 October 20, 2015
October 20, 2015
Hon. Kathleen H. Burgess
Secretary, Public Service Commission
Three Empire State Plaza
Albany, NY 12223-1350
Dear Ms. Burgess,
New York State’s digital economy is in trouble.
While providers claim portions of New York achieve some of the top broadband speeds in the country, the vast majority of the state has been left behind by cable and phone companies that have never been in a hurry to deliver the top shelf telecom services that New Yorkers need and deserve.
The deregulation policies of the recent past have resulted in entrenched de facto monopoly and duopoly markets with little or no oversight. Those policies, instead of benefiting New Yorkers, are ultimately responsible for allowing two companies to dominate the state’s telecommunications marketplace.
In virtually all of upstate New York, the services consumers receive depend entirely on the business priorities of local incumbent providers, not market forces or customer demand. As a result, New Yorkers face relentless, unchecked rate increases, well-documented abysmal and unresponsive customer service, and inadequate broadband provided by a workforce under siege from downsizing, cost-cutting, and outsourcing.
Certain markets, particularly those in the New York City area, have at least secured a promise of better broadband from Verizon’s FiOS fiber to the home upgrade. But at least 100,000 New Yorkers have languished on Verizon’s “waiting list,” as the company drags its feet on Non Standard Installation orders.[1] In upstate New York, Verizon walked away from its FiOS expansion effort five years ago, leaving only a handful of wealthy suburbs furnished with fiber service while effectively abandoning urban communities like Buffalo and Syracuse with nothing better than Verizon’s outdated DSL, which does not meet the FCC’s minimum definition of broadband – 25Mbps.[2]
Cablevision’s broadband performance dramatically improved because of investment in network upgrades, and the company has been well-regarded for its broadband service ever since.[3] But the proposed new owner of Cablevision – Altice, NV — has sought “cost savings” from cuts totaling $900 million a year, which will almost certainly devastate that provider’s future investments, its engineering and repair crews, and customer service.[4]
At least downstate New York has the prospect for +100Mbps broadband service. In upstate New York, three providers define the broadband landscape for most cities and towns:
- Time Warner Cable dominates upstate New York with its cable broadband service and has the largest market share for High Speed Internet. As of today, Time Warner Cable’s top broadband speed outside of New York City is just 50Mbps, far less than the 1,000Mbps service cities in other states are now on track to receive or are already getting.[5]
- Verizon Communications is the largest ILEC in upstate New York. Outside of its very limited FiOS service areas, customers depend on Verizon’s DSL service at speeds no better than 15Mbps, below the FCC’s minimum speed to qualify as broadband;[6]
- Frontier Communications has acquired FiOS networks from Verizon in Indiana and the Pacific Northwest, and AT&T U-verse in Connecticut. Frontier has made no significant investment or effort to bring FiOS or U-verse into New York State. In fact, in its largest New York service area, Rochester, there are significant areas that can receive no better than 3.1Mbps DSL from Frontier. The vast majority of Frontier customers in New York do not receive service that meets the FCC’s minimum definition of broadband, and some investors predict the company is “headed for financial disaster.”[7]
The competitive markets the DPS staff envisions in its report to the Commission are largely a mirage. When an ILEC like Frontier Communications admits its residential broadband market share “is less than 25% in our 27 states excluding Connecticut,” that is clear evidence the marketplace has rejected Frontier’s legacy DSL service and does not consider the company an effective competitor.[8]
While incumbent cable and phone companies tout ‘robust competition’ for service in New York, if the Commission investigated the market share of Time Warner Cable upstate, it would quickly realize that ‘robust competition’ has been eroding for years, with an ongoing shift away from DSL providers towards cable broadband.[9]
Frontier’s primary market focus is on rural communities where it often enjoys a monopoly and can deliver what we believe to be inadequate service to a captive customer base. The company is currently facing a class action lawsuit in West Virginia, where it is alleged to have failed to provide advertised broadband speeds and delivers poor service.[10]
Verizon’s ongoing investment in its legacy wireline network (and expansion of DSL to serve new customers) has been regularly criticized as woefully inadequate.[11] From all indications, we expect the company will eventually sell its legacy wireline networks, particularly those upstate, within the next 5-10 years as it has done in northern New England (sold to FairPoint Communications) and proposes to do in Texas, California, and Florida.[12] (Verizon also sold off its service areas in Hawaii, West Virginia, and much of its territory acquired from GTE.)
Across New York, service problems and controversial deals between telecom providers have made headlines. Here are just a few:
- Superstorm Sandy’s impact on Verizon’s legacy wireline network on Fire Island and in other downstate communities left many without service. Instead of repairing the damage, Verizon proposed to scrap its wireline network and substitute inferior wireless service with no possibility of wired broadband.[13] The DPS received a large number of comments from the public and local elected officials fiercely opposed to this proposal, one that Verizon eventually withdrew in the face of overwhelming opposition.[14]
- There are growing allegations Verizon may be underspending on its legacy wireline network and even worse, may be misallocating costs and revenues to deceive the Commission.[15] Some allege much of the company’s ongoing investments, charged to the wireline operation, in reality are for the benefit of its wireless network. This may have allowed Verizon Communications/New York to claim significant losses on its wireline books the company then argued justified rate increases on ratepayers.[16] A full scale accounting of Verizon’s books is essential for all concerned and corrective action may be necessary if these allegations are proven true.
- Verizon’s foot-dragging on FiOS buildouts in New York City led to a damning audit report commissioned by New York City Mayor Bill de Blasio this summer and oversight hearings were held last week by the City Council of New York.[17] [18] Despite Verizon’s creative definition of “homes passed,” a substantial number of New Yorkers cannot receive the benefits of “today’s networks” the DPS staff refers to. Instead, many are stuck with poorly-performing DSL or no service at all.[19] Regardless of whether fiber passes in front of, over, in between, or behind buildings, Verizon signed an agreement compelling them to give customers a clear timeline to establish FiOS service. It is apparent Verizon is not meeting its obligations.[20]
- The proposed sale of Time Warner Cable to Comcast led the Commission’s staff to admit the majority of respondents to requests for public input were strongly opposed to the merger and without substantial modifications concluded would not be in the public interest.[21] Comcast eventually withdrew its proposal in the face of overwhelming opposition.
- The proposed sale of Time Warner Cable to Charter Communications, where the DPS staff concluded as the application stood, there would be no public interest benefits to the transaction.[22]
Those are just a few examples of why aggressive oversight of telecommunications is critical for all New Yorkers. In most of these examples, the DPS never ruled one way or the other. The companies individually made their own decisions, and we believe they would have decided differently if they did not face grassroots opposition from consumers.
New Yorkers deserve an active DPS prepared to aggressively represent our interests, ready to investigate what Verizon is doing with its legacy wireline network, legacy wired broadband services, FiOS and Verizon Wireless. With Time Warner Cable having such a dominant presence in western and central New York, its sale should never be taken lightly, as it will impact millions of New Yorkers for years to come.
While the DPS seems prepared to passively wait around to discover what Time Warner Cable, Frontier and Verizon are planning next, the rest of the country is getting speed upgrades New York can only dream about.
Google Fiber and AT&T, among others, are aggressively rolling out 1,000Mbps fiber service upgrades in other states, while a disinterested Verizon refuses to invest further in FiOS expansion, leaving millions of New York customers with nothing better than DSL.
The lack of significant competition upstate is why we believe Time Warner Cable has not yet chosen any market in New York except New York City for its Maxx upgrade program, which offers substantially faster speeds and better service.[23] There is no compelling competitive reason for Time Warner to hurry upgrades into areas where they already enjoy a vast market share and no threat of a broadband speed race. So much for robust competition.
Charter’s proposed acquisition of Time Warner Cable proposes a modest upgrade of broadband speeds to 60-100Mbps, but as we wrote in our comments to the DPS regarding the merger proposal, upstate New York would be better off waiting for Time Warner Cable to complete its own Maxx upgrades over what will likely be 100% of its footprint in the next 24-30 months.[24] Time Warner Cable Maxx offers maximum broadband speeds three times faster than what Charter proposes for upstate New York, while also preserving affordable broadband options for those less fortunate. Approving a Charter buyout of Time Warner Cable will only set upstate New York back further.
We confess we were bewildered after reviewing the initial staff assessment of telecommunications services competition in New York. Its conclusions simply do not reflect reality on the ground, particularly in upstate communities.
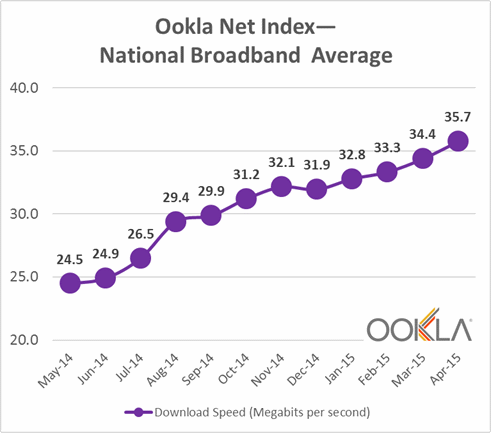
It was this type of incomplete analysis that allowed New York to fall into the trap of irresponsible deregulation and abdication of oversight that has utterly failed to deliver the promised competition that would check rate hikes, guarantee better customer service, and provide New York with best-in-class service. In reality, we have none of those things. Rates continue to spiral higher, poor customer service continues, and New York has been left behind with sub-standard broadband that achieves no better than 50Mbps speeds in most upstate communities.
This summer, the American Customer Satisfaction Index told us something we already know. Americans dislike their cable company more than any other industry in the nation.[25] A survey of more than 14,000 customers by ACSI found service satisfaction achieving a new all-time low, scoring 63 out of 100.
“Customers expect a lot more than what the companies deliver,” said ACSI managing director David VanAmburg, who called poor customer service from cable operators “endemic.”
This year, Time Warner Cable again scored the worst in the country. As the only cable provider for virtually all of upstate New York, if residents in New York are given a choice between Time Warner Cable and the phone company’s slow-speed DSL, they are still likely to choose Time Warner Cable, but only because they have no other choices for broadband that meets the FCC definition of broadband.
Providers are quick to suggest consumers can turn to so-called competitors like satellite broadband or wireless Internet from mobile providers. They conveniently ignore the fact satellite-delivered Internet is such a provider of last resort, less than 1% of New Yorkers choose this option. Those that have used satellite broadband tell the companies providing it they rarely achieve the claimed speeds and are heavily speed throttled and usage capped.[26] It’s also costly, particularly when measuring the price against its performance.
Mobile Internet, which some ILECs have advocated as a possible replacement for rural wireline networks, is also a very poor substitute for wired Internet access. Wireless broadband pricing is high and usage allowances are low. Attempts to convince New Yorkers to abandon Verizon landline service in favor of Verizon’s 4G LTE wireless replacement have led to consumer complaints after learning their existing unlimited Verizon DSL service would be substituted for a wireless plan starting at $60 a month with a 10GB usage allowance.[27]
A customer with a 6Mbps DSL line from Verizon consuming 30GB of usage a month – hardly a heavy user – pays Verizon $29.99 a month for DSL service during the first year. In contrast, that same customer using Verizon Wireless’ home 2-5Mbps wireless LTE plan will pay $120 a month – four times more, with the added risk of incurring a $10 per gigabyte overlimit fee for usage in excess of their allowance.[28]
None of this information is a secret, yet it seems to have escaped the notice of the DPS staff in its report. Part of the reason why may be the complete lack of public input to help illuminate and counter incumbent providers’ well-financed public and government relations self-praise campaigns. If only actual customers agreed with their conclusions, we’d be well on our way to deregulation-inspired broadband nirvana.
Except New Yorkers do not agree all is well.
Consumer Reports:
Our latest survey of 81,848 customers of home telecommunications services found almost universally low ratings for value across services—especially for TV and Internet. Those who bundled the three services together for a discount still seemed unimpressed with what they were getting for their money. Even WOW and Verizon FiOS, which got high marks for service satisfaction, rated middling or lower for value, and out of 14 providers, nine got the lowest possible value rating.
What is it about home telecommunications that leaves such a sour taste in customers’ mouths? When we asked Consumer Reports’ Facebook followers to tell us their telecom stories, the few happy anecdotes of attentive service technicians and reliable service were overwhelmed by a tidal wave of consumer woe involving high prices, complicated equipment, and terrible service.[29]
The effective competition that would rely on market forces to deter abusive pricing and poor customer service is simply not available in a monopoly/duopoly marketplace. New entrants face enormous start-up costs, particularly provisioning last-mile service.
The nation’s telephone network was first constructed in the early half of the last century by providers guaranteed monopoly status. The cable industry developed during a period where regulators frequently considered operators to be a “natural monopoly,” unable to survive sustained competition.[30] Many cable operators were granted exclusive franchise agreements which helped them present a solid business case to investors to fund a costly network buildout. The end of franchise exclusivity happened years after most cable operators were already well established.
Today, those marketplace protections are unavailable to new entrants who face a variety of hurdles to achieve success. Some are competitive, others are regulatory. Google Fiber, which provides competitive service in states other than New York, publishes a guide for local communities to make them more attractive prospects for future Google Fiber expansion.[31]
For many overbuilders, pole attachment issues, zoning and permitting are significant obstacles to making new service available to residential and commercial customers. New York must ensure pole owners provide timely, non-discriminatory, and reasonable cost access. Permitting and zoning issues should be resolved on similar terms to speed network deployment.
Because a long history of experience tells us it is unreasonable to expect a competing telephone or cable company to enter another provider’s territory, in many cases the only significant possibility for competition will come from a new municipal/co-op/public-owned broadband alternative.
The hurdles these would-be providers face are significant. Incumbent provider opposition can be substantial, especially on a large-scale buildout. In rural areas, incumbents can and do refuse to cooperate, even on projects that seek to prioritize access first to unserved/underserved areas currently bypassed by those incumbents.
The effort to wire the Adirondack Park region is a case in point. Time Warner Cable has refused to provide detailed mapping information about their existing network, making it difficult to assess the viability of a municipal and/or a commercial broadband expansion project into these areas. Time Warner Cable maintains it has exclusivity to granular map data showing existing networks for “competitive reasons,” effectively maintaining an advantageous position from which it can strategically apply for state broadband expansion funding to expand its network using public funds.
Time Warner Cable benefits from access to publicly-owned rights of way and sanctioned easements. Without this access, their network would likely be untenable. As a beneficiary of that public access, making granular map data available to broadband planners is a fair exchange, and nothing precludes Time Warner from building its network into those unserved/underserved areas – something that might deter a would-be competitor’s business argument to overbuild a high-cost, rural area. The Commission should ask itself how many rural New York communities have two (or more) competing cable companies serving the same customers. If the answer is none, Time Warner Cable does not have a valid argument.
There is ample evidence the Commission needs to begin a full and comprehensive review of telecommunications in this state. It must build a factual, evidence-based record on which the Commission can build a case that oversight is needed to guarantee New Yorkers get the high quality telecommunications services they deserve.
Broadband and telephone service is not just a convenience. In September 2015, the Obama Administration declared broadband was now a “core utility,” just as important as telephone, electric, and natural gas service. Isn’t it about time the Department of Public Service oversee it as such?[32]
Respectfully submitted for your consideration,
Phillip M. Dampier
Director, Stop the Cap!
[1] http://stopthecap.com/2015/10/19/n-y-city-council-investigates-verizon-foot-dragging-fios-possible-contract-violations/
[2] http://www.wsj.com/articles/SB10001424052702303410404575151773432729614
[3] https://www.fcc.gov/reports/measuring-broadband-america-2014
[4] http://variety.com/2015/biz/news/altice-group-patrick-drahi-cablevision-bid-1201599986/
[5] http://www.pcmag.com/slideshow/story/310861/if-you-want-gigabit-internet-move-here/1
[6] https://www.fcc.gov/document/fcc-finds-us-broadband-deployment-not-keeping-pace
[7] http://seekingalpha.com/article/2888876-frontier-communications-headed-for-financial-disaster
[8] https://seekingalpha.com/article/2633375-frontier-communications-ftr-ceo-maggie-wilderotter-q3-2014-results-earnings-call-transcript
[9] http://www.leichtmanresearch.com/press/051515release.html
[10] http://www.wvgazettemail.com/article/20141020/GZ01/141029992
[11] http://www.cwa-union.org/news/entry/cwa_calls_for_regulators_to_investigate_verizons_refusal_to_invest_in_landl
[12] http://stopthecap.com/2015/05/05/fla-utility-says-negotiations-with-verizon-make-it-clear-verizon-will-exit-the-wireline-business-within-10-years/
[13] http://money.cnn.com/2013/07/22/technology/verizon-wireless-sandy/
[14] http://documents.dps.ny.gov/public/MatterManagement/CaseMaster.aspx?Mattercaseno=13-C-0197
[15] http://www.cwa-union.org/news/entry/cwa_calls_for_regulators_to_investigate_verizons_refusal_to_invest_in_landl
[16] http://newnetworks.com/publicnn.pdf/
[17] http://www1.nyc.gov/office-of-the-mayor/news/415-15/de-blasio-administration-releases-audit-report-verizon-s-citywide-fios-implementation
[18] http://arstechnica.com/business/2015/10/verizon-tries-to-avoid-building-more-fiber-by-re-defining-the-word-pass/
[19] http://www.nytimes.com/2015/08/27/nyregion/new-york-city-and-verizon-battle-over-fios-service.html?_r=0
[20] http://www.nyc.gov/html/doitt/downloads/pdf/verizon-audit.pdf
[21] http://documents.dps.ny.gov/public/Common/ViewDoc.aspx?DocRefId={0A5EAC88-6AB7-4F79-862C-B6C6B6D2E4ED}
[22] http://documents.dps.ny.gov/public/Common/ViewDoc.aspx?DocRefId=%7BC60985CC-BEE8-43A7-84E8-5A4B4D8E0F54%7D
[23] http://www.timewarnercable.com/en/enjoy/better-twc/internet.html
[24] http://documents.dps.ny.gov/public/Common/ViewDoc.aspx?DocRefId={FCB40F67-B91F-4F65-8CCD-66D8C22AF6B1}
[25] http://www.marketwatch.com/story/the-most-hated-cable-company-in-america-is-2015-06-02
[26] https://community.myhughesnet.com/hughesnet?topic_list%5Bsettings%5D%5Btype%5D=problem
[27] http://www.verizon.com/home/highspeedinternet/
[28] HTTPS://www.verizonwireless.com/home-services/lte-internet-installed/
[29] http://www.consumerreports.org//cro/magazine/2014/05/how-to-save-money-on-triple-play-cable-services/index.htm
[30] http://www.citi.columbia.edu/elinoam/articles/Is_Cable_Television_Natural_Monopoly.pdf (p.255)
[31] https://fiber.storage.googleapis.com/legal/googlefibercitychecklist2-24-14.pdf
[32] http://thehill.com/policy/technology/254431-obama-administration-declares-broadband-core-utility-in-report


 Subscribe
Subscribe


 Cox plans to limit its gigabit customers to 2TB of usage a month. AT&T U-verse with GigaPower has a (currently unenforced) limit of 1TB a month, while Suddenlink thinks 550GB is more than enough for its gigabit customers. Comcast is market testing 300GB usage caps in several cities but strangely has no usage cap on its usage-gobbling gigabit plan. Why cap the customers least-equipped to run up usage into the ionosphere while giving gigabit customers a free pass? It doesn’t make much sense.
Cox plans to limit its gigabit customers to 2TB of usage a month. AT&T U-verse with GigaPower has a (currently unenforced) limit of 1TB a month, while Suddenlink thinks 550GB is more than enough for its gigabit customers. Comcast is market testing 300GB usage caps in several cities but strangely has no usage cap on its usage-gobbling gigabit plan. Why cap the customers least-equipped to run up usage into the ionosphere while giving gigabit customers a free pass? It doesn’t make much sense.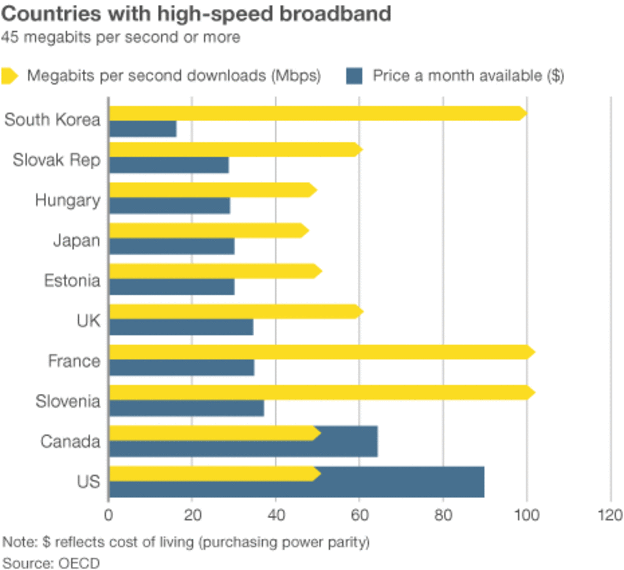
 The abuses were so bad, Congress finally stepped in and authorized regulators to break up the railroad monopolies and regulate abusive pricing. We may be headed in the same direction with broadband. We do not advocate regulation for the sake of regulation. Competition is a much more efficient way to check abusive business practices. But where an effective monopoly or duopoly exists, competition alone will not help. Without consumer-conscious oversight, the forthcoming gigabit broadband revolution will be stalled by speed bumps and toll booths for the benefit of a few giant telecommunications corporations. That will allow other countries to once again leap ahead of the United States and Canada, just as they have done with Internet speeds, delivering superior service at a lower price.
The abuses were so bad, Congress finally stepped in and authorized regulators to break up the railroad monopolies and regulate abusive pricing. We may be headed in the same direction with broadband. We do not advocate regulation for the sake of regulation. Competition is a much more efficient way to check abusive business practices. But where an effective monopoly or duopoly exists, competition alone will not help. Without consumer-conscious oversight, the forthcoming gigabit broadband revolution will be stalled by speed bumps and toll booths for the benefit of a few giant telecommunications corporations. That will allow other countries to once again leap ahead of the United States and Canada, just as they have done with Internet speeds, delivering superior service at a lower price. To attract investment and competition, the government declared all value-added services like Internet access deregulated and guaranteed the complete privatization of all government telecom facilities no later than 1998. It also initially limited the number of companies that could compete against PLDT in each region to two new entrants. The government felt that would be necessary to attract competitors that knew they would have to quickly invest millions, if not billions, to build telecom infrastructure in the Philippines. It would be hard to make a case for investment in a region where a half-dozen companies all engaged in a price war fighting for customers while stringing new telephone lines and building cell towers.
To attract investment and competition, the government declared all value-added services like Internet access deregulated and guaranteed the complete privatization of all government telecom facilities no later than 1998. It also initially limited the number of companies that could compete against PLDT in each region to two new entrants. The government felt that would be necessary to attract competitors that knew they would have to quickly invest millions, if not billions, to build telecom infrastructure in the Philippines. It would be hard to make a case for investment in a region where a half-dozen companies all engaged in a price war fighting for customers while stringing new telephone lines and building cell towers. The NTC remained more “hands-off” than the FCC, avoiding significant involvement in critical interconnection issues — how competing telephone companies handle calls from subscribers of a competing provider. That was last an issue in the United States in the early 1900s, where rare independent competitors to the rapidly consolidating Bell System faced a telecom giant that initially refused to handle calls from customers of other companies. American regulators eventually demanded interconnection policies that guaranteed customers could reach any other telephone customer, regardless of what company handled their service. In the Philippines, the NTC eventually mandated less-demanding access, allowing companies to charge long distance rates to reach customers of other companies. In the 1990s, it was not uncommon to find businesses maintaining at least two telephone lines with different companies to escape long distance expenses and stay accessible to all of their potential customers.
The NTC remained more “hands-off” than the FCC, avoiding significant involvement in critical interconnection issues — how competing telephone companies handle calls from subscribers of a competing provider. That was last an issue in the United States in the early 1900s, where rare independent competitors to the rapidly consolidating Bell System faced a telecom giant that initially refused to handle calls from customers of other companies. American regulators eventually demanded interconnection policies that guaranteed customers could reach any other telephone customer, regardless of what company handled their service. In the Philippines, the NTC eventually mandated less-demanding access, allowing companies to charge long distance rates to reach customers of other companies. In the 1990s, it was not uncommon to find businesses maintaining at least two telephone lines with different companies to escape long distance expenses and stay accessible to all of their potential customers.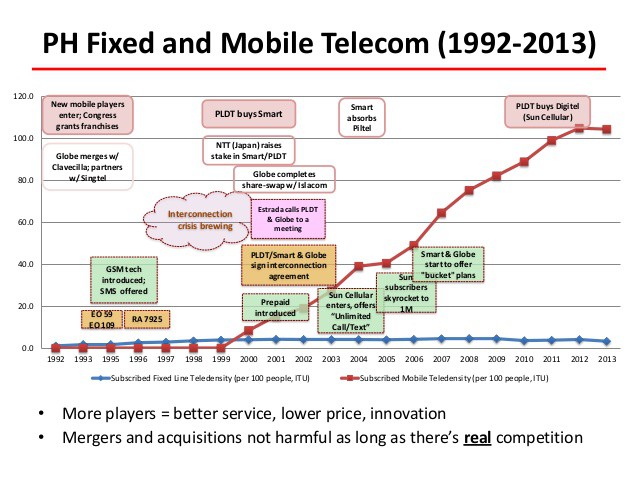
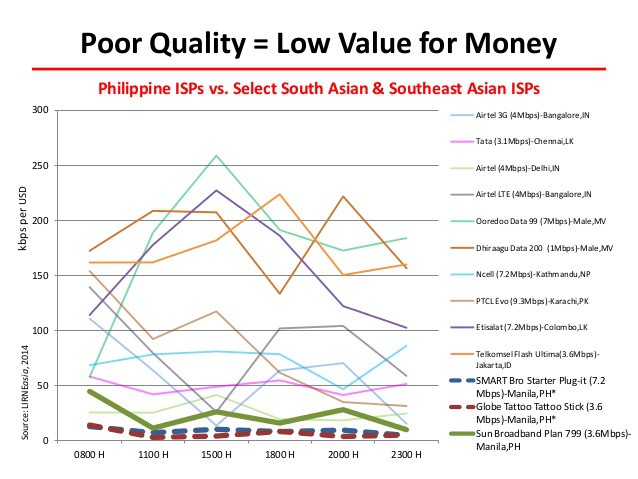

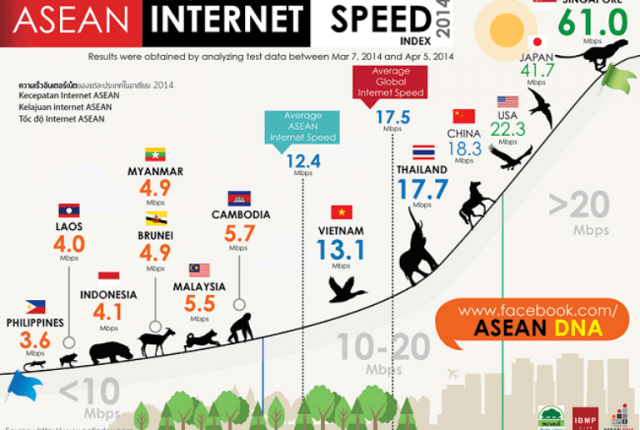

 While segmenting out popular mobile apps for special treatment, Philippine mobile providers have also taken Verizon and AT&T’s lead, pushing plans like
While segmenting out popular mobile apps for special treatment, Philippine mobile providers have also taken Verizon and AT&T’s lead, pushing plans like  Providers in the Philippines have learned a lot from America’s telecommunications lobbyists. Their advocacy campaigns revolve around the theme that the United States has the best wireless networks in the world, developed under a largely hands-off regulatory philosophy that the Philippine government should follow.
Providers in the Philippines have learned a lot from America’s telecommunications lobbyists. Their advocacy campaigns revolve around the theme that the United States has the best wireless networks in the world, developed under a largely hands-off regulatory philosophy that the Philippine government should follow. The NTC is
The NTC is  Unless a broadband provider can deliver the same kind of profitability earned by U.S. cable operators, don’t expect significant private investment in broadband expansion even if the company can easily turn a profit.
Unless a broadband provider can deliver the same kind of profitability earned by U.S. cable operators, don’t expect significant private investment in broadband expansion even if the company can easily turn a profit. Moffett was also critical of AT&T’s planned expansion of gigabit fiber broadband.
Moffett was also critical of AT&T’s planned expansion of gigabit fiber broadband.
 “As everyone understands, the cable video business is facing unprecedented pressure,” Moffett testified. “Cord cutting has been talked about for years but is finally starting to show up in a meaningful way in the numbers. And soaring programming costs are eating away at video profit margins. From a cable operator’s perspective, the video business and the broadband business are opposite sides of the same coin. It is, after all, all one infrastructure. Pressure on the video profit pool will therefore naturally trigger a pricing response in broadband, where cable operators will have greater pricing leverage.”
“As everyone understands, the cable video business is facing unprecedented pressure,” Moffett testified. “Cord cutting has been talked about for years but is finally starting to show up in a meaningful way in the numbers. And soaring programming costs are eating away at video profit margins. From a cable operator’s perspective, the video business and the broadband business are opposite sides of the same coin. It is, after all, all one infrastructure. Pressure on the video profit pool will therefore naturally trigger a pricing response in broadband, where cable operators will have greater pricing leverage.”