
AT&T warns DSL customers they can watch 10 High Definition movies per month... and use their Internet connection for absolutely nothing else, unless they want to incur an overlimit fee of $10.
AT&T has released a phoney baloney video for their customers purporting to “explain” broadband usage and the company’s completely arbitrary usage limits on DSL and U-verse customers: “A single high-traffic user can utilize the same amount of data capacity as 19 typical households. Lopsided usage patterns can cause congestion at certain points in the network, which can slow Internet speeds and interfere with other customers’ access to and use of the network.”
Too bad these claims are not verified with actual facts.
Meaningless statistics
AT&T’s claim that less than two percent of their customers use 20 percent of available bandwidth is frankly meaningless to the company’s DSL and U-verse hybrid fiber-copper networks. For years, phone companies made a marketing point that unlike cable broadband’s shared network, their DSL service was never shared with anyone else in a neighborhood. Therefore, running it at a trickle or full speed ahead should have no impact on any other customer. The only exception to this rule comes from phone companies that under-invest in their middle mile and backbone networks. For AT&T, that means trying to serve too many customers on inadequate equipment ranging from a poorly planned network of D-SLAMs, which connect individual customers with a fatter pipeline back to the central office, or an inadequate network between the central office and AT&T’s regional backbones. Fiber, such as that used by AT&T’s more modern U-verse system, completely solves any capacity issues. Broadband traffic is only a tiny percentage of the bandwidth consumed by AT&T’s IPTV video service — the one that delivers U-verse TV to your home. AT&T imposes no viewing limits on customers, of course.
Any actual capacity crunch would only show up during peak usage periods — when AT&T customers of all kinds pile on their broadband connection at the same time. AT&T’s usage cap regime does next to nothing to mitigate that kind of congestion. Here’s why:
Since AT&T and other broadband companies routinely claim the average use per customer is well under 20GB per month, and only 2 percent of customers are currently deemed “heavy users” by AT&T, that tiny percentage of customers cannot create sufficient drag on AT&T’s DSL network even if they opened up their connections to full speed traffic. In reality, the 98 percent of “average” users piling on the network during prime time would be the only thing capable of the kind of critical mass needed to create visible congestion. What uses more capacity? Two customers using their 7Mbps DSL lines to stream online videos concurrently or 98 customers all using their 7Mbps DSL lines at the same time for virtually any online activity?
The math simply doesn’t add up.
The Congestion Myth

AT&T targets their broadband customers with an unwarranted, arbitrary Internet Overcharging scheme they cannot effectively explain to customers.
As two week’s of hearings this month have demonstrated, Bell Canada’s similar arguments for its usage caps simply come without any evidence of actual congestion. In fact, company officials modified their position to talk more about peak usage congestion, a problem that cannot be controlled with a usage cap well in excess of the average consumer’s usage. In fact, only a speed throttle could control network congestion at the times it actually occurred. AT&T also ignores when its customers are using its network. Is a heavy user downloading files at 3 in the morning creating a problem for other users? No. Are the majority of their average-usage customers all jumping online after school or work creating a problem? Perhaps, if you believed AT&T even had a congestion problem.
Industry maven Dave Burstein does not, and Burstein talked to two chief technology officers at AT&T who told him wired broadband congestion is a “minimal” problem for the phone company.
Upgrades and Cord-Cutting, Delayed
Two things usage caps can do is help your company delay necessary upgrades to meet customers’ broadband needs, whether they are “heavy users” or not. AT&T has shown itself historically to be slow to invest, and cheap when it does. AT&T’s wireless network is bottom-rated by consumers thanks to inadequate network capacity. The company elected to upgrade on-the-cheap to an IPTV platform that still relies on copper phone lines to deliver service that simply cannot compete in quality and capacity with Verizon’s FiOS fiber to the home network. But investors love the fact the company counts every penny, even if it means inconveniencing and overcharging customers for their services, usually offered in duopoly or monopoly markets.
AT&T’s usage caps on U-verse are even less credible than those imposed on their DSL service. U-verse is a fiber to the neighborhood network with near limitless capacity for broadband and video. In fact, the only “congestion” comes from the copper phone lines that limit how much bandwidth can be supplied to your individual home. But no matter how much you use, you will not affect your neighbors because your copper phone line is shared with nobody else. In fact, the biggest chunk of U-verse’s bandwidth is reserved for their video services, which makes arguments about excessive Internet usage on that pipeline un-credible.
What AT&T’s usage cap does assure is that you will not drop that video package from your U-verse service anytime soon. That lucrative revenue from expensive video packages cannot be forfeit without a fight, and a nice deterrent in the form of an arbitrary usage cap does wonders to keep that cord cutting to a minimum.
Meters That Don’t Measure
One of the worst ongoing problems with Internet Overcharging schemes like AT&T’s is the broken usage meter. Stop the Cap! has received hundreds of e-mails from AT&T DSL and U-verse customers who report AT&T’s usage meter is either unavailable, broken, or is wildly inaccurate. With absolutely no independent oversight, and no consistently accurate usage measurement, charging anyone overlimit fees with a broken meter doing the counting is unconscionable. Yet AT&T may well try. The company has already been sued by one law firm for what it alleges is an unfair usage meter on the company’s wireless service — a meter that consistently overcounts usage in AT&T’s favor.
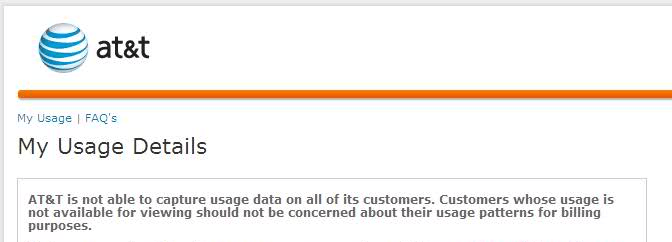
AT&T admits they cannot even accurately measure their own customers' usage.
Once getting over the broken meter, customers are directed to a pointless usage-estimator — the ones that tell you about how many tens of thousands of e-mails you can send and receive under AT&T’s cap regime. In fact, these statistics are irrelevant for the vast majority of customers who never think of sending 10,000 e-mails or exchanging 2,000 pictures or songs. That’s because customers do not use the Internet to exclusively do those things. Even with the guestimator, they are left checking a broken usage meter to ponder whether or not they can watch one more show or download another file without incurring a $10 overlimit penalty (or more). That “generous” limit AT&T touts suddenly doesn’t look so ample when the company gets to the wildly popular activity of streamed video. AT&T’s own video warns you can only watch 10HD movies a month over your broadband connection — and absolutely nothing else. No web browsing, e-mail, or photos or music. Ten movies a month. Still thinking of dropping your U-verse video subscription now?
Yet AT&T has the nerve to claim, “Our goal is to provide you with the best Internet service possible.” Really?
 Thankfully, not every member of the investor class is thrilled with nickle-and-diming broadband consumers for usage that costs the providing company next to nothing.
Thankfully, not every member of the investor class is thrilled with nickle-and-diming broadband consumers for usage that costs the providing company next to nothing.
The Economist excoriated AT&T for its unwarranted usage limits on its blog earlier this year:
The use of caps allows providers to dish out bandwidth with one hand and take it away with the other. The companies have vastly increased the capacity of various copper, coaxial and fibre lines, but artificially separate out a portion—at least half and often much more—for video which a set-top box or a broadband modem spits out as an apparently distinct service. Cable firms simultaneously push out hundreds of digital channels, while telecoms firms rely on multiple digital streams from live broadcast or cable TV or on-demand pay-per-view. It is as though the water main were divided as it entered the home and a steady, modest stream was made available for showers and at the tap, while most of it was always at the ready for a coin-operated washing machine.
Increasing speed on the internet portion, which would allow consumers to give up on TV subscriptions, is balanced by capping volume. If a consumer does not monitor usage, his internet access can be withdrawn or, in AT&T’s case, overage fees of $10 charged for every additional 50 GB of usage. […] [That] $10 charge applies whether the limit was breached by 1 MB or a smidgen under 50 GB.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/ATT Usage.flv[/flv]
AT&T’s new video on broadband usage is based on facts not in evidence and only adds to consumer confusion about arbitrary Internet Overcharging schemes. (4 minutes)
 New Zealand is one of a handful of countries stuck with pervasive Internet Overcharging schemes that limit usage or throttle broadband speeds because of international connectivity limitations. But as international underseas fiber cables ease traffic congestion, Internet Service Providers are increasingly relaxing usage caps and reducing the level of speed throttling during prime time usage hours.
New Zealand is one of a handful of countries stuck with pervasive Internet Overcharging schemes that limit usage or throttle broadband speeds because of international connectivity limitations. But as international underseas fiber cables ease traffic congestion, Internet Service Providers are increasingly relaxing usage caps and reducing the level of speed throttling during prime time usage hours. Like many providers in the South Pacific, Slingshot uses “network management” to prioritize traffic under this scheme, in order of highest priority to least:
Like many providers in the South Pacific, Slingshot uses “network management” to prioritize traffic under this scheme, in order of highest priority to least:

 Subscribe
Subscribe








