 Although Spectrum Cable customers will face higher cable TV bills starting next month, the company’s shareholders are delighted, boosting Charter’s stock price more than $50 a share on the news.
Although Spectrum Cable customers will face higher cable TV bills starting next month, the company’s shareholders are delighted, boosting Charter’s stock price more than $50 a share on the news.
Spectrum’s latest increase (the second in four months) of its Broadcast TV Surcharge will set a uniform national fee of $11.99 a month for all of its cable television customers.
In 2018, customers paid an average of $8.75 a month in local TV surcharges. But last November, Charter raised the surcharge to $9.95 a month. Now, just a few months into 2019, Spectrum wants another $2 a month — a 20% increase — to watch local television signals that are available for free to those with an antenna. That’s a steep increase for what began as a $2 surcharge for some customers starting in 2015.
Charter’s investors reacted positively to the latest rate hike, jumping the stock price from $289.91 a share to $340.95 — a $51.04 boost after the fee increase was first reported by the Los Angeles Times.
The new surcharge will be reflected on customer bills beginning as early as Feb. 21.
Charter blamed broadcasters for the “rapidly rising cost” of including local TV stations on the cable lineup. In a letter to some state telecommunications regulators, the cable operator claimed it would be inefficient to not raise prices.
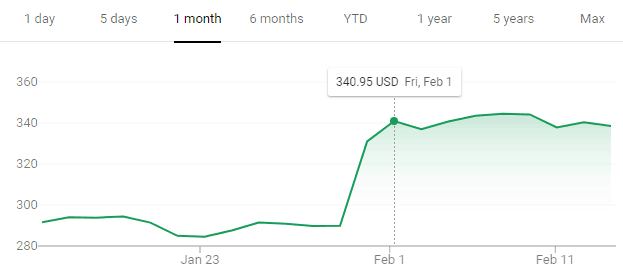
Charter’s share price shot up on the news it was increasing its Broadcast TV Surcharge by 20% just four months after the last increase.
“Containing costs and efficiently managing our operations are critical to providing customers with the best value possible,” wrote Melinda Kinney, Charter’s senior director of government affairs for Charter’s Northeast Division. “Like every business, Charter faces rising costs that require occasional price adjustments.”
But many customers, especially those in marginal reception areas, are loudly complaining that Charter is raising its Broadcast TV Fee even as it drops regional over the air stations from its cable lineup. In 2017, Spectrum customers in western Massachusetts reported a gradual exodus of local TV stations from their lineup, starting with WWLP, the NBC affiliate in Springfield with strong local news coverage of the western half of the state. Today, Spectrum only provides western Massachusetts with a single NBC station — WNYT in Albany, N.Y., which keeps viewers up to date with the latest political machinations of the New York State legislature.
Next to go was Boston’s ABC affiliate, WCVB — airing the strongest coverage of local and state news of any ABC affiliate in the state. In its place, viewers now receive WTEN, the ABC station in Albany, which is covering Sen. Jim Tedisco’s support for splitting New York into two separate states — a ‘crucial’ issue for subscribers living in the Berkshires and beyond.
Other states facing “out of market” channel losses include Connecticut, California, Nevada, and Nebraska. Many of the affected stations were dropped as Charter upgraded its cable systems to all-digital television, perhaps counting on subscriber confusion amidst other changes to the cable system.

Barrett on Charter: “Greed”
The loss of local stations while rapidly increasing the surcharge for those stations has some people calling foul.
Massachusetts State Rep. John Barrett III (D-North Adams) called it “greed.” Charter mandates the Broadcast TV Fee be paid by all video customers, including those on “price locked” promotions. By breaking the fee out of the cost of the cable television package, Charter Spectrum gets to advertise packages to new and returning customers at a low cost, only to deliver bill shock when customers discover the surcharge, along with equipment and franchise fees, that collectively increases their total monthly bill.
As the second largest cable company in the country, Charter is estimated to be collecting an extra $211 million annually from its first increase in November 2018 and $391 million annually from the latest increase now taking effect. Together, that amounts to $602 million annually in new revenue starting in March. Charter will not disclose exactly how much of this money is paid to each local television station.
Charter also has a habit of boosting its set-top box equipment fees about $1 a month per box each year — an increase we are likely to see later this year, and the company already slightly increased prices for internet service late last year.
Charter executives told shareholders on its most recent quarterly results conference call that the company’s revenue increased 4.9% in 2018 to $43.6 billion. Combining that extra revenue with a $1.9 billion cut in upgrades for 2019 will allow the company to focus on additional share buybacks, increased payouts to Charter shareholders, and debt reduction.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 It will take until 2019 to fully integrate all of Charter’s customers onto a single platform that will no longer distinguish if a customer was a long-standing Charter customer or a former TWC or BH subscriber.
It will take until 2019 to fully integrate all of Charter’s customers onto a single platform that will no longer distinguish if a customer was a long-standing Charter customer or a former TWC or BH subscriber. Charter did not restart its digital television conversion program until June of 2017, and 30% of Time Warner Cable and 50% of Bright House Networks customers are still watching analog cable television as a result. Company officials promise digital conversion will be completed nationwide by the end of this year, the first step the company will take to make dramatic broadband speed increases possible.
Charter did not restart its digital television conversion program until June of 2017, and 30% of Time Warner Cable and 50% of Bright House Networks customers are still watching analog cable television as a result. Company officials promise digital conversion will be completed nationwide by the end of this year, the first step the company will take to make dramatic broadband speed increases possible.



 Some believed this problem could eventually resolve itself with Charter Communications’ buyout of Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks. Would Charter bring their own policies to affected TWC/BH customers, or will Charter customers soon have to contend with the CCI CopyOnce flag loved by Time Warner Cable as well.
Some believed this problem could eventually resolve itself with Charter Communications’ buyout of Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks. Would Charter bring their own policies to affected TWC/BH customers, or will Charter customers soon have to contend with the CCI CopyOnce flag loved by Time Warner Cable as well.
 If you cut the cord and are watching all of your HD programming over-the-air, we have some bad news. Your current television set will soon be obsolete.
If you cut the cord and are watching all of your HD programming over-the-air, we have some bad news. Your current television set will soon be obsolete. To avoid a firestorm from the public, some station owners are thinking about a stop-gap measure that would launch a “digital bouquet” of participating local stations using lower bit rate Standard Definition on a single legacy ATSC 1.0 transmitter for at least a year or two until consumers upgrade their existing equipment. Then, one by one, existing HD stations would switch to ATSC 3.0 and effectively disappear from the dial of sets made before 2016. The good news is you would still have access to free television. The bad news is the picture will be significantly degraded.
To avoid a firestorm from the public, some station owners are thinking about a stop-gap measure that would launch a “digital bouquet” of participating local stations using lower bit rate Standard Definition on a single legacy ATSC 1.0 transmitter for at least a year or two until consumers upgrade their existing equipment. Then, one by one, existing HD stations would switch to ATSC 3.0 and effectively disappear from the dial of sets made before 2016. The good news is you would still have access to free television. The bad news is the picture will be significantly degraded.