
Now what: AT&T Next and Verizon Edge
Wireless carriers know that the average relationship between a smartphone and its owner is becoming shorter every day. Sometimes the relationship is over when a customer drops or loses their phone and needs a replacement. Others simply covet the next best thing. When a large enough contingent of customers is willing to open their wallets and let their money fall out, what’s a poor wireless company to do? Ignore the pile of twenties falling to the floor? Not on your life.
AT&T last month announced it was dumping its 20-month early upgrade offer, following Verizon (again) which announced it was pulling the rug out on a similar plan in April. ‘Customers should wait a full 24 months before expecting a new subsidized phone,’ said both companies.
Then came scrappy T-Mobile, the company AT&T originally wanted to put out of business. TMO decided to apply some European competitive logic in the U.S. market. No more two-year contracts with nasty termination fees, declared CEO John Legere. But no more “phone subsidy” either. In return for the end of contracts, customers should expect to pay retail price for their smartphone, but at least they can finance it through T-Mobile and have the somewhat affordable monthly installments added to their bill.
Now, in a remarkable about-face for Verizon Wireless and AT&T, the features and promotions diet imposed on customers that has eroded discounts, ended early upgrades, and slapped on early termination fees and opaque junk bill charges might be coming to an end. Early upgrades are back… for a price.
It is the first step in a major shift away from the North American wireless business model which traditionally offers customers cheap devices at massive discounts known as “device subsidies.” Since the early days of cell phones, wireless companies in the U.S. and Canada typically grant customers up to $350 off their phone purchase in return for a 24 month contract (until recently, 36 months in Canada). But wireless providers don’t just give away free money. Carriers get back every penny of this subsidy over the life of a cell phone contract by setting their plan rates artificially high.
T-Mobile isn’t giving away the store either, but at least everything is on sale. By jettisoning the subsidy, T-Mobile’s plan rates are dramatically lower than those offered by its competitors. That is no surprise because TMO no longer has to worry about recouping device subsidies.
When a customer walks into a T-Mobile store, they can buy the latest iPhone for $650 or agree to finance it at the retail price through the carrier. They can even buy it somewhere else. But T-Mobile’s new Jump plan also offers customers a chance to “jump” to a newer phone every 6-9 months with its trade-in program. For avid phone upgraders, the end effect is like leasing your phone. You will always have a device newer than the next guy, and you will always be paying a monthly fee for the phone itself. That looks a lot more attractive than trying to wait 24 months with AT&T or Verizon or frequently buying a new phone for north of $500 and trying to recoup part of the cost by selling your old phone on eBay or Craigslist.
Wall Street would normally punish carriers that do anything to shorten the 24-month traditional upgrade cycle because investors generally hate the whole concept of the phone subsidy. It costs companies liquidity to tie up money fronting that $350 discount and waiting up to two years to get the money back. But since T-Mobile can immediately book the full purchase price of a phone for accounting purposes and does not need to show the amount of money dedicated towards phone subsidies, analysts are not pummeling the stock into the ground.
As Stop the Cap! has written for more than a year, the wireless Golden Calf Wall Street really wants to worship is a cell phone plan priced artificially high to recover a subsidy providers no longer give. That’s a plan only Ma Bell and its shareholders could love. But nobody thought AT&T and Verizon Wireless could get away with it.
Silly people.
Introducing The Wireless Trojan Horses: AT&T Next from AT&T and VZ Edge from Verizon

Yay!: No more expensive subsidies and extra free money
AT&T yesterday introduced AT&T Next — the company’s response to T-Mobile’s Jump with AT&T’s usual gouging touch.
The highlights of the plan include:
- No membership, activation or upgrade fees;
- Buying a new phone under AT&T Next does not require a down payment, any finance charges, or early payoff penalty;
- Customers can trade-in for an upgrade after one year or keep the device for 20 months and own it.
VZ Edge is still a rumor, but leaked promotional material indicates it is nearly identical to AT&T Next, with some important exceptions:
- VZ Edge appears to be an extension of Verizon’s existing 12-month financing plan, limited to two devices at a time with a combined financed balance not to exceed $1,000;
- First payment due at time of purchase with a recurring finance charge of $2 for each month there is a remaining balance;
- No upgrade fees, no contracts, no pre-payment/payoff penalty;
- Customer qualifies for their next upgrade after 50 percent of their current phone’s retail price is paid;
The leaked document does not include details about the disposition of your device when beginning an upgrade. Presumably, Verizon will accept it for trade-in or the customer can pay the remaining balance off immediately and own it.
What sets Verizon and AT&T far apart from T-Mobile are the prices of their service plans. Both AT&T and Verizon are effectively ending their subsidy program for those participating in these early upgrade plans. Customers must purchase (or finance) their next device at the regular retail price, which will range between $500-650 for most top-of-the-line smartphones.
Bunco
But neither Verizon or AT&T are lowering their service plan pricing, which was specifically designed to recoup a subsidy they are no longer providing. T-Mobile has appropriately lowered their plan pricing because the company no longer needs to win back that $350 subsidy they might have given you for the newest Apple iPhone or Galaxy device. That means you are effectively paying AT&T and Verizon twice for the same phone. It’s Wall Street’s dream come true: kill the subsidy and keep the money still being charged to recoup it. That amounts to as much as $29 a month out of your bank account and into theirs.
For now, only those itching for fast upgrades will get the pinch, at least until AT&T and Verizon decide this is the new and improved way to sell phones to everyone without a two-year contract. Now if we can only get AT&T and Verizon to rescind the contract taken out on our wallets….


 Subscribe
Subscribe Verizon Wireless customers and public safety personnel are upset that the cell phone company was caught unprepared after a rural roaming agreement with AT&T expired at the end of June, leaving police officers without communications and others with no way to reach 911.
Verizon Wireless customers and public safety personnel are upset that the cell phone company was caught unprepared after a rural roaming agreement with AT&T expired at the end of June, leaving police officers without communications and others with no way to reach 911.
 After negative media coverage reported Verizon’s inability to provide quality cell service in rural Montana, the company agreed to temporarily deploy portable cell towers to improve coverage.
After negative media coverage reported Verizon’s inability to provide quality cell service in rural Montana, the company agreed to temporarily deploy portable cell towers to improve coverage.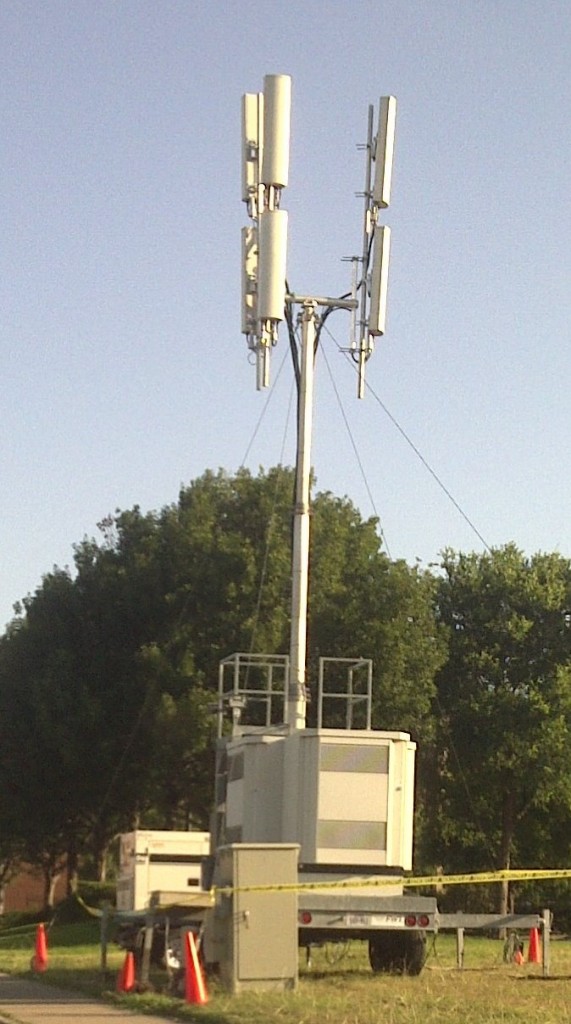
 Canadian telecom regulators have announced new rules that will limit “gotcha” fees for mobile customers caught exceeding their data allowance, push for an end to the ubiquitous three-year service contract, and force carriers to unlock cell phones after 90 days.
Canadian telecom regulators have announced new rules that will limit “gotcha” fees for mobile customers caught exceeding their data allowance, push for an end to the ubiquitous three-year service contract, and force carriers to unlock cell phones after 90 days.

 “This requirement does limit consumer choice in the marketplace, and could make a customer’s up-front purchase price of a smartphone more expensive than current offerings,” said Bernard Lord, head of the Canadian Wireless Telecommunications Association (CWTA).
“This requirement does limit consumer choice in the marketplace, and could make a customer’s up-front purchase price of a smartphone more expensive than current offerings,” said Bernard Lord, head of the Canadian Wireless Telecommunications Association (CWTA).





