestrial licensees with predictability about the areas in which satellite will locate.”
“Sharing is essential for the future of spectrum utilization. Many of the high-frequency bands we will make available for 5G currently have some satellite users, and some federal users, or at least the possibility of future satellite and federal users,” Wheeler noted. “This means sharing will be required between satellite and terrestrial wireless; an issue that is especially relevant in the 28GHz band. It is also a consideration in the additional bands we will identify for future exploration. We will strike a balance that offers flexibility for satellite users to expand, while providing terrestrial licensees with predictability about the areas in which satellite will locate.”
The CTIA – The Wireless Association, America’s largest mobile carrier lobbying and trade association, is all for opening up new spectrum for the use of their members — AT&T, Verizon Wireless, Sprint, T-Mobile, among others. They just don’t want to share it. Ironically, they are calling on the FCC to regulate who gets access to what frequencies and what services can use them. They’d also appreciate federal rules restricting or preempting local officials responsible for approving where new cell towers can be located, and some form of price regulation for backhaul services would also be nice:
First, we need the right rules for high-band spectrum based on a time-tested regulatory framework. It must strike a reasonable balance for licensed and unlicensed use while promoting investment with clear service and licensing rules. We should avoid experimenting with novel spectrum sharing regimes or new technology mandates.
Second, we need the right rules to help build our 5G infrastructure. Traditional spectrum travels many miles, depending on large cell towers to transmit signals. In contrast, high-band spectrum – capable of carrying greater amounts of data –travels meters, not miles and will require the deployment of thousands of new small cells the size of smoke alarms. This network evolution requires a new infrastructure approach, and Congress, the FCC and states must streamline and simplify local siting and rights of way rules.
Wheeler recognizes that 5G services will work very differently from the 3G and 4G networks we’ve used in the past.

CTIA is the wireless industry’s biggest lobbyist and trade association.
“5G will use much higher-frequency bands than previously thought viable for mobile broadband and other applications,” Wheeler said. “Such millimeter wave signals have physical properties that are both a limitation and a strength: they tend to travel best in narrow and straight lines, and do not go through physical obstacles very well. This means that very narrow signals in an urban environment tend to bounce around buildings and other obstacles making it difficult to connect to a moving point. But it also means that the spectrum can be reused over and over again.”
In other words, think about 5G as an initially limited range wireless network that may turn out to be best suited for fixed wireless service or limited range hotspots, especially before network densification helps make 5G service more ubiquitous. The wireless industry doesn’t think Wheeler’s vision will be enough to resolve capacity issues in the short term, and is calling on the FCC to release even more low and mid-band spectrum in the 600MHz range that can travel inside buildings and offer a wider coverage area.
Wheeler’s recognition that 5G’s shorter range signals will likely require a massive overlay of new infrastructure has also opened the door for the CTIA to call on the FCC to revisit local zoning and antenna placement rules and policies, with the likely goal of preempting or watering down local authority to accept or reject where cell phone companies want to place their next small cell or cell tower. Wireless companies are also expected to push for easy access to utility poles, time limits to approve new cell tower construction applications, and pricing regulation for fiber lines needed to connect 5G infrastructure to backhaul networks.

Cell tower camouflage failure.
On the issue of backhaul — the connection between a cell tower and the wireless carrier’s network, the FCC is planning a pro-regulatory “anchor pricing” approach to benefit wireless companies. Consumers can also relate to being overcharged for slow speed Internet access with little or no competition, but the FCC is only acting for the benefit of the wireless companies for now — the same companies that would undoubtedly complain loudly if anchor pricing was ever applied to them.
“Lack of competition doesn’t just hurt the deployment of wireless networks today, it threatens as well to delay the buildout of 5G networks with its demand for many, many more backhaul connections to many, many more antennae,” complained Wheeler. “Before the end of this year the Commission will take up a reform proposal – supported by the nation’s leading wireless carriers, save one – that will encourage innovation and investment in Business Data Services while ensuring that lack of competition in some places cannot be used to hold 5G hostage.”
While Wheeler’s goals are laudable, there are stunning examples of hypocrisy and self-interest from the wireless industry. Yet again, the industry is seeking regulatory protection from having to share spectrum with unlicensed users, existing licensees, or competitors. No letting the “free market” decide here. Second, there are absolutely no assurances the wireless industry will deliver substantial home broadband competition. Verizon and AT&T will be effectively competing with themselves in areas where they already offer wired broadband. Is there a willingness from AT&T and Verizon to sell unlimited broadband over 5G networks or will customers be expected to pay “usage pack”-prices as high as $10 per gigabyte, which doesn’t include the monthly cost of the service itself. Offering customers unlimited 5G could cannibalize the massive profits earned selling data plans to wireless customers.
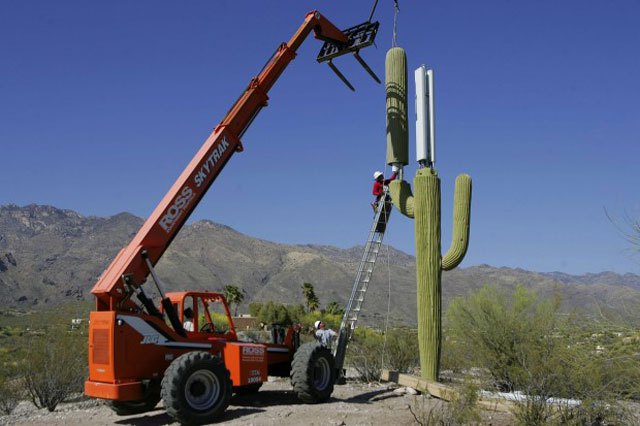

Cactus or cell tower
Upgrading to 5G service will be expensive and take years to reach many neighborhoods. Verizon’s chief financial officer believes 5G wireless will be more cost-effective to deploy than its FiOS fiber to the home network, but considering Verizon largely ended its deployment of FiOS several years ago and has allowed its DSL customers to languish just as long, 5G will need to be far more profitable to stimulate Verizon’s interest in spending tens of billions on 5G infrastructure. It does not seem likely the result will be $25/month unlimited, fiber-like fast, Internet plans.
Although the mobile industry will argue its investment dollars should be reason enough to further deregulate and dis-empower local officials that oversee the placement of cellular infrastructure, it would be a tremendous mistake to allow wireless carriers to erect cell towers and small cells wherever they see fit. Most small cells aren’t much larger than a toaster and will probably fit easily on utility poles. But it will likely spark another wave of pole access controversies. The aesthetics of traditional cell tower placement, especially in historical districts, parks, and suburbs, almost always create controversy. The FCC should not tip the balance of authority for tower placement away from those that have to live with the results.
The mobile industry doesn’t make investments for free, and before we reward them for investing in their networks, let’s recall the United States pays some of the highest mobile service prices in the world. The industry argues what you get in return for that $100+ wireless bill is better than ever, an argument similarly used by the cable industry to justify charging $80 a month for hundreds of channels you don’t watch or want. Therefore, incentives offered to the wireless industry should be tied to permanent pro-consumer commitments, such as unlimited 5G broadband, better rural coverage, and the power to unbundle current wireless packages and ditch services like unlimited texting many customers don’t need. Otherwise, it’s just another one-sided corporate welfare plan we can’t afford.

 “I think it’s vital to put our country’s well being ahead of party,” he said in a statement provided by the Clinton campaign. “Hillary Clinton is experienced, qualified, and will make a fine president. The alternative, I fear, would set our nation on a very dark path.”
“I think it’s vital to put our country’s well being ahead of party,” he said in a statement provided by the Clinton campaign. “Hillary Clinton is experienced, qualified, and will make a fine president. The alternative, I fear, would set our nation on a very dark path.” Cicconi would be pleased to see someone like former Tennessee congressman Harold Ford, Jr., take a seat at the FCC under a future Clinton Administration instead. Ford has served as an honorary co-chairman of Broadband for America, an industry-sponsored astroturf operation, for most of Obama’s two terms in office. He remains a close friend of both Bill and Hillary and is never far from the public eye, turning up regularly on MSNBC.
Cicconi would be pleased to see someone like former Tennessee congressman Harold Ford, Jr., take a seat at the FCC under a future Clinton Administration instead. Ford has served as an honorary co-chairman of Broadband for America, an industry-sponsored astroturf operation, for most of Obama’s two terms in office. He remains a close friend of both Bill and Hillary and is never far from the public eye, turning up regularly on MSNBC.

 Subscribe
Subscribe The Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission  Polka pointed to AT&T’s acquisition of DirecTV as an example of how disproportionate fees cost small independent cable companies much more on a per-subscriber basis than telecom giant AT&T has to pay for almost 20 million DirecTV satellite customers.
Polka pointed to AT&T’s acquisition of DirecTV as an example of how disproportionate fees cost small independent cable companies much more on a per-subscriber basis than telecom giant AT&T has to pay for almost 20 million DirecTV satellite customers.![This spring, The Consumerist broke down a typical AT&T U-verse bill loaded in junk fees and surcharges. (The RED numbers [1, 4-10, 13-14, 17-20, 22] are AT&T-originating fees; BLUE numbers [2-3, 11-12, 15-16, 21, 23-25] are government fees)](https://stopthecap.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/att-fees-640x926.png)
 An effort by a House Republican to scale back the FCC’s Lifeline subsidy program failed on a largely party-line vote Tuesday.
An effort by a House Republican to scale back the FCC’s Lifeline subsidy program failed on a largely party-line vote Tuesday.

 “Sharing is essential for the future of spectrum utilization. Many of the high-frequency bands we will make available for 5G currently have some satellite users, and some federal users, or at least the possibility of future satellite and federal users,” Wheeler noted. “This means sharing will be required between satellite and terrestrial wireless; an issue that is especially relevant in the 28GHz band. It is also a consideration in the additional bands we will identify for future exploration. We will strike a balance that offers flexibility for satellite users to expand, while providing terrestrial licensees with predictability about the areas in which satellite will locate.”
“Sharing is essential for the future of spectrum utilization. Many of the high-frequency bands we will make available for 5G currently have some satellite users, and some federal users, or at least the possibility of future satellite and federal users,” Wheeler noted. “This means sharing will be required between satellite and terrestrial wireless; an issue that is especially relevant in the 28GHz band. It is also a consideration in the additional bands we will identify for future exploration. We will strike a balance that offers flexibility for satellite users to expand, while providing terrestrial licensees with predictability about the areas in which satellite will locate.”



