 Most Charter Communications customers should now be experiencing Spectrum’s free holiday season speed upgrade as the company rolls out speed tiers ranging from 100-1,000Mbps. Customers have been sharing their stories about the speed changes, especially for former Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers that, in many areas, languished with maximum speeds of around 50Mbps for years.
Most Charter Communications customers should now be experiencing Spectrum’s free holiday season speed upgrade as the company rolls out speed tiers ranging from 100-1,000Mbps. Customers have been sharing their stories about the speed changes, especially for former Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers that, in many areas, languished with maximum speeds of around 50Mbps for years.
Most of the changes were noticed by customers around mid-December when Charter reprovisioned customer modems to reflect the new speed tiers. But some customers have had to call to get their modems refreshed to get the new speed upgrades. Others may need a new modem to take advantage of faster speeds. Since Spectrum does not charge a customer modem rental fee, if your speeds are inadequate with your current modem, it may not hurt to try one of theirs. Just remember they will often attempt to sell you added Wi-Fi service which you may not need for an additional $5 a month. This feature can be disabled to avoid the fee on any modem they provide if you already have your own router.
There has also been confusion because some cities are not yet fully upgraded to receive some of Spectrum’s fastest tiers and some current customers will not automatically qualify for speed upgrades until they talk to Spectrum customer service.
Premium Speed Price Reductions Arrive
Some good news — the premium prices Spectrum charges for its highest speed tiers are dropping to make room for the company’s new gigabit plan ($124.99), currently only available in a very limited service area. Spectrum Internet Ultra, which ranges in speed between 120-400Mbps depending on your service area is dropping from $104.99/mo to $89.99/mo ($79.99 if you have a television package). The original Spectrum Ultra upgrade setup fee – $199.99, has been reduced to $49.99.
If you subscribe to Internet Ultra, you may need to contact Spectrum to make sure they have provisioned your service at the new lower price. If you have any problems, refer them to Charter’s non-promotional rate card for your area, which should now show the new non-promotional/regular pricing.
Remember too that customers with legacy Time Warner Cable or Bright House packages and pricing will not receive speed upgrades.
Speed Changes in Select Areas
For many Spectrum customers, the speed increase introduces 100Mbps as the new Standard Spectrum internet speed, but in more than a dozen markets, even faster speeds are now available, at least for some customers.
In Austin, Tex., Charlotte, N.C., Cincinnati, Oh., Kansas City, Mo., New York, N.Y., Raleigh, N.C., and San Antonio, Tex.:
- Spectrum Internet Gig (up to 940/35Mbps) is now available
- Spectrum Internet Ultra (up to 400/20Mbps) for new customers (existing customers should check to see if they are still stuck at 300Mbps, the old speed)
- Spectrum Internet Standard (up to 200/10Mbps) for all customers, which includes a free speed boost.
Note: Current Internet Ultra customers may need to contact Spectrum to make arrangements for the speed upgrade. You may also need a new modem to qualify for 400Mbps speed.
In Bowling Green, Ky., Burlington, Vt., Dayton, Oh., Dallas-Ft. Worth, Tex., Evansville, Ind., Green Bay, Wisc., Greensboro, N.C., Greenville, N.C., Houston, Tex., Lexington, Ky., Los Angeles, Calif., Louisville, Ky., Milwaukee, Wisc., Palm Springs, Calif., San Diego, Calif., Syracuse, N.Y., Utica, N.Y., Waco, Tex., Watertown, N.Y., Wilmington, N.C., and Yuma, Ariz.:
- Spectrum Internet Ultra (up to 400/20Mbps) for new customers
- Spectrum Internet Ultra (up to 300/20Mbps) for existing customers, which represents no change.
Note: Some existing customers claim they have been upgraded to 400Mbps speed automatically, but others have had to contact Spectrum to make arrangements for the upgrade. You may also need a new modem to qualify for 400Mbps speed.
Experiencing Spectrum’s Gigabit Service

Technicolor 4400 DOCSIS 3.1 modem
Upgrading to gigabit speed will take more than a phone call with customer service. For now, Charter Communications insists on an in-home service call and a setup fee that was originally set at $199.99 but may have recently dropped. Some customers report getting the fee waived by complaining about it on Twitter and referencing @Ask_Spectrum in the tweet.
We have heard from customers in Texas and Hawaii that signed up for gigabit service and their stories are similar.
- Expect a service call lasting up to two hours. A technician, or more likely a few of them will be thoroughly testing the condition of your current cable lines, both inside and outside of the home. They have new testing equipment that is more sensitive than older testing equipment, and can spot signal problems, interference, or deteriorating infrastructure that will need to be repaired or replaced before service can be installed. In most cases, this can be done during the same service call.
- There are no authorized customer-owned modems for Spectrum’s gigabit internet at this time. Customers have received Technicolor TC4400-AM DOCSIS 3.1 modems during these early days of gigabit service. There will likely be others offered in the future.
- Customers can expect speeds to approach 940Mbps of download speed and close to 40Mbps for uploads if they own gigabit capable routers and reasonably modern computers. Expect wireless speeds to be significantly lower — sometimes by more than half, depending on the device, distance from the router, and the router itself. Spectrum technicians will probably strongly recommend the use of one of their routers.
- Faster speeds were noticeable downloading large files and streaming very high bandwidth multimedia, but average users may not notice a dramatic difference from gigabit speed while doing basic web browsing and other similar activities. But the larger installed base of gigabit-capable consumers will likely inspire future applications built to take advantage of that higher bandwidth.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
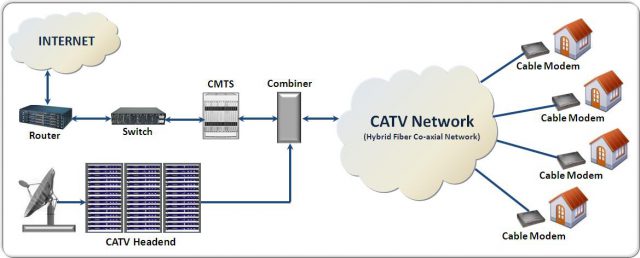
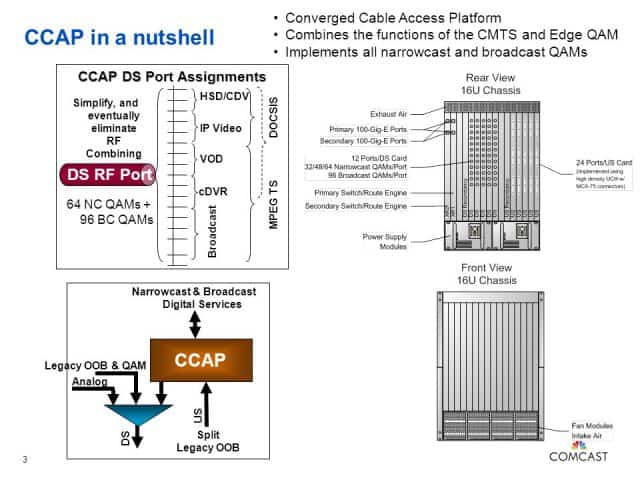


 Despite claims from some industry-backed researchers and former members of Congress that Net Neutrality
Despite claims from some industry-backed researchers and former members of Congress that Net Neutrality 


 But despite Webpass’ claim its performance is comparable to fiber, its inability to guarantee customers a certain speed level and its tremendous performance variability from 100 to 1,000Mbps exposes one of the weaknesses of fixed wireless networks. At a time when capacity is king, only fiber optic networks have shown a consistent ability to deliver synchronous broadband speeds that do not suffer the variability of shared networks, poor antenna placement/signal levels, or harmful interference.
But despite Webpass’ claim its performance is comparable to fiber, its inability to guarantee customers a certain speed level and its tremendous performance variability from 100 to 1,000Mbps exposes one of the weaknesses of fixed wireless networks. At a time when capacity is king, only fiber optic networks have shown a consistent ability to deliver synchronous broadband speeds that do not suffer the variability of shared networks, poor antenna placement/signal levels, or harmful interference. At Stop the Cap!, we believe these developments further the argument broadband is an essential utility best administered for the public good and not solely as a profit-motivated venture. The path to fiber to the home service in rural, suburban, and urban communities has and will continue to come from a mix of private and public utilities, just as local public and private gas and electric companies have served this country for the last century. Where there is a business model for fiber to the home service that investors support, there is a for-profit fiber provider. Where there isn’t, now there is often no service at all. So far, the FCC in conjunction with Congress has seen fit to solve broadband availability problems by bribing private providers into offering service (usually low-speed DSL that does not even meet the FCC’s definition of broadband) with cash subsidies, tax write-offs, or occasional tax abatement schemes. Imagine if we followed that model with the nation’s public roads and highways. We would today be paying tolls or a subscription to travel down roads built and owned by a private company often financed by tax dollars.
At Stop the Cap!, we believe these developments further the argument broadband is an essential utility best administered for the public good and not solely as a profit-motivated venture. The path to fiber to the home service in rural, suburban, and urban communities has and will continue to come from a mix of private and public utilities, just as local public and private gas and electric companies have served this country for the last century. Where there is a business model for fiber to the home service that investors support, there is a for-profit fiber provider. Where there isn’t, now there is often no service at all. So far, the FCC in conjunction with Congress has seen fit to solve broadband availability problems by bribing private providers into offering service (usually low-speed DSL that does not even meet the FCC’s definition of broadband) with cash subsidies, tax write-offs, or occasional tax abatement schemes. Imagine if we followed that model with the nation’s public roads and highways. We would today be paying tolls or a subscription to travel down roads built and owned by a private company often financed by tax dollars.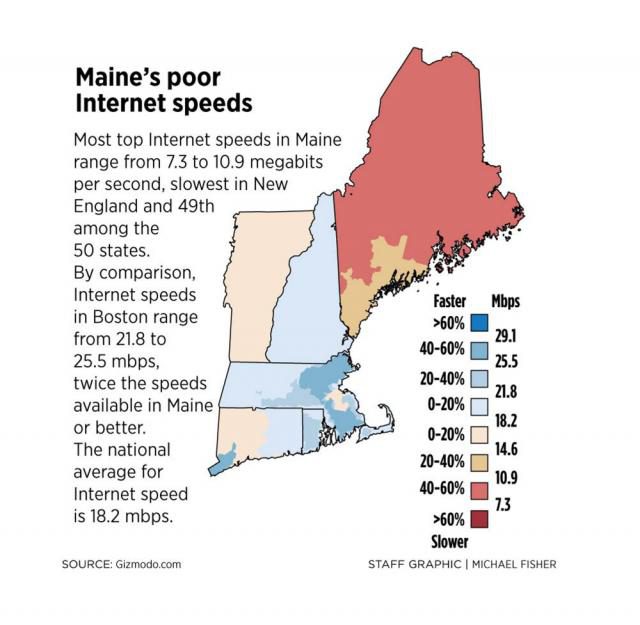
 Cox Communications will push broadband speed upgrades as high as a gigabit to customers over an upgraded network heavy on fiber and much lighter on copper coaxial cable.
Cox Communications will push broadband speed upgrades as high as a gigabit to customers over an upgraded network heavy on fiber and much lighter on copper coaxial cable.