 Years of broadcast and cable networks relying on cheap reality TV fare, game shows, and lurid news magazines to save money are coming to an end as media companies realize the only way to stop the viewing shift to Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon is to create better programming viewers want to see.
Years of broadcast and cable networks relying on cheap reality TV fare, game shows, and lurid news magazines to save money are coming to an end as media companies realize the only way to stop the viewing shift to Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon is to create better programming viewers want to see.
With online video services like Netflix spending millions to create original content like House of Cards and Fuller House, viewers are becoming disenchanted with shoveled reality fare and reruns littering basic cable networks.
A decade ago, cable networks started pushing the envelope on their programming lineups to boost ratings. Sober educational history documentaries on The History Channel began to make way in 2008 for reality shows like Pawn Stars and Ax Men, along with dubious pseudo-documentaries like Ancient Aliens and UFO Hunters. Consistent weather forecast information on The Weather Channel often had to wait for various weather chasing reality shows and other long form programming. Even The Learning Channel ditched educational programming as early as 2001 to feature “lifestyle” shows maligned and lampooned by critics as “freak show” television.
Broadcast networks suffering through an interminable advertising recession increasingly ditched scripted dramas for much cheaper reality and game shows. Even though some of these shows are considered popular, the total number of households viewing them have been in decline for years.
With the advent of series and movies created and funded by online video providers, traditional television networks and cable outlets have realized they can no longer rely on Law & Order reruns and shows like The Real Housewives of Dallas to keep viewers. They have to spend more money to create quality new shows.
 Bloomberg News reports networks hit the panic button after learning Netflix intends to spend almost $5 billion this year alone on programming, far more than any broadcast or cable network would ever consider.
Bloomberg News reports networks hit the panic button after learning Netflix intends to spend almost $5 billion this year alone on programming, far more than any broadcast or cable network would ever consider.
The new strategy in response: spend, spend, spend.
“All these companies have been raising the amount they’re spending on programming pretty consistently,” said Doug Creutz, an analyst with Cowen & Co. “TV is losing audiences, and you’re trying to have new stuff to keep audiences engaged with your programming.”
Discovery Communications, Viacom and Starz are among those planning spending boosts to deliver better programming to compete. Although that may be great news for television aficionados, consumers are likely to be handed the bill in the form of higher cable rates to cover the “increased programming expenses.”
The large broadcast networks, movie studios, and cable networks may have created this problem for themselves after they began dramatically boosting the cost of licensing movies and TV shows for ventures like Netflix, in hopes of limiting its growth while also profiting handsomely from their deep content libraries. In response to growing restrictions on licensing content, Netflix embarked on a plan to create some of their own exclusive content instead. Many entertainment executives did not take Netflix seriously until the arrival of House of Cards, a series that could easily have been created and financed by any major network.
Other online video companies quickly followed suit, often using the British TV model of creating affordable, high quality mini-series that might include 8-10 episodes per season instead of the usual two dozen common on American networks. Co-productions with content-starved networks abroad also helped share expenses, secure talent, and move into something beyond conventional programming.
Cable networks have also had increasing success creating shows not just for the American market, but also for export to the rest of the English-speaking world, particularly Great Britain, Ireland, Australia, and Canada.
 Some Wall Street analysts like Rich Greenfield at BTIG Research have gone as far as predicting the traditional cable TV bundle is threatened with extinction as cost conscious viewers continue to abandon linear/live television for on-demand content like that offered by Netflix instead. That has delivered a three-way punch: pressures on revenue as program creation spending increases, growing cord-cutting, and cable rate inflation cable executives are increasingly desperate to control.
Some Wall Street analysts like Rich Greenfield at BTIG Research have gone as far as predicting the traditional cable TV bundle is threatened with extinction as cost conscious viewers continue to abandon linear/live television for on-demand content like that offered by Netflix instead. That has delivered a three-way punch: pressures on revenue as program creation spending increases, growing cord-cutting, and cable rate inflation cable executives are increasingly desperate to control.
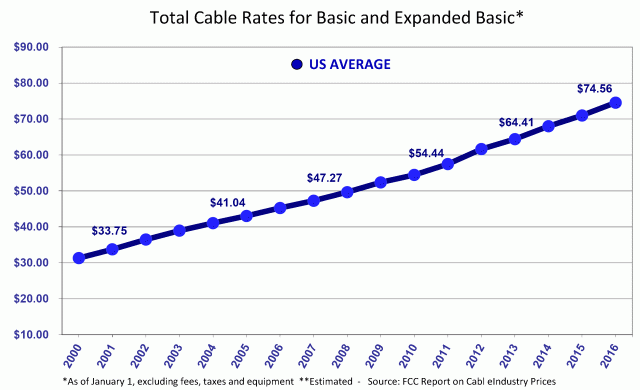
The day the 500 channel cable package model falls apart may not be too far off. The cost of programming at Discovery’s cable networks, other than sports, has grown 55% from 2013 to 2016, according to projections from researcher MoffettNathanson.
Discovery is using the money to push aside some of its near-endless reality TV fare for scripted programming, developing 10 shows with Lions Gate Entertainment. Viacom, another major cable programmer, saw expenses rise more than 25%, in part to create a new night of programming on VH1, doubling animation at Nickelodeon, and budgeting for more special events programming on BET. Some smaller cable operators were not impressed with the asking price and dropped all of Viacom’s networks from their cable systems.
 Starz, dwarfed by HBO and Showtime, is spending $250 million on its own original programming including Outlander, Survivor’s Remorse and Power. Subscribers who want more will get it as Starz increases budgets enough to allow producers to create 80-90 original episodes this year, up from 75 in 2015. To introduce subscribers to the shows, Starz commonly offers cable subscribers free trials as part of ongoing cable company promotions.
Starz, dwarfed by HBO and Showtime, is spending $250 million on its own original programming including Outlander, Survivor’s Remorse and Power. Subscribers who want more will get it as Starz increases budgets enough to allow producers to create 80-90 original episodes this year, up from 75 in 2015. To introduce subscribers to the shows, Starz commonly offers cable subscribers free trials as part of ongoing cable company promotions.
If you run an entertainment studio, are employed in the entertainment field, or can act, these are good times. In fact, demand for scripted shows may be outpacing the capacity of studios to produce them.
John Landgraf, CEO of Fox’s FX Networks, asserted there’s “too much TV,” noting over 400 scripted shows were filmed last year.
Until the late 1980s, most of the demand for scripted shows came from NBC, CBS, ABC, and the then-new FOX, because they were the only ones with enough money to afford the high production costs. Today, cable subscribers foot the bill for most cable network original shows, causing cable rates to spiral. With Netflix ready to spend at least $11 billion on programming over the next five years, the days of rate hikes are far from over.


 Subscribe
Subscribe As Discovery Communications completes its $11.9 billion acquisition of Scripps Networks Interactive Inc., the newly supersized basic cable network powerhouse will lay the foundation to launch
As Discovery Communications completes its $11.9 billion acquisition of Scripps Networks Interactive Inc., the newly supersized basic cable network powerhouse will lay the foundation to launch  In order to drive subscriptions, Discovery’s streaming service is expected to be budget priced and include a large library of on-demand content, possibly including programming from other networks not owned by Discovery down the road.
In order to drive subscriptions, Discovery’s streaming service is expected to be budget priced and include a large library of on-demand content, possibly including programming from other networks not owned by Discovery down the road.
 Years of broadcast and cable networks relying on cheap reality TV fare, game shows, and lurid news magazines to save money are coming to an end as media companies realize the only way to stop the viewing shift to Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon is to create better programming viewers want to see.
Years of broadcast and cable networks relying on cheap reality TV fare, game shows, and lurid news magazines to save money are coming to an end as media companies realize the only way to stop the viewing shift to Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon is to create better programming viewers want to see. Bloomberg News
Bloomberg News  Some Wall Street analysts like Rich Greenfield at BTIG Research have gone as far as predicting the traditional cable TV bundle is threatened with extinction as cost conscious viewers continue to abandon linear/live television for on-demand content like that offered by Netflix instead. That has delivered a three-way punch: pressures on revenue as program creation spending increases, growing cord-cutting, and cable rate inflation cable executives are increasingly desperate to control.
Some Wall Street analysts like Rich Greenfield at BTIG Research have gone as far as predicting the traditional cable TV bundle is threatened with extinction as cost conscious viewers continue to abandon linear/live television for on-demand content like that offered by Netflix instead. That has delivered a three-way punch: pressures on revenue as program creation spending increases, growing cord-cutting, and cable rate inflation cable executives are increasingly desperate to control. Starz, dwarfed by HBO and Showtime, is spending $250 million on its own original programming including Outlander, Survivor’s Remorse and Power. Subscribers who want more will get it as Starz increases budgets enough to allow producers to create 80-90 original episodes this year, up from 75 in 2015. To introduce subscribers to the shows, Starz commonly offers cable subscribers free trials as part of ongoing cable company promotions.
Starz, dwarfed by HBO and Showtime, is spending $250 million on its own original programming including Outlander, Survivor’s Remorse and Power. Subscribers who want more will get it as Starz increases budgets enough to allow producers to create 80-90 original episodes this year, up from 75 in 2015. To introduce subscribers to the shows, Starz commonly offers cable subscribers free trials as part of ongoing cable company promotions.
 Since Malone sold TCI, the multi-billionaire has built a significant cable empire in Europe and is today the largest private landowner in the United States. In the U.S., he is best known as the current owner of SiriusXM satellite radio. The two satellite companies merged with an agreement not to raise rates for a few years. As soon as that agreement expired, Malone’s combined Sirius/XM operation began a series of rate hikes and maintain a satellite radio monopoly in the U.S.
Since Malone sold TCI, the multi-billionaire has built a significant cable empire in Europe and is today the largest private landowner in the United States. In the U.S., he is best known as the current owner of SiriusXM satellite radio. The two satellite companies merged with an agreement not to raise rates for a few years. As soon as that agreement expired, Malone’s combined Sirius/XM operation began a series of rate hikes and maintain a satellite radio monopoly in the U.S.