Phillip "Try the Gouda" Dampier
Welcome to the Broadband Usage Whine & Cheese Festival
Midcontinent Communications earlier this month announced a big boost in broadband speeds for more than 250,000 customers in the Dakotas and Minnesota, bringing up to 100/15Mbps service to customers who wanted or needed that speed.
MidcoNet Xstream Wideband, made possible with a DOCSIS 3 upgrade, delivers 1/1Mbps ($30.95), 30/5Mbps ($44.95), 50/10Mbps ($64.95), or 100/15Mbps ($104.95) service. Those are mighty fast speeds for an upper midwestern cable company, especially in states where 1-3Mbps DSL is much more common.
The cable provider was excited to introduce the speed upgrades earlier this month, telling customers:
At up to 100 Mbps, MidcoNet Xstream® Wideband is fast. But today’s online experience is about more than speed. It’s about the power and capacity to run every streaming, blogging, downloading, surfing, gaming, chatting, working, playing, connected device in the house. All at the same time. MidcoNet Xstream Wideband delivers…it’s everyone in your entire family online at once, doing the most intense online activities, no problem.
But now there is a problem. Customers spending upwards of $105 a month for the fastest Internet speeds are actually using them to leverage the Internet’s most bandwidth-intensive services, and evidently Midco isn’t too happy about that. Todd Spangler, a columnist for cable industry trade magazine Multichannel News, was given a usage chart by Midco, and used it to lecture readers about the need for usage caps: “One thing is clear: Broadband service providers will all need to do something to contain the rapidly rising flood of Internet data.” The implication left with readers is that limiting broadband usage is the only way to stem the tide.
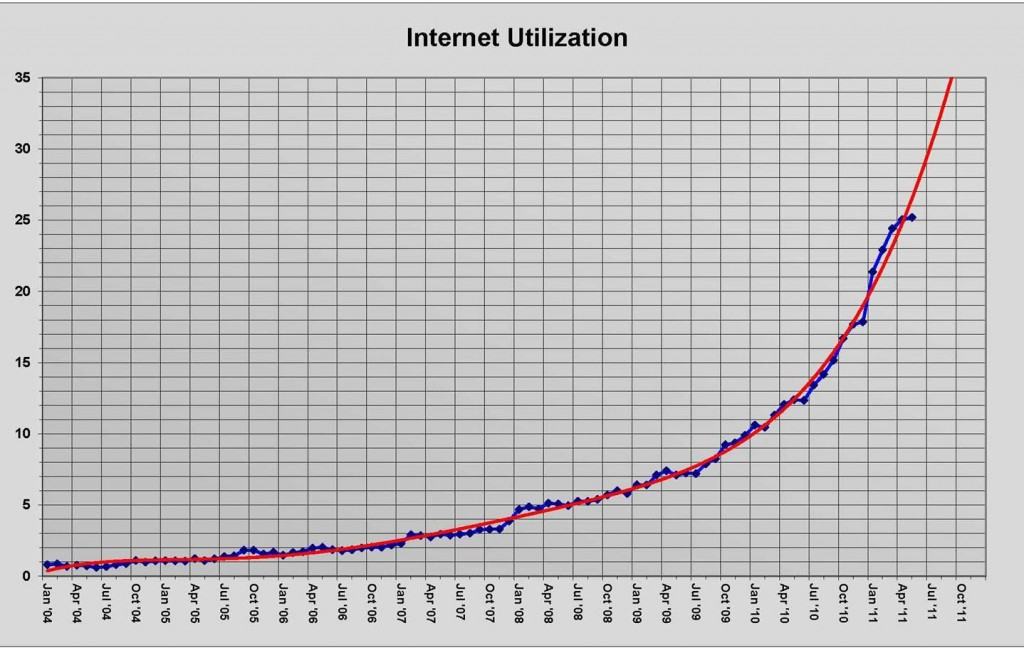
Midco's not-so-useful chart looks mighty scary, showing usage growth on their 100Gbps backbone network, but leaves an enormous amount of information out of the equation. (Source: Midcontinent Communications via Multichannel News)
Spangler quotes Midco’s vice president of technology Jon Pederson: “Like most network providers we have evaluated this possibility, but have no immediate plans to implement bandwidth-usage caps,” he said.
So Midco is more than happy to pocket up to $105 a month from their customers, so long as they don’t actually use the broadband service they are paying top dollar to receive. It’s an ironic case of a provider desiring to improve service, but then getting upset when customers actually use it.
We say ironic because, from all outward appearances, Midco is well-aware of the transformational usage of broadband service in the United States these days:
If you have ever once said “my Internet is too slow,” then you need MidcoNet Xstream Wideband. With it, you can do all the cool things you’ve heard people are doing online. Explore all the great stuff your online world has to offer. Play the most intense games. Try things you could never do before, from entertainment to finance, video chat or video streaming. Like we said, MidcoNet Xstream Wideband is all about speed, capacity, choice and control.
What this means for you is that you’ll be able to do things like:
- Download and start enjoying entire HD movies in seconds, not minutes.
- Stream video and music without a hitch while you simultaneously perform other intense online tasks.
- Choose from three different pipelines, from 3.0 to 1.0, for the capacity and price your family needs.
- Monitor your bandwidth use to determine if you need more capacity or can do what you want with less.
- Upload files or signals, such as webcam footage, faster than ever before possible for a better online experience.
- Watch ESPN3.com. Your Favorite Sports. Live. Online.
 Just don’t do any of these things too much. Indeed, when providers start toying with usage caps, it’s clear they want you to use your service the same way you did in 2004 — reading your e-mail and browsing web pages. Real Audio stream anyone?
Just don’t do any of these things too much. Indeed, when providers start toying with usage caps, it’s clear they want you to use your service the same way you did in 2004 — reading your e-mail and browsing web pages. Real Audio stream anyone?
Let’s ponder the facts Mr. Spangler didn’t entertain in his piece.
Midco upgraded their network to DOCSIS 3 technology to deliver faster speeds and provide more broadband capacity to customers who are using the Internet much differently than a decade ago, when cable modems first became common. Some providers and their trade press friends seem to think it’s perfectly reasonable to collect the proceeds of premium-priced broadband service while claiming shock over the reality that someone prepared to spend $100 a month for that product will use it far more than the average user.
Part of the price premium charged for faster service is supposed to cover whatever broadband usage growth comes as a result. That’s why Comcast’s 250GB usage cap never made any sense. Why would someone pay the company a premium for 50Mbps service that has precisely the same limit someone paying for standard service has to endure?

Cringely
Midcontinent Communications is a private company so we do not have access to their financial reports, but among larger providers the trend is quite clear: revenues from premium speed accounts are being pocketed without a corresponding increase in investment to upgrade their networks to meet demand. Inevitably that brings the kind of complaining about usage that leads to calls for usage caps or speed throttles to control the growth.
We’re uncertain if Midco is making the case for usage caps, or simply Mr. Spangler. We’ll explain that in a moment. But if we are to fully grasp Midco’s broadband challenges, we need much more than a single usage growth chart. A “shocking” usage graph is no more impressive than those showing an exponential increase in hard drive capacity over the same period. The only difference is consumers are paying about the same for hard drives today and getting a lot more capacity, while broadband users are paying much more and now being told to use less. Here is what we’d like to see to assemble a true picture of Midco’s usage “dilemma:”
- How much average revenue per customer does Midco collect from broadband customers. Traditional evidence shows ARPU for broadband is growing at a rapid rate, as consumers upgrade to faster speeds at higher prices. We’d like to compare numbers over the last five years;
- How much does Midco spend on capital improvements to their network, and plot that spending over the last 10 years to see whether it has increased, remained level, or decreased. The latter is most common for cable operators, as the percentage spent in relation to revenue is dropping fast;
- How many subscribers have adopted broadband service over the period their usage chart illustrates, and at what rate of growth?
- What does Midco pay for upstream connectivity and has that amount gone up, down, or stayed the same over the past few years. Traditionally, those costs are plummeting.
- If the expenses for broadband upgrades and connectivity have decreased, what has Midco done with the savings and why are they not prepared to spend that money now to improve their network?
While Midco expresses concern about the costs of connectivity and ponders usage caps, there was plenty of money available for their recent purchase of U.S. Cable, a state-of-the-art fiber system serving 33,000 customers — a significant addition for a cable company that serves around 250,000 customers.
A journey through Midco’s own website seems to tell a very different story from the one Mr. Spangler is promoting. The aforementioned Mr. Pederson is all over the website with YouTube videos which cast doubt on all of Spangler’s arguments. Midco has plentiful bandwidth, Mr. Pederson declares — both to neighborhoods and to the Internet backbone. Their network upgrades were designed precisely to handle today’s realistic use of the Internet. They are marketing content add-ons that include bandwidth-heavy multimedia. Why would a provider sell customers on using their broadband service for high-bandwidth applications and then ponder limiting their use? Mr. Pederson seems well-aware of the implications of an increasingly connected world, and higher usage comes along with that.
That’s why we’d prefer to attack Mr. Spangler’s “evidence” used to favor usage caps instead of simply vilifying Midco — they have so far rejected usage limits for their customers, and should be applauded for that.
Robert X. Cringely approached Midco’s usage chart from a different angle on his blog, delivering facts our readers already know: Americans are overpaying for their broadband service, and the threat of usage caps simply disguises a big fat rate hike. He found Midco’s chart the same place we did — on Multichannel News’ website. He dismisses its relevance in the usage cap debate. Cringley’s article explores the costs of broadband connectivity, which we have repeatedly documented are dropping, and he has several charts to illustrate that fact.
You’ll notice for example that backbone costs in Tokyo, where broadband connections typically run at 100 megabits-per-second, are about four times higher than they are in New York or London. Yet broadband connections in Tokyo cost halfwhat they do in New York, and that’s for a connection at least four times a fast!
So Softbank BB in Tokyo pays four times as much per megabit for backbone capacity and offers four times the speed for half the price of Verizon in New York. Yet Softbank BB is profitable.
No matter what your ISP says, their backbone costs are inconsequential and to argue otherwise is probably a lie.
Cue up Time Warner Cable CEO Glenn Britt, who said precisely as much Thursday morning when he admitted bandwidth costs are not terribly relevant to broadband pricing.
We knew that, but it’s great to hear him say it.
Cringely’s excellent analysis puts a price tag on what ISP’s want to cap for their own benefit — their maximum cost to deliver the service:
That 250 gigabytes-per-month works out to about one megabit-per-second, which costs $8 in New York. So your American ISP, who has been spending $0.40 per month to buy the bandwidth they’ve been selling to you for $30, wants to cap their maximum backbone cost per-subscriber at $8.
[…] IP Transit costs will continue to drop. That $8 price will most likely continue to fall at the historical annual rate of 22 percent. So what’s presented as an ISP insurance policy is really a guaranteed profit increase of 22 percent that will be compounded over time because consumption will continue to rise and customers will be for the first time charged for that increased consumption.
This isn’t about capping ISP losses, but are about increasing ISP profits. The caps are a built-in revenue bump that will kick-in 2-3 years from now, circumventing any existing regulatory structure for setting rates. The regulators just haven’t realized it yet. By the time they do it may be too late.
Unfortunately, even if they knew, we have legislators in Washington who are well-paid in campaign money to look the other way unless consumers launch a revolution against duopoly broadband pricing.
Cringely believes usage caps will be the form of your provider’s next rate increase for broadband, but he need not wait that long. As the aforementioned CEO of Time Warner Cable has already admitted, the pricing power of broadband is such that the cable and phone companies are already increasing rates — repeatedly — for a service many still want to cap. Why? Because they can.
Consumers who have educated themselves with actual facts instead of succumbing to ISP “re-education” efforts designed to sell usage limits under the guise of “fairness” are well-equipped to answer Mr. Spangler’s question about whether bandwidth caps are necessary.
The answer was no, is no, and will always be no.
[flv width=”640″ height=”500″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Midco D3 Upgrade Promo 7-11.flv[/flv]
Jon Pederson’s comments on Midcontinent’s own website promoting its new faster broadband speeds can’t be missed. He counts the number of devices in his own home that connect to the Internet, explains how our use of the Internet has been transformed in the past several years, and declares Midco well-prepared to deliver customers the capacity they need. Perhaps Mr. Spangler used the wrong company to promote his desire for Internet usage caps. Pederson handily, albeit indirectly, obliterates Spangler’s own talking points, which makes us wonder why this company even pondered Internet Overcharging schemes like usage caps in the first place. (10 minutes)
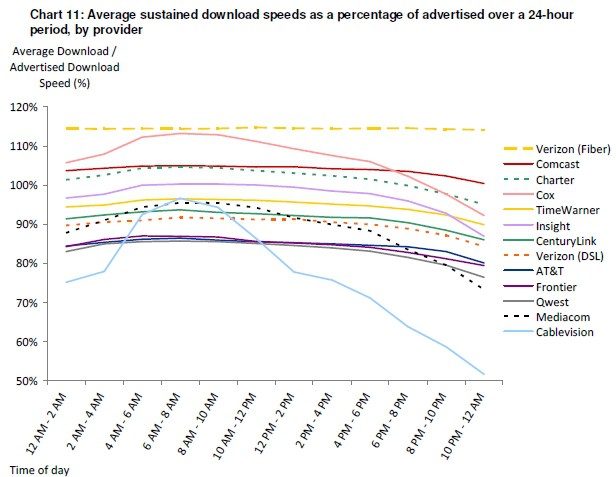
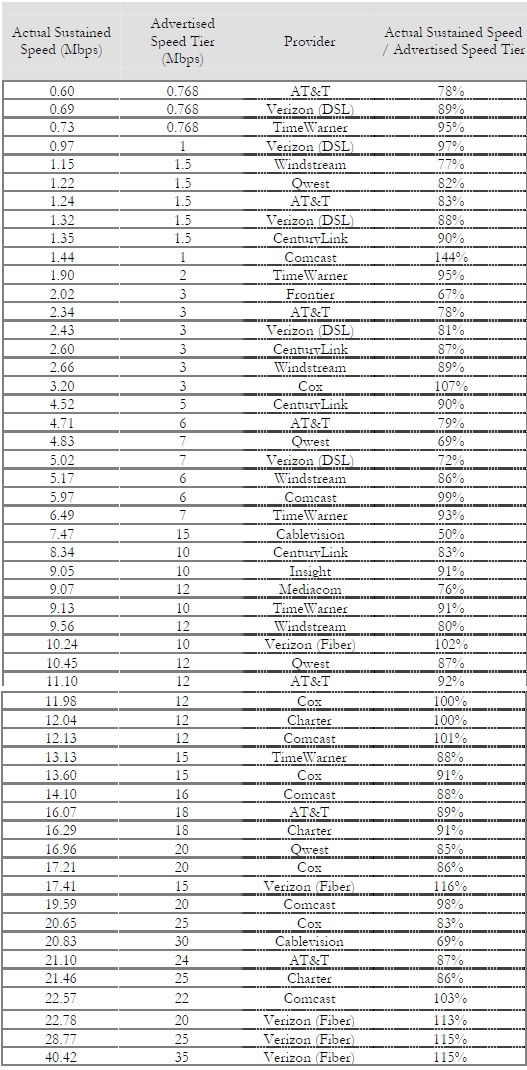 More than 78,000 consumers volunteered to participate in the study and a total of approximately 9,000 consumers were selected as potential participants and were supplied with specially configured routers. The data in the report is based on a statistically selected subset of those consumers—approximately 6,800 individuals—and the measurements taken in their homes during March 2011. The participants in the volunteer consumer panel were recruited with the goal of covering ISPs within the U.S. across all broadband technologies, although only results from three major technologies—DSL, cable, and fiber-to-the-home—are reflected in the report.
More than 78,000 consumers volunteered to participate in the study and a total of approximately 9,000 consumers were selected as potential participants and were supplied with specially configured routers. The data in the report is based on a statistically selected subset of those consumers—approximately 6,800 individuals—and the measurements taken in their homes during March 2011. The participants in the volunteer consumer panel were recruited with the goal of covering ISPs within the U.S. across all broadband technologies, although only results from three major technologies—DSL, cable, and fiber-to-the-home—are reflected in the report.

 Subscribe
Subscribe