 Nearly every wireless provider in the United States is intentionally slowing down your data service, detrimentally affecting smartphone apps and video streaming.
Nearly every wireless provider in the United States is intentionally slowing down your data service, detrimentally affecting smartphone apps and video streaming.
That is the conclusion of researchers at Northeastern University, University of Massachusetts — Amherst and Stony Brook University, studying the results of more than 100,000 Wehe app users that have run 719,417 tests in 135 countries verifying net neutrality compliance, before and after the open internet rules were repealed in the U.S. earlier this year.
The raw data collected from the app is used as part of a validated, peer-reviewed method of determining which ISPs are throttling their customers’ connections and what services are being targeted.
Nearly Every Mobile Provider Is Throttling Your Speed, Even on “Unlimited” Plans
The researchers concluded that nearly every wireless provider is throttling at least one streaming video service, some reducing speeds the most for customers on budget priced plans while higher value customers are throttled less. No ISP consistently throttled all online video, setting up an unfair playing field for companies that benefit from not being throttled against those that are. Few customers noticed much difference in the performance of streaming video after the repeal of net neutrality in the U.S., largely because the wireless companies involved — AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile, Sprint and others — were already quietly throttling video.
“Our data shows that all of the U.S. Cellular ISPs that throttled after June 11th were already throttling prior to this date,” the researchers wrote. “In short, it appears that U.S. Cellular ISPs were ignoring the [former FCC Chairman Thomas] Wheeler FCC rules pertaining to ‘no throttling’ while those rules were still in effect.”
Summary of Detected Throttling
For each ISP, the researchers included tests only where a user’s set of tests indicated differentiation (speed throttling of specific apps or services) for at least one app and did not detect differentiation for at least one other app. This helps to filter out many false positives. As a result, the number of tests in this table is substantially lower than the total number of tests Wehe users ran. The researchers sorted the Cellular ISPs based on the number of tests from users of each ISP. If they did not detect differentiation, researchers used the entry “Not detected.” The researchers claim that offers enough evidence that throttling is not happening. In some cases researchers do not have enough tests to confirm whether there is throttling, indicated by “No data.”
The table has two column groups for the results: before the new FCC rules took effect on June 11th, and after. If behavior changed from after June 11th, it is highlighted in bold.
| SP |
App |
Before Jun 11th |
After Jun 11th |
| Throttling rate (s) |
# tests |
# users* |
Throttling rate |
# tests |
# users* |
| Verizon (cellular) |
Youtube |
1.9 Mbps
4.0 Mbps |
10630 |
2859 |
1.9 Mbps
3.9 Mbps |
2441 |
702 |
|
Netflix |
1.9 Mbps
3.8 Mbps |
8540 |
2609 |
1.9 Mbps
3.9 Mbps |
2395 |
754 |
|
Amazon |
1.9 Mbps
3.9 Mbps |
5819 |
1949 |
1.9 Mbps
3.9 Mbps |
1267 |
440 |
| ATT (cellular) |
Youtube |
1.4 Mbps |
9142 |
2466 |
1.4 Mbps |
1708 |
571 |
|
Netflix |
1.4 Mbps |
4538 |
1540 |
1.5 Mbps |
1316 |
498 |
|
NBCSports |
1.5 Mbps |
3368 |
1326 |
1.5 Mbps |
589 |
238 |
| TMobile (cellular) |
Youtube |
1.4 Mbps |
3562 |
962 |
1.4 Mbps |
1185 |
373 |
|
Netflix |
1.4 Mbps |
1813 |
637 |
1.4 Mbps |
1074 |
387 |
|
Amazon |
1.4 Mbps |
1422 |
477 |
1.4 Mbps |
1422 |
318 |
|
NBCSports |
1.4 Mbps |
1588 |
626 |
1.4 Mbps |
579 |
231 |
| Sprint (cellular) |
Skype |
0.5 Mbps
1.4 Mbps |
533 |
210 |
1.4 Mbps |
132 |
46 |
|
Youtube |
2.1 Mbps |
224 |
56 |
2.0 Mbps |
39 |
12 |
|
Netflix |
1.9 Mbps
8.8 Mbps |
277 |
100 |
2.0 Mbps
8.9 Mbps |
40 |
15 |
|
Amazon |
2.1 Mbps |
116 |
45 |
2.1 Mbps |
24 |
8 |
| cricket (cellular) |
Youtube |
1.2 Mbps |
296 |
59 |
1.3 Mbps |
58 |
14 |
|
Amazon |
1.2 Mbps |
79 |
22 |
1.2 Mbps |
16 |
4 |
| MetroPCS (cellular) |
Youtube |
1.5 Mbps |
302 |
85 |
1.5 Mbps |
72 |
20 |
|
Amazon |
1.4 Mbps |
211 |
74 |
1.4 Mbps |
45 |
16 |
|
Netflix |
1.4 Mbps |
190 |
71 |
1.3 Mbps |
60 |
20 |
|
NBCSports |
1.5 Mbps |
152 |
67 |
1.5 Mbps |
39 |
16 |
| BoostMobile (cellular) |
Youtube |
2.0 Mbps |
80 |
12 |
2.1 Mbps |
10 |
1 |
|
Netflix |
1.9 Mbps |
52 |
8 |
2.0 Mbps |
14 |
4 |
|
Amazon |
2.1 Mbps |
55 |
8 |
2.1 Mbps |
6 |
1 |
|
Skype |
0.5 Mbps |
32 |
10 |
0.5 Mbps |
9 |
4 |
| TFW (cellular) |
Youtube |
1.2 Mbps
3.9 Mbps |
39 |
4 |
1.3 Mbps |
10 |
2 |
|
Amazon |
1.3 Mbps |
19 |
2 |
1.2 Mbps |
3 |
1 |
|
Netflix |
3.9 Mbps |
8 |
3 |
Not detected |
5 |
2 |
| ViaSatInc (WiFi) |
Youtube |
0.8 Mbps |
35 |
7 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Netflix |
1.0 Mbps |
19 |
5 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Amazon |
0.9 Mbps |
15 |
5 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Spotify |
1.1 Mbps |
16 |
5 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Vimeo |
1.2 Mbps |
8 |
4 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
NBCSports |
1.2 Mbps |
7 |
3 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
| HughesNetworkSystems (WiFi) |
Youtube |
0.4 Mbps |
24 |
2 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Netflix |
0.7 Mbps |
16 |
2 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
| CSpire (cellular) |
Youtube |
0.9 Mbps |
19 |
2 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
| GCI (cellular) |
Youtube |
0.9 Mbps
2.2 Mbps |
18 |
4 |
2.0 Mbps |
4 |
1 |
|
Netflix |
2.0 Mbps |
13 |
4 |
2.1 Mbps |
4 |
1 |
|
NBCSports |
2.2 Mbps |
7 |
3 |
1.2 Mbps |
5 |
1 |
|
Amazon |
2.2 Mbps |
4 |
2 |
2.0 Mbps |
4 |
1 |
|
Vimeo |
0.9 Mbps |
3 |
0 |
2.2 Mbps |
4 |
1 |
| SIMPLEMOBILE (cellular) |
Youtube |
1.4 Mbps |
14 |
5 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Amazon |
1.5 Mbps |
9 |
3 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
NBCSports |
1.4 Mbps |
6 |
2 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Netflix |
1.4 Mbps |
9 |
3 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
| XfinityMobile (cellular) |
Youtube |
3.9 Mbps |
8 |
3 |
1.9 Mbps |
34 |
7 |
|
Netflix |
3.9 Mbps |
12 |
4 |
2.0 Mbps |
28 |
7 |
|
Amazon |
Not detected |
61 |
3 |
1.9 Mbps |
15 |
7 |
| NextlinkBroadband (WiFi) |
Youtube |
4.5 Mbps |
10 |
3 |
3.2 Mbps |
3 |
1 |
|
Vimeo |
5.1 Mbps |
6 |
1 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Amazon |
1.2 Mbps
4.1 Mbps |
5 |
1 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Netflix |
4.1 Mbps |
4 |
1 |
Not detected |
1 |
1 |
| FamilyMobile (cellular) |
Youtube |
1.4 Mbps |
13 |
5 |
Not detected |
9 |
1 |
|
Amazon |
1.4 Mbps |
9 |
4 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Netflix |
1.4 Mbps |
8 |
4 |
1.3 Mbps |
4 |
2 |
|
NBCSports |
1.4 Mbps |
6 |
3 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
| Cellcom (cellular) |
Youtube |
3.9 Mbps |
9 |
4 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Netflix |
3.2 Mbps |
5 |
2 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Amazon |
3.9 Mbps |
7 |
3 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
| iWireless (cellular) |
NBCSports |
2.8 Mbps |
8 |
2 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Youtube |
2.9 Mbps |
6 |
2 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Amazon |
2.8 Mbps |
7 |
2 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Spotify |
2.9 Mbps |
8 |
3 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
|
Netflix |
2.8 Mbps |
6 |
2 |
No data |
No data |
No data |
Sprint’s Skype Throttle
The researchers found that video was not the only service impacted by speed throttles. Sprint (and its subsidiary, prepaid provider Boost), for example, is actively throttling Skype.
“This is interesting because Skype’s telephony service directly competes with the telephony service provided by Sprint,” the researchers wrote. But curiously, the throttle almost entirely impacts Android phone users, while iOS devices have less than a 4% chance of being speed throttled. But isolating the exact trigger for throttling remains elusive, the researchers claim.
“While we have strong evidence of Skype throttling from our users’ tests, we could not reproduce this throttling with a data plan that we purchased from Sprint earlier this year,” the researchers admit. “This is likely because it affects only certain subscription plans, but not the one that we purchased.”
When asked to comment, Sprint said: “Sprint does not single out Skype or any individual content provider in this way.” The test results indicate otherwise, suggest the researchers.
T-Mobile’s “Boosting” Throttle Can Mess Up Streaming Video
Some providers, like T-Mobile, attempt to sell their throttled speeds as pro-consumer. In return for reduced definition video, customers are free to watch more online content over their portable devices without it counting against a data cap. But T-Mobile’s video throttle is unique among providers as it initially allows a short burst of regular speed to buffer the first few seconds of a streamed video before quickly throttling video playback speed. Many video players do not expect to see initial robust speeds quickly and severely throttled. Consumers report video playback is often interrupted, sometimes several times, as the player gradually adapts to the low-speed, throttled connection. Consumers receive lower quality video as a consequence.
T-Mobile Plays Favorites
Through extensive testing, research found throttling begins after a certain number of bytes have been transferred, and it is not based strictly on time; below is a list of the detected byte limits for the “boosted” (i.e., unthrottled video streaming) period.
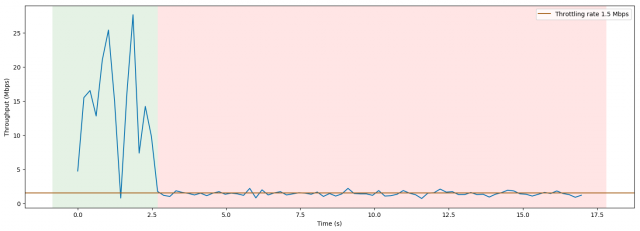
The impact of T-Mobile’s “boosting” speed throttle. Initial speeds of streaming video reach 25 Mbps before being throttled to a consistent 1.5 Mbps.
| App |
Boosting bytes |
| Netflix |
7 MB |
| NBCSports |
7 MB |
| Amazon Prime Video |
6 MB |
| YouTube |
Throttling, but no boosting |
| Vimeo |
No throttling or boosting |
More concerning to the researchers is their finding that video apps are treated differently by T-Mobile.
“T-Mobile throttles YouTube without giving it a boosting period, while T-Mobile does not throttle Vimeo at all,” the researchers report. “Such behavior highlights the risks of content-based filtering: there is fundamentally no way to treat all video services the same (because not all video services can be identified), and any additional content-specific policies — such as boosting — can lead to unfair advantages for some providers, and poor network performance for others.”
The team of researchers had just one conclusion after reviewing the available data.
“Net neutrality violations are rampant, and have been since we launched Wehe,” the researchers report. “Further, the implementation of such throttling practices creates an unlevel playing field for video streaming providers while also imposing engineering challenges related to efficiently handling a variety of throttling rates and other behavior like boosting. Last, we find that video streaming is not the only type of application affected, as there is evidence of Skype throttling in our data. Taken together, our findings indicate that the openness and fairness properties that led to the Internet’s success are at risk in the U.S.”
The team “strongly encourages” policymakers to rely on fact-based data to make informed decisions about internet regulations, implying that provider-supplied data about net neutrality policies may not reveal the full impact of speed throttles and other traffic favoritism that is common where net neutrality protections do not exist.


 Subscribe
Subscribe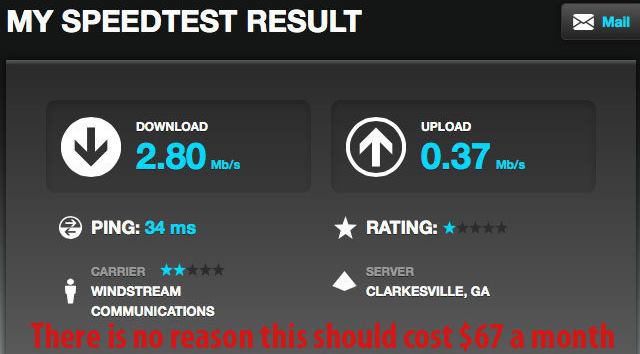
 “It took a service technician coming out to make it clear to us there was no way we would ever get faster speed because there was too much copper wiring between their office and our homes,” Brown said. “The technician felt for us, and about half of his service calls were disappointing customers like us.”
“It took a service technician coming out to make it clear to us there was no way we would ever get faster speed because there was too much copper wiring between their office and our homes,” Brown said. “The technician felt for us, and about half of his service calls were disappointing customers like us.” “We are paying for internet speed that we aren’t receiving,” Ruth complained. “It is so slow that we have a hard time getting a short 50 second video to load. Forget watching a YouTube video, it’s not going to happen.”
“We are paying for internet speed that we aren’t receiving,” Ruth complained. “It is so slow that we have a hard time getting a short 50 second video to load. Forget watching a YouTube video, it’s not going to happen.” Wall Street balks at the dollar amounts it would take for Windstream to fully update its network to offer broadband speeds that were common for cable subscribers a decade ago. That kind of network investment would likely drive down the share price, impact shareholder dividends or stock buyback plans, and increase debt. Instead, many phone companies are hoping the federal government will come to the rescue and subsidize rural network improvements through the FCC’s Connect America Fund or government grants. But many of those grants won’t deliver service improvements to existing customers. Instead it will allow rural phone companies to bring broadband to customers who never had it before.
Wall Street balks at the dollar amounts it would take for Windstream to fully update its network to offer broadband speeds that were common for cable subscribers a decade ago. That kind of network investment would likely drive down the share price, impact shareholder dividends or stock buyback plans, and increase debt. Instead, many phone companies are hoping the federal government will come to the rescue and subsidize rural network improvements through the FCC’s Connect America Fund or government grants. But many of those grants won’t deliver service improvements to existing customers. Instead it will allow rural phone companies to bring broadband to customers who never had it before.
 The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has proposed a new policy allowing cable companies to deduct the fair market value of their obligations to serve the public interest from franchise fee payments to towns and cities.
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has proposed a new policy allowing cable companies to deduct the fair market value of their obligations to serve the public interest from franchise fee payments to towns and cities.

 Under the FCC’s proposal, Alabama’s Constitution would be violated by allowing cable operators near carte-blanche access to public rights-of-way without fair compensation or permission, the League argued.
Under the FCC’s proposal, Alabama’s Constitution would be violated by allowing cable operators near carte-blanche access to public rights-of-way without fair compensation or permission, the League argued.

 “Even if it was passed by the House, the Republican-controlled Senate would not likely support it. Even if they miraculously passed a bill, President Trump would no doubt veto it, having previously spoken out against net neutrality,” Wheeler said. “The only foreseeable legislative path would be with the support of the network companies, and that support would come at the price of watering down the proposal to render it virtually meaningless.”
“Even if it was passed by the House, the Republican-controlled Senate would not likely support it. Even if they miraculously passed a bill, President Trump would no doubt veto it, having previously spoken out against net neutrality,” Wheeler said. “The only foreseeable legislative path would be with the support of the network companies, and that support would come at the price of watering down the proposal to render it virtually meaningless.” Nearly every wireless provider in the United States is intentionally slowing down your data service, detrimentally affecting smartphone apps and video streaming.
Nearly every wireless provider in the United States is intentionally slowing down your data service, detrimentally affecting smartphone apps and video streaming.
