
The meter is lurking
AT&T may soon approach your electricity provider to encourage the introduction of prepaid electrical service, powered by AT&T’s wireless network.
AT&T is looking beyond traditional cell phone service to keep profits flowing into its lucrative wireless business. A growing segment of revenue is anticipated to come from so-called “machine to machine” communications. One application, Meter Data Management (MDM), provides connectivity to wireless-enabled smart utility meters, and is expected to grow 300 percent to $221 million by 2014.
Although now uncommon in the United States, prepaying for electric service is found in many parts of the world where cash-strapped consumers tend to renege on the bill. With late and non-paying customers remaining a consequence of the current American economy, AT&T is encouraging utilities to adopt pay-for-use technology that will cut the 10 percent of late-payers off the grid and save utilities money spent to collect past-due bills.
AT&T argues the next generation of “smart meters” can do a lot more than report meter readings over a wireless network. The technology can be leveraged to offer risk-free utility service, targeting credit compromised customers and those seeking to avoid billing surprises from excessive energy use.
Customers switched to prepaid electric service fill their meter with an allotment of energy usage from prepaid top-up cards sold by area convenience stores, supermarkets and even street vendors. Customers can also use credit cards or authorize checking accounts to be debited on a regular basis. Customers who exceed their allowance quickly find their service shut off automatically, depending on state laws. Making a payment switches the power back on within minutes.
 “Nearly 30 percent of people are on a prepay mobile plan in 2013,” said Ed Davalos, lead product marketing manager at AT&T, during a recent Greentech Media webinar. “That cannot be overlooked. The consumer has already changed.”
“Nearly 30 percent of people are on a prepay mobile plan in 2013,” said Ed Davalos, lead product marketing manager at AT&T, during a recent Greentech Media webinar. “That cannot be overlooked. The consumer has already changed.”
Getting utilities to adopt the system may require AT&T, in partnership with other vendors, to front some of the costs to switch to smart meter and prepaid billing technology. A study commissioned by AT&T found the biggest hurdle to adopting prepaid electric service is understanding who pays to implement it. One-third of American utility companies would launch prepaid service if it could be done for no or low-cost. Another one-third say they would seriously consider it if someone else put up the money to introduce it.
Since customers can only use energy they already paid to use, there is no payment risk to the utility company. AT&T estimates nearly 10 percent of all utility customers receive disconnect notices every month. The utilities eventually cut service to 3-5 percent of those who still don’t pay, which usually requires a truck to be sent to the customer’s home.
Using prepaid electric service offers utilities the power to switch off service at the office without a costly truck roll and prevent customers from running up an enormous past due balance. If just 10 percent of customers switched to prepaid electric service, AT&T estimates an average utility with 250,000 customers would save $5-15 million per year in costs. Those using prepaid service are so wary of exceeding their power allowance, they use about 11 percent less electricity than non-prepaid customers, reducing demand on electricity generation.
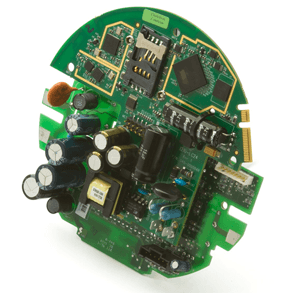
This cellular module is designed to fit within many power meters.
Customers enrolled in prepaid service get to check their energy usage and some utilities offer different rates depending on the time of day. That means cost-conscious customers might hold off doing laundry until rates drop overnight. Others might avoid air conditioning use in the late afternoons, when fluctuating power rates are typically at their highest.
Campbell McCool, chief marketing officer of SmartSynch said the actual costs to the wireless network to manage prepaid was “well under” $0.50 per meter, per month — and SmartSynch executives have offered it can be as little as pennies per meter, per month depending on volume.
Verizon is also involved in the business, announcing a partnership with eMeter to offer cloud-based, scalable MDM for utilities.
Forty-two percent of U.S. electric customers now have digital meters, up from less than 5 percent in 2008. In 2015, more than 50 percent will have them, according to one consultant.
With the introduction of smart meters come risks, warns some consumer advocates.
Last month, the U.S. power market regulator moved towards charging JPMorgan with manipulating higher fluctuating electricity prices with fraudulent trading schemes, impacting customers in California and the Midwest.
Third party electricity marketers have also become a problem in many deregulated power states, with come-ons ranging from rebate checks to introductory rates that expire and leave the customer paying skyrocketing electricity rates well above the cost of buying service direct from the local utility. Many also impose lengthy contracts with steep early termination fees.
Smart meters allow utility providers to conjure up a number of marketing programs, such as a “free power day” offered once per week. Customers signing up for promotions like that typically avoid running the washing machine, dryer, and dishwasher except on days when they won’t pay to use the appliances. Others have to wait until after midnight for savings to kick in from overnight energy discounts.
But many of the programs have been designed to promise more savings than they deliver. Power providers have been criticized for aggressive door-to-door marketing, fraudulent utility switches reminiscent of days when phone customers found their long distance carrier switched without their permission, and tricky promotional checks that, once deposited, commit a customer to several years of service with a provider at whatever rates they choose to charge.
But lack of savings isn’t the only problem. In Texas, utilities can cut power service to customers within 24 hours of warning them they have exhausted their prepaid balance.
[flv width=”480″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/ABS-CBN Regulators promoting use of prepaid electricity 10-25-12.flv[/flv]
In the Philippines, prepaid electric service was introduced to cope with customer complaints about high electricity rates. ABS-CBN News reports the meters don’t cut the price of electricity, they just help customers better manage bills by suggesting ways to reduce usage. (Oct. 2012) (2 minutes)
 Time Warner Cable is one of three New York businesses that are the latest to be awarded almost 1 megawatt of inexpensive hydropower under the state’s ReCharge New York program.
Time Warner Cable is one of three New York businesses that are the latest to be awarded almost 1 megawatt of inexpensive hydropower under the state’s ReCharge New York program.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Comcast is likely getting into the electricity business in Pennsylvania, offering customers a “quad play” bundle of Internet, telephone, television, and electricity service with discounts for one or more services.
Comcast is likely getting into the electricity business in Pennsylvania, offering customers a “quad play” bundle of Internet, telephone, television, and electricity service with discounts for one or more services.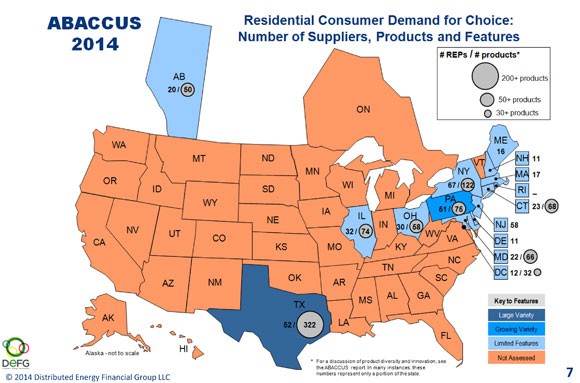
 The state of Texas is the largest deregulated power market in the country, where hundreds of suppliers compete in the retail energy market. Pennsylvania
The state of Texas is the largest deregulated power market in the country, where hundreds of suppliers compete in the retail energy market. Pennsylvania  Two years after energy conservation groups revealed many television set-top boxes use almost as much electricity as a typical refrigerator, a voluntary agreement has been reached to cut the energy use of the devices 10-45 percent by 2017.
Two years after energy conservation groups revealed many television set-top boxes use almost as much electricity as a typical refrigerator, a voluntary agreement has been reached to cut the energy use of the devices 10-45 percent by 2017.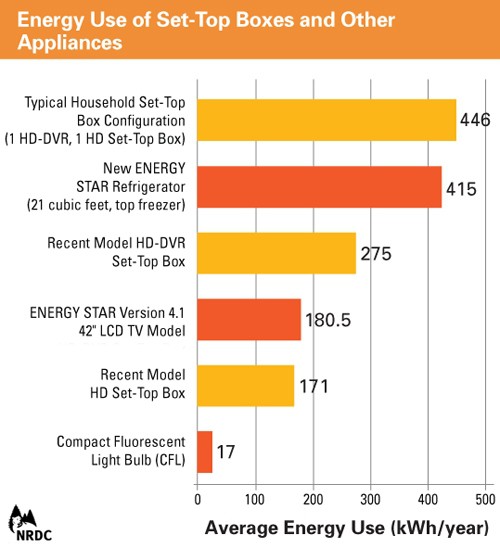
 That bi-monthly visit from your local utility’s meter reader may eventually be a thing of the past.
That bi-monthly visit from your local utility’s meter reader may eventually be a thing of the past.
 “Nearly 30 percent of people are on a prepay mobile plan in 2013,” said Ed Davalos, lead product marketing manager at AT&T, during a recent Greentech Media webinar. “That cannot be overlooked. The consumer has already changed.”
“Nearly 30 percent of people are on a prepay mobile plan in 2013,” said Ed Davalos, lead product marketing manager at AT&T, during a recent Greentech Media webinar. “That cannot be overlooked. The consumer has already changed.”
