 AT&T customers in Carbon Hill, Ala. received an unwelcome surprise in their mailbox recently when AT&T informed them they will be part of an experiment ending traditional landline service in favor of a Voice over IP or wireless alternative.
AT&T customers in Carbon Hill, Ala. received an unwelcome surprise in their mailbox recently when AT&T informed them they will be part of an experiment ending traditional landline service in favor of a Voice over IP or wireless alternative.
Affected customers are involuntary participants in what AT&T calls an “exciting opportunity for our customers and for our company,” but many residents want no part of it.
The Wall Street Journal reports Carbon Hill city clerk Janice Pendley says some people in the former mining town are not pleased.
“Some of them like their landline, and they like it just the way it is,” she says.
AT&T’s experiment will force new and existing customers to switch to its more-expensive U-verse broadband platform, use a mobile phone, or a home landline replacement that works over AT&T’s cellular network. The FCC has granted AT&T permission to impose its experimental plan to end traditional landline service in two communities where regulatory protections for landline customers are weak to non-existent — Alabama’s Carbon Hill and Delray Beach, Fla.
Carbon Hill is a small town of around 880 households in extreme western Walker County. It is the kind of rural town AT&T would likely never consider for a U-verse upgrade. AT&T embarked on a second major push to extend U-verse into more communities last year, but also indicated it would strongly advocate for a wireless replacement for its landline network in the rest of its service areas. Because Carbon Hill is an experiment, AT&T will offer U-verse to at least part of the community regardless of the usual financial Return on Investment requirements AT&T usually imposes on its U-verse expansion efforts.
 AT&T is pushing forward despite the fact it has no idea how it will offer service to at least 4% of isolated Carbon Hill residents not scheduled to be provided U-verse and not within an AT&T wireless coverage area. There are also no guarantees customers will be able to correctly reach 911, although AT&T says the technology “supports 911 functionality.” Serious questions among consumer advocates remain about whether the replacement technology will support burglar alarms, pacemakers and even systems used by air-traffic controllers.
AT&T is pushing forward despite the fact it has no idea how it will offer service to at least 4% of isolated Carbon Hill residents not scheduled to be provided U-verse and not within an AT&T wireless coverage area. There are also no guarantees customers will be able to correctly reach 911, although AT&T says the technology “supports 911 functionality.” Serious questions among consumer advocates remain about whether the replacement technology will support burglar alarms, pacemakers and even systems used by air-traffic controllers.
The difficulties service Carbon Hill relate to its rural makeup and income profile. In Delray Beach, it is all about customer demographics. Half of the city is home to residents over 65 years old — the group most likely to prefer their existing landline service. Many are likely to be unhappy about a transition to new technology that will not work in the event of power interruptions, will require the installation of new equipment, or will be tied to a wireless platform that some say reduces the intelligibility of telephone conversations and often introduces audio artifacts like echo, background noise, and dropouts.
In both cities, customers only offered wireless-based service will no longer have access to DSL or wired broadband service of any kind. The wireless alternative from AT&T comes at a high cost and a low usage allowance.
The benefits to AT&T are unquestionable, however. The company will win almost universal deregulation as a Voice over IP or wireless telephone provider. Legacy regulations on customer service requirements, pricing, and obligations to provide affordable phone service to any customer that requests it are swept away by the new technologies. Competitors are also worried AT&T will be able to walk away from regulations governing open and fair access to AT&T’s network.
 The Wall Street Journal reports:
The Wall Street Journal reports:
The all-Internet protocol “transition holds many promises for consumers, but losing access to affordable voice and broadband services cannot be part of that bargain,” wrote Angie Kronenberg, general counsel of Comptel, in a letter to the FCC last month on behalf of the small-carrier trade group, several companies and public-interest groups.
AARP said it believes AT&T’s plan has “numerous problems.” The technology might not be reliable enough or fail when calling 911 in an emergency, the advocacy group for seniors told regulators in its comment letter. The FCC is reviewing hundreds of comments received in response to AT&T’s request.
EarthLink piggybacks on the “incumbents as little as economically possible” and has laid nearly 30,000 miles of fiber-optic cables throughout the U.S. to help it reach more than a million customers, says Rolla Huff, a former EarthLink chief executive. Still, the company needs access to the connections built by AT&T and Verizon into buildings.
Telecom carriers such as Windstream in Little Rock, Ark., and sellers of broadband data services like EarthLink and XO Communications LLC, of Herndon, Va., have had the right to buy last-mile access at regulated prices since the last major overhaul of federal telecom laws in 1996.
 If AT&T ends its traditional network, those competing service providers will have to negotiate with AT&T for access at whatever price AT&T elects to charge.
If AT&T ends its traditional network, those competing service providers will have to negotiate with AT&T for access at whatever price AT&T elects to charge.
A preview of what is likely to happen has already been experienced by TW Telecom, an independent firm selling phone and Internet services to businesses over more than 30,000 miles of fiber lines. But that fiber network means nothing if a customer’s last mile connection is handled by a local phone company no longer subject to regulated pricing and access rules.
In Tampa, where Verizon has deployed FiOS as an unregulated replacement for its older, regulated copper-based network, TW Telecom learned first hand what this could ultimately mean:

Rochester Telephone Corporation was born in 1921 after a merger between the Rochester Telephonic Exchange, a branch of the Bell Company of Buffalo and locally owned independent Rochester Telephone Company, which was not allowed to use Bell’s long distance network.
TW Telecom approached Verizon in 2012 to seek last-mile access to a Tampa, Fla., building being converted into a bank from a restaurant. Verizon had installed only FiOS at the building.
Verizon said no, telling TW Telecom to build its own connection or pay Verizon thousands of dollars to do the job. TW Telecom declined to pay and lost the customer’s business.
“When it happens, it’s devastating,” says Kristie Ince, who oversees regulatory policy at TW Telecom. Similar snarls have cost the company at least six customers since then. Other carriers say they have had similar clashes.
In Illinois, Sprint’s business phone network has run into a barricade manned by AT&T. Sprint needs AT&T to interconnect calls placed on Sprint’s network intended for AT&T’s customers. The two companies cannot agree on an asking price under the deregulation scheme so Sprint converts its Voice over IP calls to older technology still subject to regulation just so calls will successfully reach AT&T’s customers. AT&T promptly converts those calls back to Voice over IP technology as it completes them.
AT&T said it has “no duty” to connect its Internet protocol traffic with Sprint’s.
If the FCC keeps IP-based traffic deregulated, if and when the old landline network is decommissioned, AT&T will have the last word on access, potentially putting competitors out of business.
Our great-great grandparents experienced similar problems in the early days of telephone service, when high rates from the local Bell telephone subsidiary provoked local competition. But Bell companies routinely refused to handle calls placed on competitors’ networks, forcing customers to maintain a telephone line with both companies to reach every subscriber. Additionally, only Bell-owned providers had access to the long distance network – a competitive disadvantage to competing startups.
Regulatory changes, a handful of mergers and the eventual establishment of the well-regulated Bell System eventually solved problems which threaten to return if AT&T has its way.



 Subscribe
Subscribe Time Warner Cable is nearing the end of its $60 million “Maxx” upgrade of San Antonio, company officials said in a news release.
Time Warner Cable is nearing the end of its $60 million “Maxx” upgrade of San Antonio, company officials said in a news release.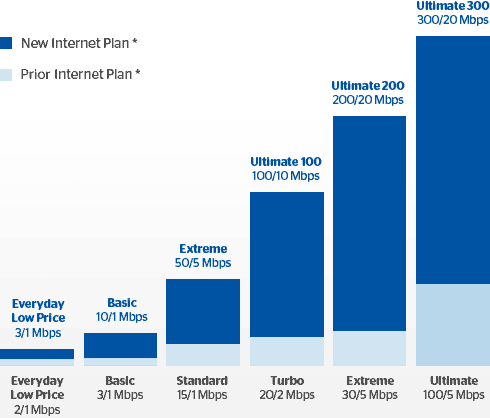
 Earthlink customers in New York, Los Angeles and Austin are receiving letters from Time Warner Cable advising them they qualify for the same speeds Time Warner Cable broadband customers are receiving as part of the TWC Maxx upgrade program.
Earthlink customers in New York, Los Angeles and Austin are receiving letters from Time Warner Cable advising them they qualify for the same speeds Time Warner Cable broadband customers are receiving as part of the TWC Maxx upgrade program. Stop the Cap! reader Iris was immediately suspicious about the tone of Time Warner’s letter, which has the potential of confusing customers that own their own cable modems. The letter suggests customer-owned equipment might not be compatible with the speed upgrades. Customers are given a phone number to verify their eligibility, and some who have contacted Time Warner Cable report back they have been given a brief sales pitch to ditch their own modem in favor of one from Time Warner Cable, which costs $5.99 a month forever.
Stop the Cap! reader Iris was immediately suspicious about the tone of Time Warner’s letter, which has the potential of confusing customers that own their own cable modems. The letter suggests customer-owned equipment might not be compatible with the speed upgrades. Customers are given a phone number to verify their eligibility, and some who have contacted Time Warner Cable report back they have been given a brief sales pitch to ditch their own modem in favor of one from Time Warner Cable, which costs $5.99 a month forever.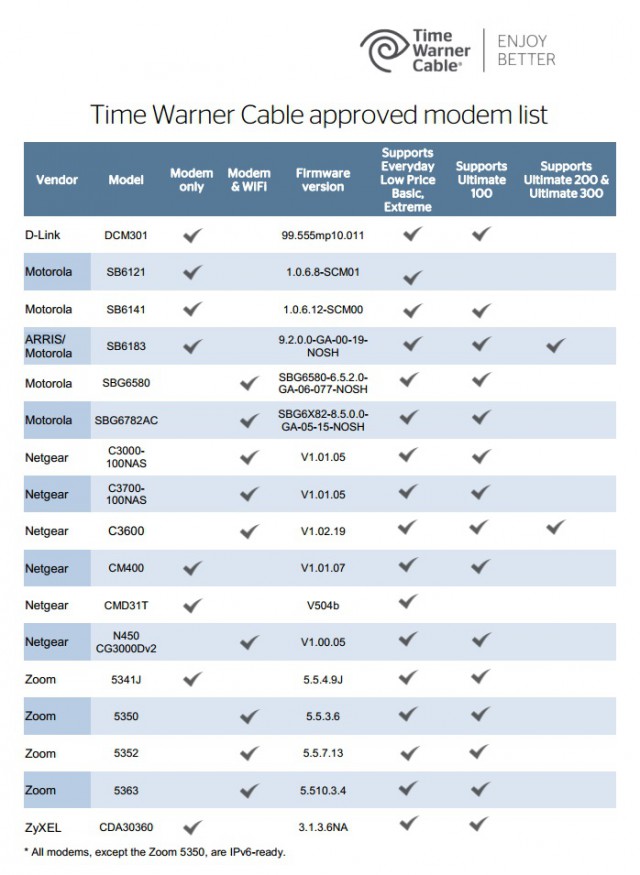
 Sprint has
Sprint has  In practice, WiMAX in the United States never achieved great success. Sprint and Clearwire’s network was never built out sufficiently to provide nationwide coverage, and because it relied on very high frequencies, even customers inside claimed service areas often dealt with reception problems, especially indoors. Clearwire’s home broadband replacement often required reception equipment be placed near a window, preferably one without a thermal coating that could block or degrade the signal.
In practice, WiMAX in the United States never achieved great success. Sprint and Clearwire’s network was never built out sufficiently to provide nationwide coverage, and because it relied on very high frequencies, even customers inside claimed service areas often dealt with reception problems, especially indoors. Clearwire’s home broadband replacement often required reception equipment be placed near a window, preferably one without a thermal coating that could block or degrade the signal. Despite the promise of greatly enhanced data speeds with the next generation of WiMAX, dubbed WiMAX 2, many of the world’s largest wireless carriers were already preparing to move on. In particular, China Mobile (and its 600 million customers) became the decisive factor that turned WiMAX 2 into a bad bet. China Mobile decided the better choice was TD-LTE, a variant of LTE technology. With China Mobile providing service to 10 percent of the world’s mobile users all by itself, support for TD-LTE grew and attracted equipment manufacturers that saw the earnings potential from selling tens of millions of base stations.
Despite the promise of greatly enhanced data speeds with the next generation of WiMAX, dubbed WiMAX 2, many of the world’s largest wireless carriers were already preparing to move on. In particular, China Mobile (and its 600 million customers) became the decisive factor that turned WiMAX 2 into a bad bet. China Mobile decided the better choice was TD-LTE, a variant of LTE technology. With China Mobile providing service to 10 percent of the world’s mobile users all by itself, support for TD-LTE grew and attracted equipment manufacturers that saw the earnings potential from selling tens of millions of base stations. AT&T customers in Carbon Hill, Ala. received an unwelcome surprise in their mailbox recently when AT&T informed them they will be part of an experiment ending traditional landline service in favor of a Voice over IP or wireless alternative.
AT&T customers in Carbon Hill, Ala. received an unwelcome surprise in their mailbox recently when AT&T informed them they will be part of an experiment ending traditional landline service in favor of a Voice over IP or wireless alternative. AT&T is pushing forward despite the fact it has no idea how it will offer service to at least 4% of isolated Carbon Hill residents not scheduled to be provided U-verse and not within an AT&T wireless coverage area. There are also no guarantees customers will be able to correctly reach 911, although AT&T says the technology “supports 911 functionality.” Serious questions among consumer advocates remain about whether the replacement technology will support burglar alarms, pacemakers and even systems used by air-traffic controllers.
AT&T is pushing forward despite the fact it has no idea how it will offer service to at least 4% of isolated Carbon Hill residents not scheduled to be provided U-verse and not within an AT&T wireless coverage area. There are also no guarantees customers will be able to correctly reach 911, although AT&T says the technology “supports 911 functionality.” Serious questions among consumer advocates remain about whether the replacement technology will support burglar alarms, pacemakers and even systems used by air-traffic controllers. The Wall Street Journal reports:
The Wall Street Journal reports: If AT&T ends its traditional network, those competing service providers will have to negotiate with AT&T for access at whatever price AT&T elects to charge.
If AT&T ends its traditional network, those competing service providers will have to negotiate with AT&T for access at whatever price AT&T elects to charge.
