A new report published by the Federal Communications Commission this week finds Americans are being ripped off by their broadband providers who promise speeds 50 percent faster than they actually receive.
A new report published by the Federal Communications Commission this week finds Americans are being ripped off by their broadband providers who promise speeds 50 percent faster than they actually receive.
In a generically named report, “Broadband Performance,” the FCC finds Americans love spending increasing amounts of time on the Internet, but face providers making bogus marketing claims for speeds they’ll never actually receive.
In 2009, average […] advertised download speeds were 7–8 Mbps, across technologies. However, FCC analysis shows that the median actual speed consumers experienced in the first half of 2009 was roughly 3 Mbps, while the average (mean) actual speed was approximately 4 Mbps. Therefore actual download speeds experienced by U.S. consumers appear to lag advertised speeds by roughly 50%.[…] The “up to” speed, however, does not provide an accurate measure of likely end-user broadband experience. That experience depends on multiple factors, including the actual speed that consumers realize, taking into account the impact of network congestion; and other metrics like the availability of the network, latency, jitter and packet loss. In other words, consumers need a better, publicly agreed upon measure of broadband performance that reflects the network operation and end-user experience.
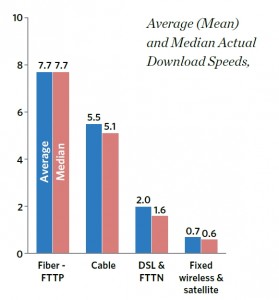
No surprises here - the FCC found fiber delivered the fastest broadband speeds with wireless and satellite service delivering the slowest
Providers in several countries have been called to account for marketing claims that never seem to be realized by customers.
For years, providers have relied on the weasel words “up to” to escape charges of outright misrepresentation of their products. The FCC doesn’t believe the status quo properly informs consumers about true broadband speeds, especially when comparison shopping.
Some of the widest gaps between advertised and actually delivered speeds came from telephone company DSL service. Many phone companies define their maximum speeds based on theoretical maximums, not the actual average speeds encountered by customers. While some providers claimed up to 10Mbps service, they only actually delivered up to 3Mbps to many customers.
The report recommends new disclosures, including average actual speeds delivered to customers, what kind of speeds customers can expect during peak usage times, and what speeds consumers will encounter while using certain online applications.
Speeds can make all the difference for certain classes of broadband users, also defined in the FCC report:
➤ Advanced. These consumers use large amounts of data and tend to use the highest quality voice, video, and other cutting-edge applications.
➤ Full media. These consumers are moderately heavy users of broadband and mobile applications, seeking to access high-quality voice, data, graphics, and video communications but, typically not in the most cutting-edge forms.
➤ Emerging multimedia. These consumers utilize some video and graphical content but still see the Internet primarily as a way to communicate and access news and entertainment in a richer format than found in offline content.
➤ Utility. These consumers are largely content to access the Internet for basic news, communication, and basic entertainment.
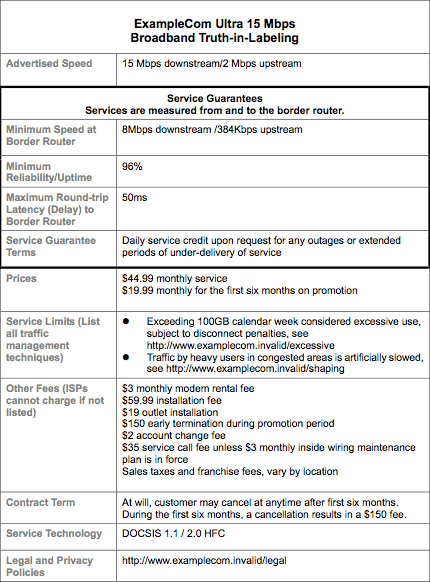
The New America Foundation thinks the gulf between promises and reality has grown so large, it’s time to bring “The Schumer Box” to broadband. Named after Sen. Chuck Schumer (D-NY), the “Schumer Box” was made a part of every credit card application and cardholder agreement. It breaks out in large print fact-based disclosures to consumers about what kind of service and pricing to expect. The Foundation wants consumers to have truth-in-labeling introduced for Internet users who will be able to comparison shop providers more effectively.
While the FCC’s findings may not reach the level of credit card-style disclosures, the agency does recognize there is a significant problem with providers misrepresenting their broadband speeds.
The report also found consumers are increasing their amount of monthly usage, often correlated to the speeds they receive. Those with the fastest broadband accounts consume the most (and typically also pay the most for service). Those with slower speeds consume less.
That finding supports the contention among many consumer groups that today’s speed-based broadband tiers fairly compensate providers for customer usage. Those who use the most pay the most for the fastest speeds. Those who use the least pay lower prices for lower speed tiers.
The agency also rated fiber to the home America’s fastest broadband technology, followed by cable broadband, then DSL service, and finally wireless/satellite-delivered service.


 Subscribe
Subscribe