 Only half of CenturyLink’s customers in well-populated areas formerly served by Qwest can buy broadband service at 40Mbps or higher, while rural customers fare considerably worse with less than 25% able to get High Speed Internet at those speeds.
Only half of CenturyLink’s customers in well-populated areas formerly served by Qwest can buy broadband service at 40Mbps or higher, while rural customers fare considerably worse with less than 25% able to get High Speed Internet at those speeds.
Customers have noticed and at least 65,000 canceled their broadband service with the phone company in the second quarter of this year, most presumably switching to their area’s cable operator.
“CenturyLink is by far the most abysmal telephone company I’ve ever had to deal with and I’m 63 years old,” shares Glen Canby in Arizona. Canby is a retired telephone company engineer that spent 40 years with a larger phone company serving the midwestern U.S. “Their reviews online echo my own experiences, which have ranged from being quoted one price while being billed another, being locked into a term contract you didn’t ask for, and getting only a fraction of the speed they claim to sell.”
Canby is counted as one of CenturyLink’s 40Mbps-qualified customers, yet he actually receives less than 6Mbps service.
But that isn’t what CenturyLink tells the Federal Communications Commission. In a semi-annual broadband deployment report, the company claimed 51 percent of their customers in urban and suburban former Qwest service areas can subscribe to 40Mbps DSL or higher. But whether a customer is “qualified” to buy 40Mbps service is not the same as actually getting the speeds the company markets.
 CenturyLink attempts to cover their claims with fine print attached to their FCC submission: “The numbers shown in this chart reflect the percentages of households served by DSLAMs that are capable of providing the specified broadband speeds.” (A DSLAM is a network device typically used to extend faster DSL speeds to customers by reducing the amount of copper wiring between the telephone company’s central office and the customer’s home. Customers in a neighborhood typically share space on a DSLAM, in effect sharing a single connection back to the phone company.)
CenturyLink attempts to cover their claims with fine print attached to their FCC submission: “The numbers shown in this chart reflect the percentages of households served by DSLAMs that are capable of providing the specified broadband speeds.” (A DSLAM is a network device typically used to extend faster DSL speeds to customers by reducing the amount of copper wiring between the telephone company’s central office and the customer’s home. Customers in a neighborhood typically share space on a DSLAM, in effect sharing a single connection back to the phone company.)
“That’s clever of them, because of course the DSLAM is just one link in the chain that ends with the ‘last mile’ between that equipment and my home, and that is where CenturyLink’s phone plant is at its weakest,” Canby writes. “I spent 20 years at a phone company dealing with last-mile DSL speed issues, so they cannot fool me.”
Canby blames the condition of CenturyLink’s infrastructure between the DSLAM serving him and his home for the problems, as well as overselling DSL service by packing too many customers onto a single DSLAM.
“It might be 40Mbps service at the remote end, but it drops to around 6Mbps on a good day by the time it reaches my house,” Canby complains. “Once the sun goes down, the speed drops to 3Mbps, which is a classic case of overselling to me because too many people are trying to share one connection at the same time. It has been this way since 2008 according to my neighbors.”
Back then, phone service was provided by Qwest, the former Baby Bell providing service in 14 sparsely populated western U.S. states — Arizona, Colorado, Idaho, Iowa, Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oregon, South Dakota, Utah, Washington, and Wyoming. Qwest was acquired by CenturyLink in 2011.
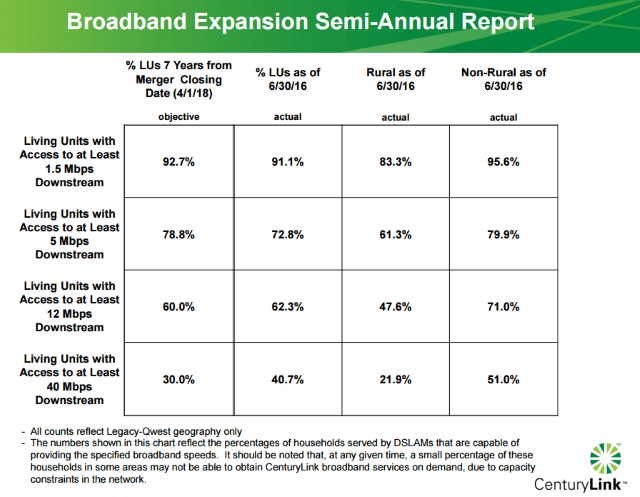
CenturyLink has promised to improve broadband speeds for former Qwest customers, but much of what counts as progress has been in more urban areas, while rural customers continue to languish. The company admits just 21.9 percent of rural households can get 40Mbps service. Only 47.6% can buy 12Mbps, 61.3% can get 5Mbps, and 83% can subscribe to 1.5Mbps. That leaves 17% of former Qwest customers with no broadband options at all. CenturyLink did not break out the percentage of customers that meet the FCC’s 25Mbps minimum speed definition of broadband.
“This is why CenturyLink loses customers to cable operators who have no problems trying to deliver internet access over their network, because it was built to support more bandwidth,” Canby shares. “They can usually deliver the same internet speed to customers no matter how far out they live while phone companies deal with a network built for making phone calls, not data.”
Company officials recognize they could do better and have promised investors another 2.5 million customers will be able to reach 40Mbps by the end of 2017. By the end of the year after that, CenturyLink hopes to reach 85% of customers with VDSL2, bonding, and vectoring technology to achieve 40Mbps service for most customers in their top 25 markets. But rural customers are likely to left waiting longer because of the costs to upgrade Qwest’s copper-based network, especially in smaller states like Idaho, the Dakotas and Wyoming.
“The only answer is cable or fiber broadband, and if you live in a small community it could be years before CenturyLink gets around to you,” Canby writes. “If it’s the same story all over town, I’d start advocating for a community-owned fiber network and not sit around and wait for CenturyLink to act, especially if there is no cable company in town.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe Community broadband advocates will have to redouble their efforts to overturn state laws that restrict or prohibit municipal broadband, because the Federal Communications Commission today signaled it will no longer be a part of that fight.
Community broadband advocates will have to redouble their efforts to overturn state laws that restrict or prohibit municipal broadband, because the Federal Communications Commission today signaled it will no longer be a part of that fight. AT&T has gone over the top donating at least $70,000 to back Republican House Speaker Paul Ryan, more than the company has ever donated to anyone else.
AT&T has gone over the top donating at least $70,000 to back Republican House Speaker Paul Ryan, more than the company has ever donated to anyone else.

 A federal appeals court has reversed an effort by the Federal Communications Commission to pre-empt state laws restricting municipal broadband expansion in Tennessee and North Carolina, ruling the FCC exceeded its authority by interfering with both states’ rights to define the boundaries where the community broadband networks can and cannot operate.
A federal appeals court has reversed an effort by the Federal Communications Commission to pre-empt state laws restricting municipal broadband expansion in Tennessee and North Carolina, ruling the FCC exceeded its authority by interfering with both states’ rights to define the boundaries where the community broadband networks can and cannot operate.


