For the past two years, we’ve watched a lot of expansive fiber broadband projects get promoted by local media as broadband nirvana for individual homes and businesses that are either stuck with molasses-slow DSL or no broadband at all. Now, we’ve found another, sold by Springfield, Mass. media as salvation from Verizon’s ‘Don’t Care’ DSL for western Massachusetts. But will the 1,300 miles of fiber actually reach the homes that need a broadband boost?
For the past two years, we’ve watched a lot of expansive fiber broadband projects get promoted by local media as broadband nirvana for individual homes and businesses that are either stuck with molasses-slow DSL or no broadband at all. Now, we’ve found another, sold by Springfield, Mass. media as salvation from Verizon’s ‘Don’t Care’ DSL for western Massachusetts. But will the 1,300 miles of fiber actually reach the homes that need a broadband boost?
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/WSHM Springfield Broadband in Berkshires 7-26-11.mp4[/flv]
WSHM-TV in Springfield covered the start of MassBroadband 123’s fiber optic project as the solution to rural broadband woes in western Massachusetts. But most residents won’t actually get to use the new network, at least initially. (2 minutes)
Last month, Gov. Duval Patrick joined public officials and firefighters at the Sandisfield Fire Department to kick-off construction of the MassBroadband 123 fiber-optic network project to expand broadband access to more than 120 communities in western and north central Massachusetts.
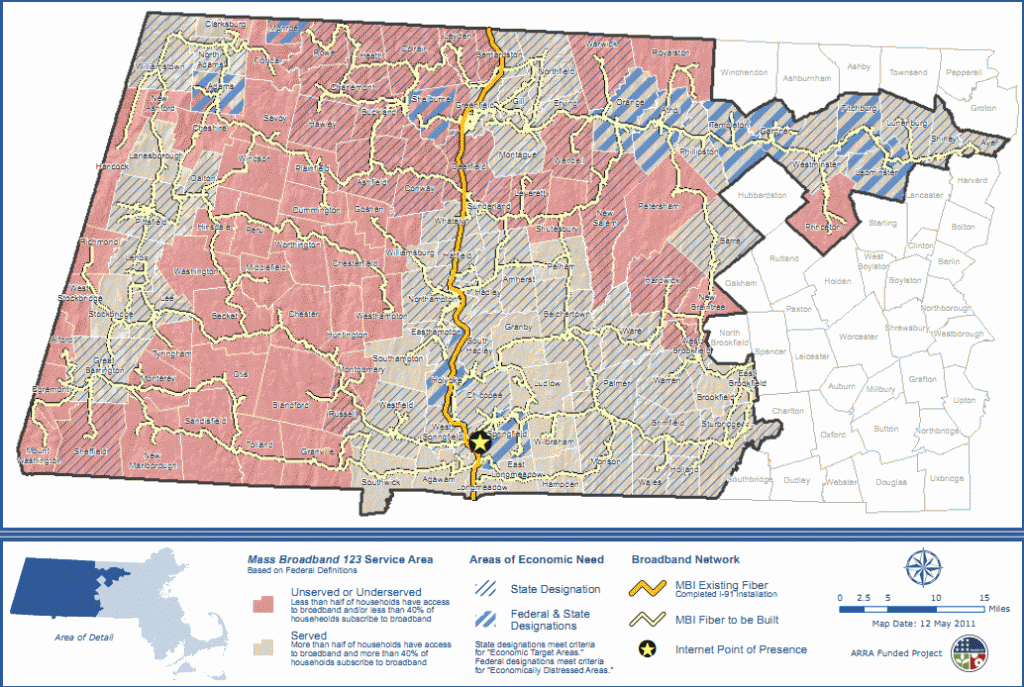
MassBroadband 123 Service Area (click to enlarge)
“For too long, families and businesses in western Massachusetts have lived without reliable and affordable high-speed Internet access,” said Governor Patrick. “Today, as we commence the installation of more than 1,000 miles of fiber-optic cable across the region, we start the critical final step in delivering broadband access to everyone. The digital divide in Massachusetts is about to close.”
Don’t hold your breath.
Don’t get me wrong. The Massachusetts Broadband Institute means well. Judith Dumont, the group’s director, is well-aware of the challenges rural Massachusetts has getting 21st century broadband. She’s helping to oversee the construction of an enormous middle-mile, fiber backbone network that will eventually reach those ten dozen communities. But much of the funding for the project precludes the possibility of directly wiring that fiber to the people who actually need it. The incumbent providers’ lobbyists have seen to that, broadly warning it would represent ISP Socialism to allow government money to deliver service to homes and businesses — customers they themselves claim to be committed to serve. But ask any resident in Sandisfield how well they manage that.

Gov. Patrick splices fiber cable at inauguration ceremony for fiber expansion project. (Courtesy: MBI)
A good part of upgraded broadband on the way in the Berkshires will be provided to government institutions like local government, public safety, schools, and libraries. There is nothing wrong with that either, but when local media blurs this distinction into belief fiber-fast Internet access is on the way to Mr. & Mrs. Jones living on Maple Street, they do a real disservice to the cause for better broadband.
Dumont optimistically believes that opening the state’s fiber network to incumbent providers on a wholesale basis will dramatically help the pervasive problem of reaching rural customers. Unfortunately, this has simply not been our observed experience watching these projects develop. The “last mile” problem doesn’t get solved with the existence of a middle mile network, because providers are rarely willing to invest in the construction costs to wire the unwired. Political and business matters too often get in the way.
Cable companies frequently boycott participation in these networks, and phone companies like Verizon Wireless -may- utilize them for backhaul connectivity to their cell towers, but don’t expect to see lightning-fast Verizon FiOS fiber to the home service springing up anytime soon in western Massachusetts, even if fiber connectivity is provided just a mile or so up the street. If they didn’t build it themselves, many providers just are not interested.
“Last mile” is often the most expensive component in a broadband network. It’s the part of the project that requires digging up streets and yards, stringing cables across phone poles, and literally wiring the inside and outside of individual homes and businesses. Verizon FiOS works in densely populated areas where large numbers of potential customers are likely to deliver a quick return on investment in the network. But Wall Street has always disagreed, declaring the capital costs too high to make sense. AT&T won’t even match Verizon’s commitment, relying instead on fiber-to-the-neighborhood networks that deliver access over a more modern type of DSL, delivered on fiber to copper wire phone lines already in place. That’s their way of not spending money rebuilding their own last mile network.

Wireless ISPs are expected to take advantage of the state's new middle-mile network.
If any part of the broadband network in rural America needed subsidies, the “last mile” is it. But Washington routinely delivers the bulk of federal assistance to the construction of middle mile networks and institutional broadband that doesn’t deliver a single connection to a homeowner or business. That suits incumbent providers just fine, judging from their lack of interest in applying for broadband subsidy funding made available two years ago and their hard lobbying against community broadband networks, or anything else smacking of “competition.”
Thus far, the limited grants that are available for “last mile” projects require substantial matching funds and are often limited to $50,000 — a ridiculously low amount to solve the “last mile” challenge. Those trying are primarily fixed wireless providers valiantly attempting to serve the areas DSL and cable forgot, but deliver woefully slow speeds at incredibly high prices. WiSpring, one such Wireless ISP, wants to expand coverage with the help of the new fiber network. But their top advertised wireless speed for residential customers is 1.5Mbps, and that will set you back $100 a month after a $500 installation charge. Oh, and their customer agreement limits use to 25GB per month with a $10/GB overlimit fee. That’s hardly the kind of broadband solution a multi-million dollar fiber network should bring to individual consumers. It’s as frustrating as filling a pool, one cup of water at a time, with an eye-dropper.
Now imagine if a quarter of the state’s $40 million investment in broadband — $10 million, was spent physically wiring individual homes with fiber broadband. Would that make a bigger splash in the lives of ordinary consumers than a middle mile network they cannot directly access? Is construction of a state-of-the-art fiber network a good investment when many of the providers scheduled to use it are Wireless ISPs delivering bandwidth suitable for e-mail and basic web browsing only?
In West Virginia, we learned last month the state is swimming in middle mile stimulus grant money it can’t spend fast enough on behalf of institutions — many who either already have super fast service or can’t afford the Cadillac pricing that represents the ongoing service charges not paid for by grant funds. Is this a good way to spend tax dollars?
Communities large and small need to think big when it comes to broadband. Building a middle mile network does not by itself solve the access problem. It’s a fine start, but absolutely requires a follow-up commitment to solve the last mile problem. Here are our recommendations:
- Demand the federal government eliminate restrictions on the kinds of network projects that can built with stimulus funds, especially those that prohibit investment in last-mile networks;
- Don’t believe for a moment large cable and telephone companies will bring better broadband to consumers just because you have a middle mile network. Historically, they have lobbied hard against last-mile projects they do not own or control, and fund conservative political groups to oppose your community’s right to develop and govern your own broadband future;
- If incumbent providers won’t provide the service your community needs, consider exploring the possibility of doing it yourself. Just as MBI contracts the wholesale part of its service out to a third party to administer, nobody says the village clerk has to be a billing agent for a community broadband service that directly serves your residents;
- Involve local citizens in rallying for better broadband instead of sitting around and waiting for the local phone or cable company to provide it. They won’t. It’s a simple matter of economics for them – will they get a sufficient return on their investment within five years? If not, you are not getting improved broadband. That works for them but doesn’t work for your community, and providers have made it clear most of the networks they intend to build are already built. That leaves a lot of communities behind.
- While wireless may be an answer for the most rural or difficult-to-reach homes, it is not a realistic solution for 21st century broadband inside village or town limits. Wireless networks often lack the capacity to sustain the growing demand for multimedia, high-bandwidth content that is becoming more important for today’s online experience. When a provider limits usage to 25GB a month, that’s a big problem for any community that will soon find itself stuck in a broadband swamp while the rest of the country passes it by.
- The biggest financial challenges seem to come to those who think small about broadband projects. Don’t rely on yesterday’s technologies for tomorrow’s networks. Fiber-based broadband will deliver the best bang for the buck and is infinitely upgradable. That’s why rural phone companies and cooperative telecom providers are constructing fiber networks themselves.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/WGBY Springfield The State Were In Judith Dumont 7-11.mp4[/flv]
WGBY-TV in Springfield talked with Judith Dumont about western Massachusetts’ broadband future. (19 minutes)
 One of the conditions Comcast had to agree to as part of its multi-billion dollar deal to acquire NBC-Universal was to throw a bone to some of America’s poorest households by offering discount Internet access for three years. Comcast agreed and is rolling out low-speed Internet at a discount in time for the upcoming school year.
One of the conditions Comcast had to agree to as part of its multi-billion dollar deal to acquire NBC-Universal was to throw a bone to some of America’s poorest households by offering discount Internet access for three years. Comcast agreed and is rolling out low-speed Internet at a discount in time for the upcoming school year. If you have been late on a Comcast bill, or owe the company for unreturned cable equipment, you also cannot receive the service.
If you have been late on a Comcast bill, or owe the company for unreturned cable equipment, you also cannot receive the service.

 Subscribe
Subscribe