 For 76,783 homes and businesses in upstate New York, the future of internet access will be a satellite dish and as little as a 20 GB data allowance per month, courtesy of the New York State Broadband Program Office’s decision to partner with HughesNet, a satellite internet provider, instead of finding a provider willing to extend wired internet access to every New Yorker.
For 76,783 homes and businesses in upstate New York, the future of internet access will be a satellite dish and as little as a 20 GB data allowance per month, courtesy of the New York State Broadband Program Office’s decision to partner with HughesNet, a satellite internet provider, instead of finding a provider willing to extend wired internet access to every New Yorker.
HughesNet Satellite “Fraudband”
For town supervisors and village mayors up and down the state, relying on HughesNet is nothing short of breaking Gov. Andrew Cuomo’s promise to bring broadband service to every New York resident.
Lewis town supervisor James Monty called HughesNet and other satellite internet providers “a dead end.”
“HughesNet is not broadband,” Monty said. “I just think it’s a gross waste of public funds to use something that isn’t going to work.”
Rural residents strongly agree, if only because many of them have directly experienced the pain and frustration of satellite internet in the past.
Bethel resident Susan Harte has two words to describe the kind of service HughesNet has provided since it launched its first satellite: “it stinks.”
She isn’t pleased the governor is walking away from rural New Yorkers.
 “Definitely broken promises there,” Harte says.
“Definitely broken promises there,” Harte says.
In the North Country, Willsboro town supervisor Shaun Gillilland believes the issue is personal between the governor and his constituents.
“The state made a promise and you’re all here expecting them to carry through on that promise, and I think what we’re finding is that that promise is falling very short,” Gillilland said.
Further west, some residents in Niagara County, near Niagara Falls, are preparing to abandon their homes and move out of state to find internet service and a state government less beholden to corporate interests.
One resident of Middleport tells Stop the Cap! “I’m in a state of disbelief that we are going to actually pull the kids from school and move. We don’t have anymore years to wait. We need internet.”
This particular resident has called out state and elected officials for months on social media to draw attention to the reality rural New Yorkers are going to be stuck with awful internet access for years, while Gov. Cuomo takes credit for a program he will claim is a success story.
A 20 GB Data Cap

HughesNet plans for New York customers at designated addresses for New York’s rural broadband program top out with a 20 GB data cap.
HughesNet appears to be ready to take $15,620,785 from New York and $13,720,697 in private and federal funds and leave residents with internet service even worse than they offer many of their regular customers.
“I’ve already been told by an insider [the only significant benefit New York is getting] is $200 off installation,” the Middleport resident tells us. “The service is exactly the same as ordinary HughesNet except NY Broadband Program Office recipients will have a 20 GB data cap instead of the 50 GB data cap offered elsewhere.”
Susan Potter, who lacks internet access to her home near Watertown, thinks there is a scam afoot.
“Why is New York giving HughesNet $15 million dollars for internet service that any New York resident could order themselves today?” she asked Stop the Cap! “Where is the money going and how exactly will it benefit New York residents? Except for a much smaller and completely inadequate data cap, I cannot find a single thing HughesNet is doing for New York except taking the government’s money for substandard internet access and giving us a break on a satellite dish that can already be discounted from promotions.”
HughesNet’s own website tells an interesting story. Residents who enter an address designated to receive satellite internet by New York are offered just two plans — 10 GB and 20 GB per month (with a 24-month term commitment). Outside of those areas, HughesNet offers up to four plans — 10, 20, 30 and 50 GB allowances per month (with the same two-year term commitment). HughesNet promises “up to 25 Mbps” but disclaims any responsibility if it fails to meet that speed.
“NYBPO officials cannot seem to understand that the technology has limitations and that they can’t offer unlimited data,” the Middleport resident and Stop the Cap! reader added.
Few Albany residents working for the state government have to contend with no internet options, and wired internet plans in New York remain uncapped with no data allowances, which may mean some public officials have yet to grasp the implications of a 20GB data cap, less than what wireless phone companies offer state residents with unlimited data plans. The average home broadband user now consumes an average of 190 GB of data per month, which means HughesNet’s offer is for strictly rationed internet access.
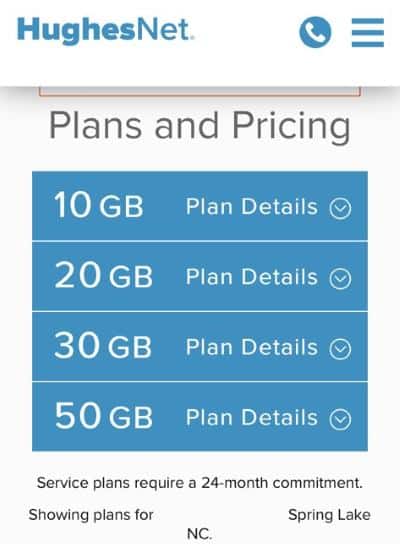
HughesNet plans in parts of North Carolina offer up to 50GB of access.
Back in Lewis, Michael Hopmeier, president of Unconventional Concepts, which provides engineering consultancy services, told the Adirondack Daily Enterprise he openly fears New York’s broadband future has been left in the hands of unqualified bureaucrats running the state’s broadband office:
“I found as an engineer and a person with a background in communications and testing evaluation, that the information that they were providing was completely unrefined,” Hopmeier said. “We were getting broad, vague numbers like ‘99 percent coverage.’”
He said he compiled a list of questions: 99 percent coverage of what? What exactly did they mean by “broadband?” Why were the contracts issued to the companies that they were? Then he and the supervisors filed a Freedom of Information Law request to the state for answers.
“The gist of the responses we received was either no answer, ‘We won’t answer that,’ or the answers made very little sense,” Hopmeier said.
With tens of millions of state taxpayer dollars on the table, Hopmeier worries the state is going to waste a huge amount of money on an unworkable solution for rural New Yorkers.
“My concerns boil down to: one, ‘How are they measuring what they are doing? Two, is there an audit going on? Is there an attempt to review and determine whether those standards and goals are actually being met? And then three, what actions will actually be taken to correct any problems if we can find them,” Hopmeier said.
He has experience using HughesNet himself, and as a result of what he calls “totally technically unacceptable” internet service, he is now sending work out of state to Virginia and Florida, where broadband service is better.
Two hours north of New York City, it is not difficult to find a broadband desert. Steve Israel, writing for the Times Herald-Record, notes Sullivan County communities like Bethel, Callicoon and Delaware, along with Ulster County towns like Marbletown and Rochester are going to be stuck with fixed wireless at 2 Mbps, HughesNet at 15 Mbps (assuming it isn’t congested that day) or for a precious few — Charter Spectrum, which is rebuilding its rural cable systems to support faster internet speeds. For others, DSL from Verizon claims to offer up to 15 Mbps, but few admit to getting service anywhere close to that speed. All of these rosy speed predictions come from the state, but residents on the ground know better.
“Thousands of folks will be left without the high-speed internet Cuomo promised,” Israel wrote.
Frontier’s Internet Nightmares – “They Talk a Lot and Don’t Accomplish Much”
 HughesNet isn’t the only provider attracting crowds armed with pitchforks and torches. Frontier Communications, which was recently awarded $9.7 million to extend DSL service to 2,735 more rural customers in the Finger Lakes, Southern Tier and North Country, attracts scorn from its existing customers.
HughesNet isn’t the only provider attracting crowds armed with pitchforks and torches. Frontier Communications, which was recently awarded $9.7 million to extend DSL service to 2,735 more rural customers in the Finger Lakes, Southern Tier and North Country, attracts scorn from its existing customers.
“There is a special place in hell reserved for Frontier’s despicable DSL service,” scowled Lillian Weber.
“Disgustingly inadequate,” fumed Wilmington resident Bob Rose, who has been at war with Frontier for months about slow or intermittent service.
“It’s like not having internet access at all — dial-up used to be faster,” added John Schneider, another unsatisfied customer.
Weber holds the record among her neighbors for the longest delay for a Frontier repair crew to show up — eight weeks, resulting from three “missed” appointments.
“They rarely bother to show up and once claimed they were here but nobody answered the door, despite the fact we spent all day on the porch staring at the driveway,” Weber. “They are even bad at lying.”
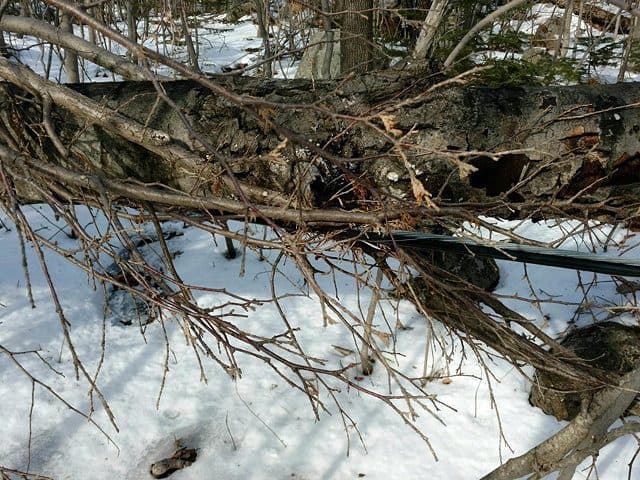

Last winter, Wilmington residents found several examples of neglected Frontier lines under pressure from overgrown tree limbs and branches. (Image courtesy: The Sun)
Rose is never sure if Frontier’s repair crews will turn up at his home either when his internet service fails, which is often.
“If I’m lucky, we have an internet connection 60 percent of the time,” Rose told The Sun. “We’ve been frustrated as hell over here, a lot of calls. We might have 1 in 10 days where we have internet all day.”
Frontier says Rose lives in a troubled, “high volume area.” Rose says his entire neighborhood has three or four homes. He now never leaves home without his Wi-Fi hotspot, because it is often the only way to stay connected.
Rose can point to at least one visible problem he saw last winter around his neighborhood. Frontier is simply not taking care of its network.
“It’s unbelievable,” he said. “Tree limbs, heavy with snow, laying right on the cable. They need to trim those trees.”
Local government officials also hear often about Frontier. Essex County Board of Supervisors chairman Randy Preston is one of them.
“Every other week, I get a complaint about Frontier,” he said. He has personally filed a complaint with the state’s attorney general and is sending a call-out to all Frontier customers dissatisfied with their internet service to do the same. He does not believe Frontier deserves a penny of state money, and the company should return what it has already received.

Essex County Board of Supervisors chairman Randy Prestonon Frontier: “They talk a lot and don’t accomplish much.”
“As far as I’m concerned, they haven’t met their commitment,” Preston told The Sun. “The grants should be pulled from them, and they should be fined. They aren’t living up to their commitment, and I don’t think that should be allowed.”
After years of dealing with Frontier, Preston has a saying about the phone company: “They talk a lot and don’t accomplish much.”
The requirements of the current round of broadband funding require participants to offer customers 100 Mbps of service, something a Frontier spokesperson confirmed.
“In general, the program requires projects to have speed capability of 100 Mbps. The Frontier projects will satisfy this requirement of the program,” the spokesperson said.
That will likely require the phone company to bring fiber to the home service to the 2,735 customers to be served. Current customers will believe it when they see it. It is also clear that existing customers will not be so lucky. When asked directly if Frontier will upgrade to fiber-fast internet speeds elsewhere in New York, Frontier Communications manager Andy Malinoski kept his answer to The Sun vague.
“Frontier is constantly investing in, expanding and improving our network as we continue to improve our customer experience in New York and across the United States,” Malinoski said. “The NY Broadband Program is one tactic we are implementing in certain communities to achieve those goals.”
The NY Public Service Commission urges New Yorkers with Frontier DSL problems to complain directly to them.
“If it were to receive a consumer complaint, PSC staff would work to resolve the issue, including bringing in other agencies if necessary,” said James Denn, a spokesman. “Going forward, all upstate New Yorkers will see dramatic improvements in service quality and availability as a result of Gov. Cuomo’s nation-leading investment program. As part of this effort, PSC staff will work closely with the NYBPO to ensure that companies receiving awards, including Frontier, provide good customer service.”
“That’s a hoot,” responded Weber. “They should spend a week with us and after that, if they are smart, they will throw Frontier out of New York right behind Charter.”



 Subscribe
Subscribe For 76,783 homes and businesses in upstate New York, the future of internet access will be a satellite dish and as little as a 20 GB data allowance per month, courtesy of the New York State Broadband Program Office’s decision to partner with HughesNet, a satellite internet provider, instead of finding a provider willing to extend wired internet access to every New Yorker.
For 76,783 homes and businesses in upstate New York, the future of internet access will be a satellite dish and as little as a 20 GB data allowance per month, courtesy of the New York State Broadband Program Office’s decision to partner with HughesNet, a satellite internet provider, instead of finding a provider willing to extend wired internet access to every New Yorker. “Definitely broken promises there,” Harte says.
“Definitely broken promises there,” Harte says.

 HughesNet isn’t the only provider attracting crowds armed with pitchforks and torches. Frontier Communications, which was recently awarded $9.7 million to extend DSL service to 2,735 more rural customers in the Finger Lakes, Southern Tier and North Country, attracts scorn from its existing customers.
HughesNet isn’t the only provider attracting crowds armed with pitchforks and torches. Frontier Communications, which was recently awarded $9.7 million to extend DSL service to 2,735 more rural customers in the Finger Lakes, Southern Tier and North Country, attracts scorn from its existing customers.

 Phone companies can beat their cable competitors, but only if they invest in fiber upgrades that can deliver as-advertised broadband service and speed.
Phone companies can beat their cable competitors, but only if they invest in fiber upgrades that can deliver as-advertised broadband service and speed. TDS has been overbuilding beyond its existing telephone service areas to deliver broadband, phone, and television service to communities evaluated as:
TDS has been overbuilding beyond its existing telephone service areas to deliver broadband, phone, and television service to communities evaluated as: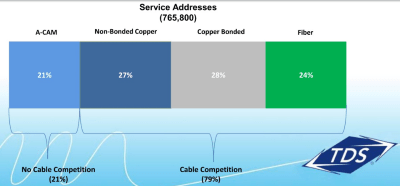 In rural areas, the company is combining federal Connect America Funds with its own money to deploy bonded DSL service in areas too unprofitable to serve with fiber. This typically delivers faster internet service than rural broadband rollouts from other phone companies like Windstream and Frontier.
In rural areas, the company is combining federal Connect America Funds with its own money to deploy bonded DSL service in areas too unprofitable to serve with fiber. This typically delivers faster internet service than rural broadband rollouts from other phone companies like Windstream and Frontier.
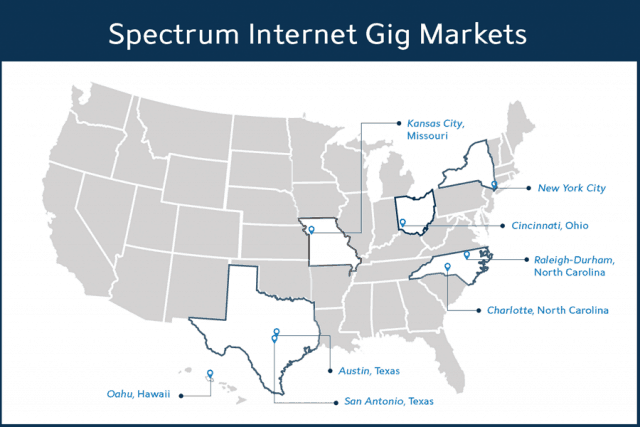
 It will take until 2019 to fully integrate all of Charter’s customers onto a single platform that will no longer distinguish if a customer was a long-standing Charter customer or a former TWC or BH subscriber.
It will take until 2019 to fully integrate all of Charter’s customers onto a single platform that will no longer distinguish if a customer was a long-standing Charter customer or a former TWC or BH subscriber. Charter did not restart its digital television conversion program until June of 2017, and 30% of Time Warner Cable and 50% of Bright House Networks customers are still watching analog cable television as a result. Company officials promise digital conversion will be completed nationwide by the end of this year, the first step the company will take to make dramatic broadband speed increases possible.
Charter did not restart its digital television conversion program until June of 2017, and 30% of Time Warner Cable and 50% of Bright House Networks customers are still watching analog cable television as a result. Company officials promise digital conversion will be completed nationwide by the end of this year, the first step the company will take to make dramatic broadband speed increases possible.