 West Virginia continues to be broadband challenged, with or without the help of Frontier Communications’ DSL service, which continues to be criticized for being woefully “oversold.”
West Virginia continues to be broadband challenged, with or without the help of Frontier Communications’ DSL service, which continues to be criticized for being woefully “oversold.”
Now some of Frontier’s most frustrated customers have found Facebook, and hope to encourage the company to deliver better speeds through their Fix Frontier DSL Now page.
Customers are especially peeved in areas where they are sold “up to 12Mbps” service, but cannot break 1Mbps during peak usage times when inadequate infrastructure cannot support customer usage demands. Some are taking their complaints to the West Virginia Public Service Commission:
I am a long-time subscriber to Frontier Communications’ “High-speed Internet Max” DSL service. I live in the Frankford, West Virginia, telephone exchange (304-497-XXXX), which is an area that has always been served by Frontier. We never had Verizon service at my home.
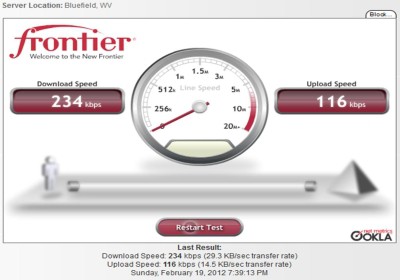
When Frontier installed DSL service in our area, we immediately cancelled our satellite Internet service and signed up. Initially, we had business-class DSL which was very satisfactory. Later, we discontinued our business operation and downgraded to the residential “High-Speed Internet Max” DSL service. That remained quite satisfactory until about a year and a half ago, when service quality deteriorated to the point of being unusable.
During the evening hours, we generally log download speeds of anywhere from 150kbps (0.15MBPS) to 450kbps (0.45MBPS) , with around 300kbps (0.3MBPS) being the norm. This is barely adequate for accessing a static web page, and is totally inadequate for common tasks such as watching a video on YouTube or even streaming music. Speeds do improve, sometimes into the range of 1500kbps (1.5MBPS), in the middle of the night and the afternoons, when we are generally asleep or at work, but are consistently unusable during the evening hours when we are home.
Customers pay around $40 a month for this level of broadband service, and customers calling for assistance are being told to wait:
I have called Frontier’s tech support and opened numerous trouble tickets. Each time, a technician will come out to our house, test the line, pronounce it “perfect” from the house to the switching station, then explain that the problem is lack of bandwidth. Sometimes they say the bottleneck is in Bluefield. Sometimes they say it is between Marlinton and Ashburn, Virginia. In other words, Frontier does not have enough bandwidth available to meet customer needs.
The last time we put in a trouble ticket, the technician didn’t even come to our home. He just called and said he would put the ticket on the stack with all of the other ones, and perhaps the problem would be solved in a couple of years. A couple of years? Yet, I am constantly bombarded with ads asking me to buy Frontier’s high-speed DSL service at rates as low as half of what I pay.
As Stop the Cap! has reported previously, Frontier has acknowledged the problems in West Virginia and promised backbone upgrades to handle the influx of new customers, particularly those adopted from Verizon Communications in 2010 when the company purchased their landline network in the state. But a schedule of promised upgrades disappeared off Frontier’s website, and according to our readers, continues to be overdue.
The loudest complainers are offered $5 monthly service credits for their troubles, but customers don’t want the money, they want something that actually qualifies as “broadband service.”
Here is how you can tell where your problem might be:
Technical Line Fault Symptoms (these can be corrected by a local technician’s service call to your home)
- Consistently low speeds that do not vary much with time of day or on weekends;
- Weather-related service interruptions or slowdowns – poor quality cables, fittings, and other problems are often most visible during the wet spring months;
- Loud hum or static on your voice line when making or receiving calls;
- Hearing conversations from other customers on your phone line;
Oversold Broadband (these problems require Frontier to regionally address problems that affect a much larger group of customers)
- Dramatically reduced speeds during evenings and weekends that consistently speed up later at night or during the workday;
- Similar speed-related issues affecting friends and neighbors in the same neighborhood or community;
- Pages that do not load completely, time out, or require refreshing to load properly;
- “Tracert” reports that indicate certain upstream connections Frontier uses to connect to its national network are timing out or require multiple attempts to get through.


 Subscribe
Subscribe






