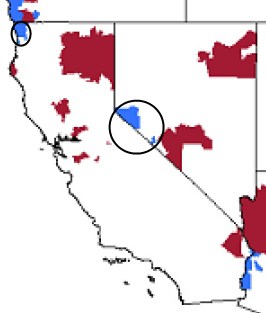
Frontier Communications has won approval from state utility commissions in California, South Carolina, and Nevada to take over telephone service currently provided by Verizon Communications. The decisions were unanimous in all three votes by Commission members, and involve telephone service in several small communities in all three states.
Verizon’s castoffs serve a small percentage of customers, which made the transaction fly under the media radar in most cases. In California, Verizon dumps customers in a small section on the northwest border with Oregon. In Nevada, several small communities south of Reno are involved. In South Carolina, Verizon drops scattered groups of customers in small clusters across the state.
These state regulatory approvals follow an October 27 announcement by Frontier that its shareholders have approved the transaction, which will result in Frontier owning Verizon’s wireline operations in all or parts of 14 states.
While the approval appeared pro forma in those three states, West Virginia is another matter. Strong employee union and consumer group protests continue across the state, with many consumers concerned about the implications of Frontier controlling nearly all wired phone lines in the state. The Communications Workers of America held a conference call with the media Wednesday to outline its opposition to the deal.
The CWA has been a vocal opponent of the deal, claiming it will risk West Virginia’s telecommunications future with a company without the financial capacity to provide the type of advanced services Verizon is providing in other states. Kenneth Peres, an economist with the Communications Workers of America, said the deal was extremely risky for consumers, workers and the affected communities.
Peres pointed to the perfect record of three out of three failures for earlier Verizon spinoffs. FairPoint Communications declared bankruptcy early this week after trying to take on the service needs of three New England states.
Peres told the Charleston Daily Mail that if the deal goes through, Frontier “will find it extremely difficult” to meet its $8 billion in debt obligations while simultaneously investing enough capital to maintain its physical plant, improve service quality, set up a new system in West Virginia, lease systems from Verizon in 13 other states, provide video service for the first time (in Indiana), and ensure adequate staffing “while paying out a lot more in dividends than it makes in profits.”
Frontier went on the attack Thursday, accusing the union of interfering just to grab concessions for itself.
Steve Crosby, Frontier spokesman, said, “They’re just throwing stuff up against the wall. They know this is a good transaction and they’re trying to extract their pound of flesh. They want more concessions. This is their opportunity to ask for more money for their union membership and more benefits. That’s what they want. Union membership across the country is declining. This is how they’re trying to extract as much as they can from either Frontier or Verizon.”
As for Frontier’s debt load, “This is actually a de-leveraging transaction,” Crosby said. “We’re taking on debt but we’re taking on a whole lot more revenue. We’re currently at a 3.8 times revenue-to-debt ratio, going down to 2.6. So we actually get better in terms of revenue to debt. And today we’re fine. We’re able to pay a nice dividend. The day the transaction closes, we are approaching investment-grade borrowings.
“Our board of directors made the decision to lower our dividend by 25 percent when the transaction closes to give us even more cash to invest in infrastructure and to give us even more financial flexibility,” Crosby said.
“Every time we have an argument we win and they bring up other stuff,” Crosby said. “They never bring up the de-leveraging because it undermines their argument. They never bring up the fact that we will reduce our dividend because it undermines their argument.
“We have said we will maintain employment levels for 18 months” after the transaction closes, Crosby said. Because of required regulatory approvals and other factors, the deal can’t close before April 2010.
“So you can figure that’s two years,” Crosby said. “Who nowadays has that kind of job security? I think we’re bending over backwards. I wish I had the pension plan, the job security the CWA has. They’re looking at extracting more from Verizon and Frontier.”
When asked by the newspaper why Frontier shareholders would approve a deal that was destined for failure, Peres told the newspaper:
Frontier’s business model is built on acquisitions. Frontier bought a portion of Global Crossing’s business which increased revenue and access lines “but that began to decline,” he said. “They bought Commonwealth Telephone but that’s flat-lining. What’s the next step? What were they going to do – improve infrastructure or go through the acquisitions route again?” Continuing with acquisitions “postpones the day of reckoning,” he said.
Commentary: Our Take
Crosby’s comments seem more suited for a talk show audience that hates unions. Obviously the union does not think this is a good deal for West Virginia, and considering the track record of earlier Verizon deals, and the correct predictions from employee unions on their inevitable outcomes, they have every right to oppose the deal on its face. Crosby apparently has time to address declining union membership, but not the much more relevant decline in the traditional phone company’s bread and butter business – landlines. Frontier, like other phone companies, continues to see disconnect requests coming from coast to coast as customers dump the phone company for a cable digital phone product, Voice Over IP line, or rely on their cellphone.
Verizon recognizes their traditional business is a dying one, which is why they are in a hurry to diversify into competitive broadband and video services over their fiber optic FiOS network. Where it doesn’t make economic sense (under their current business plan) for Verizon to deploy FiOS, decisions are being made about whether to keep those smaller phone operations within the Verizon family, or sell them off to companies like Frontier. What Frontier acquires today from the standpoint of customers and revenues could represent the high water mark, and without offering robust options for a digital future, Frontier will likely continue to see customer erosion.
FairPoint acquired seemingly healthy Verizon companies serving the entire states of Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont. When their efforts to seamlessly combine Verizon’s legacy systems with FairPoint’s own systems failed, that along with an inability to properly service customers, caused a death spiral as customers dropped service, which led FairPoint straight into bankruptcy.
Frontier’s record of investment and service in western New York speaks for itself. Time Warner Cable eats Frontier for lunch, with less expensive “digital phone” service, much faster and more reliable broadband, and a video package that Frontier doesn’t offer (reselling DISH Network is hardly the same as providing video service that doesn’t come from a third party company’s satellite dish nailed to the roof). Frontier is ready and willing to stick with DSL service at speeds that are basically maxed out. Time Warner Cable evidently doesn’t even consider Frontier a significant enough player to deploy upgrades in this area while they are in a hurry to provide them where Verizon FiOS is under construction.
When a company isn’t prepared to keep up with the rest of New York with fiber deployment to the home, the chances of that kind of service reaching West Virginia anytime soon are near zero.
But Frontier’s unique position as a specialist in “rural service” allows it to eke out an existence in areas where cable isn’t a big competitive threat, and where any broadband is better than no broadband at all, at least for now. But without a plan for keeping up with the fast changing broadband world, customers happy with 3Mbps service today will despise the company for being stuck with those speeds later. A lot of people in Rochester sure aren’t happy being stuck with Frontier DSL, and that nasty 5GB “reasonable use” language in the Acceptable Use Policy.
Crosby’s comments about CWA member job security, which he evidently envies, says more about the union’s commitment to its members than Frontier has to him. Perhaps Crosby can quit his spokesman job and switch to a position that gets him CWA membership with a pension and job security. Perhaps if the people of West Virginia say thanks, but no thanks, Frontier will be in a better economic state than it would be if this mega-deal collapses under the weight of debt and integration challenges. Then Crosby can keep his job with the evidently lousy benefits.
Peres’ assumption that Frontier lives only through acquisitions isn’t the complete story. Just like the myth sharks must constantly swim to survive, Frontier doesn’t constantly have to acquire to survive either. It does have to concern itself with an ever-consolidating telephone line industry, where the smaller independent companies continue to be snapped up by a dwindling number of players. If a Windstream or CenturyTel comes along with a great offer, Frontier itself may have a new name — Windstream or CenturyTel.
The economies of scale and cost savings are routinely cited by investors promoting consolidation. It’s no surprise Frontier shareholders voted for the deal. Bigger is often better for many investors, as long as the quarterly financials play to their interests. Listening to Frontier investor conference calls, the Wall Street bankers, and the media that support them, are constantly concerned with keeping costs cut to the bone, customer defection limited, risk reasonable, and that dividend being paid. They are satisfied with Frontier’s rural, less competitive market focus, even if the customers that end up served by them are not.


 Subscribe
Subscribe