Frontier Communications customers in the mountainous western counties of North Carolina have run out of patience waiting for web pages to load and upgrades to arrive, despite repeated promises from the phone company that its aging copper-wire DSL service would improve over time.
Frontier Communications customers in the mountainous western counties of North Carolina have run out of patience waiting for web pages to load and upgrades to arrive, despite repeated promises from the phone company that its aging copper-wire DSL service would improve over time.
Stop the Cap! readers in the region pointed us to a special investigative report by WLOS-TV, Asheville’s ABC affiliate, which reports Frontier service is so bad, speeds under 1 Mbps are common. The station saw examples of Frontier unable to supply even modest speeds of just 3 Mbps.
“I’d rather stab myself than rely on Frontier’s fake internet access,” says our reader Darrell, who lives near Brasstown. “The only thing high-speed at Frontier is how fast they hang up on you when you call to complain.”
Frontier sold him “up to 10 Mbps” speed and instead struggles to deliver 1 Mbps, despite repeated service calls and promises of improvements.
 “They keep telling us the federal government has to come up with money to help upgrade the area, and I keep wondering why a private company needs our tax dollars to build a network they will profit from for years,” Dan said. “If they cannot do the job, maybe the town should because they at least answer to us.”
“They keep telling us the federal government has to come up with money to help upgrade the area, and I keep wondering why a private company needs our tax dollars to build a network they will profit from for years,” Dan said. “If they cannot do the job, maybe the town should because they at least answer to us.”
Aiden Davis, who lives near Asheville, said he’d rather have the government give money to the cable company to extend broadband to his home, which is located about 1/4th a mile away from the nearest cable connection.
“At least the cable company can give me speeds DSL never will,” he told us.
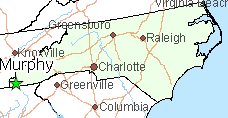
Reporters at WLOS visited Murphy, N.C., a community of 1,600 people in Cherokee — the westernmost county of the state.
Craig Marble escaped Washington, D.C. to live in the picturesque community nestled in the mountains. But his efforts to telecommute to his IT employer are frustrated by Frontier’s DSL service, which is supposed to provide up to 3 Mbps to Marble and his neighbors. But Frontier delivers far less than it advertises.

Western North Carolina
“It’s just a comedy of errors except that it’s not funny. It takes five minutes to load a single webpage,” Marble said. “This should be 3.0, not .3 [Mbps],” Marble said while showing reporters various speed tests for his service, resulting in .3 and .5, and .6 Mbps at various times throughout the morning and afternoon.
More than 50 similar complaints have been filed with the North Carolina Attorney General, some about internet speed, others about service, outages, and billing problems.
“If there are companies out there making representations to consumers that they can not back up and we hear from consumers, we will absolutely take action on their behalf,” Attorney General Josh Stein told the station. “If we determine that Frontier is not complying with the law, we’ll hold them accountable, but there’s a lot of work we still need to do.”
 But residents contend Stein does not seem to be in a hurry to chase down Frontier, and may not have the resources to follow through even if he wanted. After the Democrat won the North Carolina Attorney General race and took office in 2017, the Republican-controlled legislature slashed $10 million from his budget, forcing layoffs of dozens of staff attorneys and limiting his office’s ability to act.
But residents contend Stein does not seem to be in a hurry to chase down Frontier, and may not have the resources to follow through even if he wanted. After the Democrat won the North Carolina Attorney General race and took office in 2017, the Republican-controlled legislature slashed $10 million from his budget, forcing layoffs of dozens of staff attorneys and limiting his office’s ability to act.
Stein told the TV station he wrote to Frontier about internet speed issues in North Carolina, but hasn’t received a response.
Frontier responded to WLOS with a statement, reading in part:
“Copper-based internet service is difficult to represent consistently as it is subject to distance limitations. That is why it is sold as offering ‘up to’ a specified speed. Not all customers will have the same DSL service.”
But some customers report speeds are consistently better at times when most people are unlikely to be online, suggesting Frontier may be overselling its DSL service — forcing too many customers to share a limited bandwidth connection.
“When it is 2:30 in the morning, we always have the best speeds,” Davis reported. “They always drop as soon as the kids get home from school and keep dropping into the evening. During recent winter storms, speeds dropped to the point where the internet was unusable.”

Attorney General Joel Stein
“It’s not a technical problem, it’s a ‘reluctance to spend money to fix it’ problem,” he added.
Frontier frequently responds to speed complaints with press releases touting recent internet service improvements made possible through the federal government’s Connect America Fund, without always disclosing many of these projects pay to extend internet access into areas where it did not exist before, not improve service for customers that already have it.
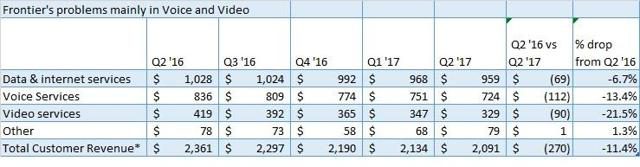
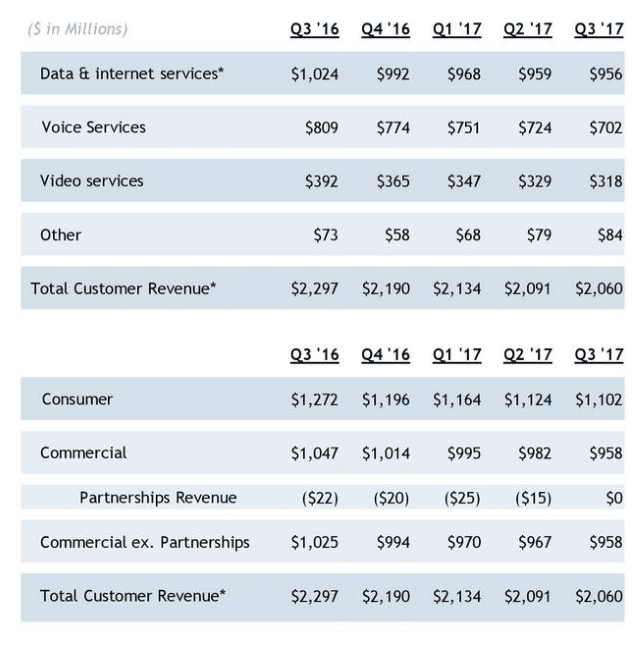
Frontier’s willingness to spend its own money on broadband improvements is often challenged by Wall Street’s demands for a dividend payout to shareholders, sending a significant portion of Frontier’s incoming revenue to investors. The company has reduced its dividend during difficult times to invest in limited upgrades. But critics claim Frontier’s devotion to a robust upgrade program comes second to shareholders and depends mostly on federal government handouts.
“The company struggles to spend $14.4 million on upgrades through 2020, but had no problem spending more than $10 billion to buyout Verizon in Florida, California, and Texas,” complained Darrell. “When you ask them specific questions, you learn that upgrade spending is window dressing that won’t address their speed problems across this part of the state.”
Marble tells WLOS that seems to be his impression as well, noting Frontier representatives didn’t give him much hope.
“They said — several of them said, ‘There are no plans for upgrades in your area, period’,” Marble said.
The TV station sent Frontier a detailed questionnaire, to which the company responded, taking care to disclaim some of the upgrade benefits many of Frontier’s own press releases seem to imply:
Question: How many customers does Frontier service in the following counties: Buncombe, Cherokee, Clay, Graham, Haywood, Henderson, Jackson, Macon, Madison, Mitchell, McDowell, Polk, Rutherford, Swain, Transylvania, Yancey? Answer: I’m not familiar enough with cities in counties etc. We have customers in the following towns: Andrews, Bryson City, Buncombe, Cashiers, Cherokee, Cullowhee, Fontana, Franklin, Garden City, Glenwood, Hayesville, Highlands, Madison, McDowell, Mitchell, Murphy, Robbinsville, Suit, Sylva, Weaverville and Yancey. Of those we serve, some are only telephone customers, some internet only customers and still others both phone and internet customers. While we do not provide market specific customer counts in any of our operating areas for competitive reasons, it is fair to say that our customer count in the areas I referenced is in the tens of thousands.
Question: How is Frontier using the Connect America Funds in western North Carolina? What’s being done to upgrade or add service? How is the money being spent? Answer: Frontier is installing fiber into network support buildings or units in western North Carolina to enable more capacity over our existing copper network.
Question: How many new customers has Frontier been able to provide service to, as a result of Connect America funds? Are the funds being used more for acquiring new customers or is it more upgrading service for existing customers and in that case, what have the service improvements been like? Answer: It starts with upgrading the network to provide a minimum of 10 Mbps service identified as CAF households to meet the requirements of the CAF Fund as established by the FCC. Customers along the path of these improvements, both existing and those who are currently not customers, can take advantage of new broadband upgrades though not necessarily at the 10 Mbps threshold. However, it is not designed to extend the network to different operating areas.
Question: How much funding has Frontier received in Connect America funds for upgrades to broadband service in those western North Carolina counties? Answer: As of 2016, Frontier began receiving approximately $3.6 million a year from the CAF to expand and upgrade the company’s network to more than 11,000 locations in North Carolina by the end of 2020, to include areas in western NC. In total, Frontier has accepted the FCC’s CAF II offer of over $330 million annually across 29 states during the six-year program, and must meet annual benchmarks for each state beginning in 2017 for passing a specified percentage of designated households.
Question: In which counties has Frontier received funds and is using them to improve or add service? Answer: We have previously used CAF II funds in Macon, Clay, Jackson and Swain counties.
Question: What projects/upgrades have been completed to date, since Frontier started receiving Connect America funds? Answer: In addition to the counties referenced above, representative counties in this latest round in 2017 included households in Cashiers, Cherokee, Franklin and Hayesville. By the of this phase of CAF II funding the intention is to have touched all of the counties we serve in Western NC, barring anything unexpected.
Question: Has Frontier over-promised service in areas in any of the above mentioned counties? If service has been over-promised, what problems is that creating and what is the remedy for solving that problem? Answer: I’m not sure what this question is asking. I would say that copper-based internet service is difficult to represent consistently as it is subject to distance limitations. That is why it is sold as offering “up to” a specified speed. However, CAF funding should have a positive impact on the end user experience.
Question: What is the best way customers who feel they’re being underserved or not getting the service that they’ve paid for can reach out to report a problem? Answer: They should call 1-800-921-8101.
Question: Has the state of North Carolina, through the state’s Attorney General office or Consumer Protection Division reached out to Frontier over service issues, failing to deliver on service promises made by the company and if so, what’s been the response back to the state? Answer: We receive individual customer complaints from these agencies, usually revolving around availability of service or insufficient internet speeds. Our marketing for internet service and our terms of service recognize that some customers may not have the same experience as others, largely because of the distance limitations of DSL service or congestion in the network. We are attempting to address both of these issues through a combination of normal capital budgets and the additional CAF II funding.
Question: What are some of the issues Frontier runs into in expanding or improving broadband service or internet access and speed issues in western North Carolina? Answer: Mostly there are geographic challenges. However, customer density is also a challenge, or lack thereof. Balancing the significant cost of expanding broadband availability in rural areas versus the potential return on that investment is always a challenge. However, we are grateful for the Connect America Fund to help spur some of that investment and know that those customers who have been impacted by the expanded capacity appreciate the service.
Question: Anything you would like to add about the Connect America funds? Answer: We are fortunate to be a participant in the CAF funding process and grateful to the FCC for making it possible. Our hope is that customers in Western NC will have better internet connectivity experiences as we move along toward the culmination of this funding in 2020.
If you live in North Carolina and want to file a complaint about your internet service with the Attorney General’s Office click here.
WLOS-TV in Asheville, N.C. aired this special investigative report about Frontier Communications’ performance problems in western North Carolina. (5:03)


 Subscribe
Subscribe If advertised claims of lightning fast DSL internet don’t match reality, it never hurts to bring evidence to the table if you want to prove your state’s biggest telecom company is lying through its teeth.
If advertised claims of lightning fast DSL internet don’t match reality, it never hurts to bring evidence to the table if you want to prove your state’s biggest telecom company is lying through its teeth.
 Verizon Communications will decommission its existing copper wire facilities in multiple markets in Delaware, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Virginia starting in 2018.
Verizon Communications will decommission its existing copper wire facilities in multiple markets in Delaware, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Virginia starting in 2018. Frontier Communications spent $2 billion in 2014 to purchase AT&T’s Connecticut wireline business, believing it could make a fortune selling internet and cable television service to wealthy Nutmeg State residents over a network AT&T upgraded to fiber-to-the-neighborhood service several years earlier.
Frontier Communications spent $2 billion in 2014 to purchase AT&T’s Connecticut wireline business, believing it could make a fortune selling internet and cable television service to wealthy Nutmeg State residents over a network AT&T upgraded to fiber-to-the-neighborhood service several years earlier.