 The stunning victory by Donald Trump in Tuesday’s election ended two years of campaigning, negativity, and divisiveness.
The stunning victory by Donald Trump in Tuesday’s election ended two years of campaigning, negativity, and divisiveness.
Wednesday probably marked the beginning of Election 2020, which will involve four years of campaigning, negativity, and divisiveness.
Before looking at the implications of the forthcoming Trump Administration, some personal words about the results from the perspective of a lifelong resident of western New York, on the periphery of the Rust Belt region that evidently made all the difference for Mr. Trump on Tuesday night.
Casting my vote here in western New York while suffering a severe cold that has now evolved into walking pneumonia, I reflected on the fact this nasty election probably gave it to me. Despite that, I have the good fortune of living in a diverse community. Our next door neighbor, and by far the closest to us personally, is an ardent Republican who supported Sen. McCain, Gov. Romney, and Mr. Trump. Across the street, a reliable panoply of Democratic candidate lawn signs sprout every other fall. I spend my Friday afternoons in a community south of Rochester where Hillary Clinton has been largely reviled since she was a senator of New York. She didn’t win in Ontario County this year either. But Sen. Chuck Schumer routinely wins his elections with little effort or opposition.
Politics in the western half of New York State (known as “somewhere around Canada” to those in New York City and Long Island) is far more comparable to the battleground state of Ohio than reliably Democratic Manhattan. Our urban centers in Buffalo, Rochester, and Syracuse are solidly Democratic, while the suburbs and rural areas are just as likely to elect Republicans to office. Among those disappointed Democrats pondering a surprising election of Donald Trump, many cannot understand how such a result is possible. But having been a lifelong resident in a region that has seen profound changes from the decimation of blue-collar, high-paying manufacturing jobs in states that still cling to tax rates that assume everyone still has one, the Trump rebellion predicted by Michael Moore was hardly outlandish. Across the Rust Belt, more than a few voters have given up believing politicians, and are still waiting for relief from the relentless pressure on the declining middle class. Some of the worst job declines came in this region during the first Bush Administration and then again under President Bill Clinton. Memories are still fresh.
The changes to local economies in this region are profound and extremely difficult to navigate for those who lack advanced degrees or special technical skills. A state like North Carolina understands these changes well. An economy quickly transformed away from tobacco and textiles towards high technology created enormous challenges for many families. Those problems still exist in many parts of the state where infrastructure and good jobs are still lacking more than two decades later.
In Rochester, the formerly solid and reliable employers like Eastman Kodak and Xerox are a fraction of the size they were in the 1980s. My father met my mother at Eastman Kodak, a company that also employed more than half my extended family. But not for long. I vividly recall watching the inauguration parade of President Bill Clinton on television in 1993 on a day that Eastman Kodak carried out another wave of draconian job cuts. My father’s job survived, but my uncle’s did not. My grandfather had retired by then.

Michael Moore correctly predicted the reality of a Trump victory with the support of a disaffected middle class in economically distressed states.
Twenty-three years later, the largest employer by far in this area is the University of Rochester/UR Medicine, which includes the university and an enormous medical treatment infrastructure. Together, this accounts for 22,500 workers. The second largest employer in Rochester is a grocery store. A great grocery store — Wegmans, founded and based here, but a grocery store nonetheless. It accounts for 13,500 jobs. Another 13,000+ workers are employed in medical treatment and hospital services that compete with the U of R. Rounding out top employers are the Rochester City School District with 5,500 teachers, administrators and staff, which is almost as big as Monroe County’s government, which accounts for 4,500 employees. The biggest remaining manufacturer is Xerox, which employs 6,300 workers. But consider this contrast: in 1982 Kodak employed 60,400 in the Rochester area. Today, that number is just 2,300.
Rochester had it easy compared to heavy manufacturing cities to our west. Buffalo, western Pennsylvania, Ohio, and Michigan have been walloped twice — first by the offshoring of heavy industry and then a second round of manufacturing job losses many voters blame on various free trade agreements. Many tens of thousands of these displaced workers have relocated to other states. Exiting residents of Rochester overwhelmingly prefer North Carolina and Arizona for various reasons, while blue-collar workers further west often end up in Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama, and other southern states. Many of those that remained behind and remember their old jobs are angry, very angry. Some of them supported Bernie Sanders, especially in Michigan. But once the choice came down to Hillary Clinton or Donald Trump, more than a few voted for Mr. Trump, not out of a great allegiance to the Republican party, but because Trump vilified free trade and business as usual in D.C. To these voters, fair or not, Hillary seemed to embody the establishment that has done little or nothing except make speeches.
The election is now over and we have the results. My candidate did not win because she did not run. (Elizabeth Warren in 2020!) On the broadband issues Stop the Cap! is concerned with, a Trump Administration is likely to be bad news for consumer protection, fair pricing, and community broadband, primarily because the people Mr. Trump has chosen thus far to advise him on tech issues are the usual sort with close ties to the largest telecommunications companies in the country, and many have penned papers that have closely aligned with those companies’ public policy positions.

Phillip Dampier: This election gave me walking pneumonia.
Trump transition team adviser Jeffrey Eisenach, for example — who we wrote about back in August, could hold considerable power over the direction President-elect Trump will take tech policy in this country. Eisenach has written papers opposing Net Neutrality, is unconcerned about data caps and zero rating policies, and called fears about consolidation blowouts like the now-dead Comcast-Time Warner Cable mega-merger overblown.
Trump did state opposition to the recent merger announcement from AT&T and Time Warner, Inc., which has Wall Street concerned the deal will be DOA by the time the merger papers are filed sometime early next year in Washington. If President Trump keeps his word on that, there are many more mergers and acquisition deals that will emerge in 2017 that will likely never be on his radar, but will be reviewed by a Federal Communications Commission stacked with commissioners closer in ideology to Ajit Pai and Michael O’Rielly than Thomas Wheeler. In our view, Commissioners Pai and O’Rielly have yet to support any significant pro-consumer policy change on broadband before the FCC. Instead, they have largely parroted Big Telecom’s talking points.
It is our suspicion that most of the merger and acquisition deals dreamed about on Wall Street that would never have gotten through the Obama Administration’s Justice Department and FCC will receive quick approval under a Trump Administration.
While Mr. Trump alludes he will prove to be a complete game-changer to business as usual in Washington, his transition team is being swarmed by the usual faces — corporate lobbyists, big donors, and political hacks angling for cabinet or agency positions. Most of them are Beltway insiders, and many have been through D.C.’s revolving door before — lobbyist -> public servant -> lobbyist.
So while Mr. Trump tells America AT&T and Time Warner is “too much concentration of power in the hands of too few,” we remain uncertain he will speak as loudly about other likely deals, particularly involving Altice, Cox, Mediacom, CenturyLink, Windstream, Frontier, Sprint, and T-Mobile — just some of the hunters and the hunted that may get consolidated in 2017.
On other issues:
- Net Neutrality: Republicans vilified Net Neutrality and a Republican-dominated FCC will likely kill or dramatically downplay any efforts to enforce it. Trump himself has never been a fan. Any new powers won by Chairman Wheeler to regulate internet providers under Title II will also likely be jettisoned by a Chairman Pai or O’Rielly;
- Data Caps/Zero Rating: This issue is important to us, but isn’t likely to see any regulatory action under a GOP-dominated FCC. Internet providers are likely to see a Trump Administration as a green light for data caps and consumption billing;
- Internet Privacy: Efforts to regulate internet privacy will also likely face a reversal from skeptical Republicans who will combine excuses for national security with a “hands off” attitude on telecommunications regulation.
- Community Broadband: The issue of turning back bans on public/municipal broadband will have to be won on the state level. We do not expect to see many friends for municipal broadband in Republican-dominated Washington. The influence of the Koch Brothers, notoriously opposed to public internet projects, has only gotten stronger after this election.
With a GOP-sweep across the Executive and Legislative branches, we expect more deregulation, which is likely to further entrench the broadband duopoly in the United States, if not further expand it with additional consolidation-related mergers and acquisitions, at least among the small and mid-sized players.
On a more personal level, I have been involved in public policy battles surrounding telecommunications issues since 1988. In the late 1980s, I fought for increased competition and regulatory relief for home satellite (TVRO) dishowners and we joined forces to help pass the 1992 Cable Act, which laid the foundation for the emergence of competitors DirecTV and Dish Networks — the first serious competition to the cable industry. That law was vetoed by President George H.W. Bush, but that veto was overridden by the U.S. Congress — the only bill to successfully become law during the first Bush Administration over his objection. Republicans pay cable bills too.

(Image courtesy: Steve Rhodes)
Administrations come and administrations go, but we are still here.
The need for robust consumer protection, true competition, and a level playing field never changes. Your involvement remains essential regardless of what party is in power in Washington. Some battles will be more challenging, but not all. Direct consumer action can make an impact on companies concerned about their brand and public image. Just as consumers are passionate about rising cable bills, broadband is always a hot button issue, especially where service is unavailable or comes only at a price that resembles extortion.
The president-elect says that America doesn’t win anymore. We sure haven’t been winning on broadband, either on speed, pricing, or availability, in comparison to Europe and Asia. The solution is not to turn the problem over to the same companies that created the conditions for broadband malaise we are dealing with now. As seen in fiercely competitive markets like France, true competition is often the only regulation you need. A duopoly answers to itself. Having the choice of four, five, six, or more competing providers answers to customers. Consolidated and entrenched markets resist innovation and the need to compete stagnates. Corporate welfare and ghost-written telecom laws that forbid community broadband restricts economic growth and kills jobs, stranding countless rural residents from the digital economy. That -is- business as usual in too many states where groups like the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) facilitate legislative fixes and legal protectionism that restricts or disadvantages competition.
If Mr. Trump truly believes the words he has spoken, he must be vigilant. He must not surround himself with the same politicians and their minders that created the very problems he promises to fix. The voters that elected him to office expect nothing less than blowing up business as usual. But the nation’s capital has a better track record of changing the politician while resisting change to the status quo.
We wish President Trump success for our country, but we’ll be watching to make certain his rhetoric meets the reality.



 Subscribe
Subscribe




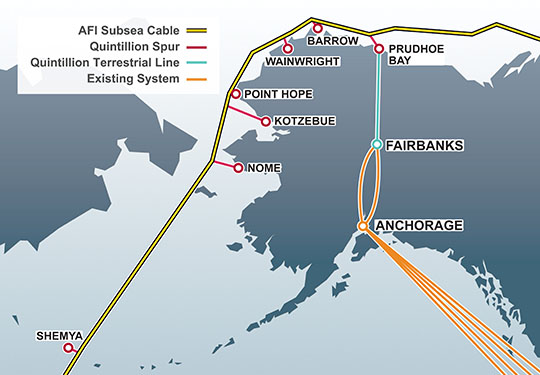
 The biggest weakness of the plan, according to its critics, is its lack of support for middle-mile networks — wired infrastructure that connects providers to a statewide broadband backbone that can manage traffic needs without having to turn to slow-speed satellite connectivity. One of Alaska’s biggest challenges is finding low-cost connectivity with Canada and the lower-48 states. Much of the state relies heavily on GCI’s still-expanding TERRA network, which provides fiber as well as microwave connectivity to 72 towns and villages in rural Alaska. Quintillion, a new player, is working on stretching fiber connectivity through the Northwest Passage. Its forthcoming 30 terabit capacity fiber network offers the possibility of dramatically lower broadband rates and no more data caps, assuming providers have the network capacity to connect their service areas and the nearest fiber access point.
The biggest weakness of the plan, according to its critics, is its lack of support for middle-mile networks — wired infrastructure that connects providers to a statewide broadband backbone that can manage traffic needs without having to turn to slow-speed satellite connectivity. One of Alaska’s biggest challenges is finding low-cost connectivity with Canada and the lower-48 states. Much of the state relies heavily on GCI’s still-expanding TERRA network, which provides fiber as well as microwave connectivity to 72 towns and villages in rural Alaska. Quintillion, a new player, is working on stretching fiber connectivity through the Northwest Passage. Its forthcoming 30 terabit capacity fiber network offers the possibility of dramatically lower broadband rates and no more data caps, assuming providers have the network capacity to connect their service areas and the nearest fiber access point. Instead, the ATA managed to convince regulators that 10/1Mbps service was good enough — speed that can be achieved by the DSL service phone companies favor. This is well below Alaska’s Broadband Task Force goal of 100Mbps for every state resident by 2020. Another free pass built into the plan is allowing providers to collect subsidies even when they do not offer 10Mbps because of network limitations, including lack of suitable middle mile networks. In those cases, the only speed requirement is 1Mbps download speeds and 256kbps uploads, the same as satellite broadband providers.
Instead, the ATA managed to convince regulators that 10/1Mbps service was good enough — speed that can be achieved by the DSL service phone companies favor. This is well below Alaska’s Broadband Task Force goal of 100Mbps for every state resident by 2020. Another free pass built into the plan is allowing providers to collect subsidies even when they do not offer 10Mbps because of network limitations, including lack of suitable middle mile networks. In those cases, the only speed requirement is 1Mbps download speeds and 256kbps uploads, the same as satellite broadband providers.


 The stunning victory by Donald Trump in Tuesday’s election ended two years of campaigning, negativity, and divisiveness.
The stunning victory by Donald Trump in Tuesday’s election ended two years of campaigning, negativity, and divisiveness.


