
Bait and switch broadband
Since 1991, Verizon telephone customers in New Jersey have paid at least $15 billion in surcharges for a promised high-speed broadband network that would reach every home in the state by 2010. But now critics charge Verizon diverted much of that money to shareholder dividend payouts and building infrastructure for its highly profitable wireless network, leaving almost half the state with slow speed DSL or no broadband at all.
In the early 1990s, Verizon’s predecessor — Bell Atlantic — launched “Opportunity New Jersey,” a plan promising the state it would have the first 100% fiber telecommunications network in the country. In return, the company enjoyed more than two decades of generous tax breaks and collected various surcharges from customers to finance network construction. But a review of Verizon’s promises vs. reality suggest the company has reneged on the deal it signed with the state back when Bill Clinton was beginning his first term as president.
Verizon promised at least 75 percent of New Jersey would have a fiber service by 1996 offering 384 television channels and 45/45Mbps broadband service for $40 a month. The network would be open to competitors and be deployed without regard to income or its potential customer base.
The state suspected trouble as far back as 1997, when the Division of the Ratepayer Advocate with the New Jersey Board of Regulatory Commissioners blasted the company’s progress five years into the project:
Bell Atlantic-New Jersey (BA-NJ) has over-earned, underspent and inequitably deployed advanced telecommunications technology to business customers, while largely neglecting schools and libraries, low-income and residential ratepayers and consumers in Urban Enterprise Zones as well as urban and rural areas.

By 2006, New Jersey was being introduced to FiOS, which some believed was part of Verizon’s commitment to the state. But a decade after Verizon’s target dates, customers were still waiting for FiOS video service, the maximum broadband speeds offered at that point were 30/5Mbps and the cost of the package ranged from $180-200 a month. Most of Verizon’s FiOS deployments were in the northern half of the state, leaving southern New Jersey with few, if any service improvements.
Despite Verizon’s repeated failures to meet its target dates, that same year New Jersey made life even easier for the phone company by passing a statewide video franchise law allowing Verizon to bypass negotiating with each town and city regarding its video services and instead run FiOS TV as it pleases anywhere in the state. The company argued a statewide video franchise would allow for more rapid deployment of Verizon’s fiber network. In reality, the company was falling further and further behind. By 2013, when Verizon sought renewal of its statewide franchise, Verizon only offered FiOS TV to 352 of the 526 communities hoping for service. At least 174 communities still waiting for FiOS are likely never going to get the fiber service, despite paying Verizon’s surcharges for more than 20 years. Verizon suspended its FiOS expansion project more than two years ago.
Bait and Switch Broadband

From promises of a cutting edge fiber future to good-enough DSL.
Despite early commitments of providing New Jersey with advanced fiber broadband speeds unheard of elsewhere in the country in the 1990s, Verizon changed its tune when it became clear the company wanted to prioritize investment in its more lucrative wireless network. Instead of a commitment of 45/45Mbps, providing basic DSL broadband at any speed was now seen as adequate. Verizon spokesman Lee Gierczynski told both Newsweek and the Inquirer the company never promised a statewide deployment of FiOS.
“Nobody knew what FiOS was 20 years ago,” Gierczynski said. “It wasn’t until 2004 when FiOS came on the scene.”
Forget about that commitment for 45/45Mbps speed as well.
“It didn’t say a minimum of 45mbps,” Gierczynski said, “it just says ‘up to’.”
That means DSL service will be a part of southern New Jersey for the near future. Customers unimpressed with the 5Mbps DSL service they get from Verizon can always pay substantially more for access to Verizon Wireless’ usage capped LTE 4G network that Gierczynski believes can be used to download movies.
In effect, ratepayers that wrote checks to pay artificially higher phone bills to help subsidize a promised 100% fiber optic future have instead funneled working capital to Verizon Wireless’ network expansion and helped enrich shareholders with generous dividend payouts.
Opportunity New Jersey Verizon: Christie Administration Proposes Letting Verizon Off the Hook Permanently

Gov. Christie
Most victims of costly bait and switch schemes get angry and demand justice. In New Jersey, the Christie Administration believes Verizon is the victim of unreasonable expectations and has proposed a sweetheart deal to both let the company off the hook and keep the surcharges it collected from New Jersey ratepayers for the last 21 years.
While the rest of the country clamors for better broadband, Governor Christie’s State Commission, his Attorney General’s Office and the state Consumer Rate Counsel believe that basic DSL is good enough, and making life difficult for Verizon by insisting it live up to its part of a mutual agreement just isn’t very nice.
All eyes were on incoming president of the Board of Public Utilities Dianne Solomon, wife of close Christie associate Lee Solomon. The BPU has direct authority over Verizon’s compliance with its promises to the state. But Dianne’s only apparent experience is as an official with the United States Tennis Association. Critics immediately pounced on the odd nomination, accusing the governor of using the BPU as a lucrative parking lot for political patronage. Three of the four current commissioners are all politically connected and their experience navigating telecommunications law is questionable.
Instead of demanding that Verizon be held to its commitment to the state, government officials are bending over backwards to let Verizon walk away from its promises forever.
A stipulation proposal would allow the company to shred its commitment to upgrade New Jersey with fiber optics. Instead, Verizon gets permission to discontinue service if you have any other option for service — including cable or wireless. Not only would this stipulation eliminate any hope bypassed communities have to eventually get Verizon FiOS, it would also let Verizon scrap its rural landline network and kill DSL, forcing customers to its lucrative wireless broadband product instead.

Solomon
The agreement also eliminates any commitment Verizon had to deliver fiber-fast speeds. Instead, Verizon will be considered in good standing if it matches the slowest speed on offer from Verizon DSL.
“Broadband is defined as delivering any technology including Verizon’s 4G wireless, fiber, copper or cable, data transmission service at speeds no less than the minimum speed of Verizon New Jersey’s Digital Subscriber line (DSL) that is provided by Verizon New Jersey today.”
New Jersey customers can file comments about the proposed agreement until March 24, 2014 with the Board of Public Utilities.
We have found a good sample letter you should edit to make your own. You can e-mail the secretary directly and/or send your message to the general e-mail address: [email protected] (be sure to include “Verizon New Jersey, Docket No. TO12020155” on the Subject line):
New Jersey Board of Public Utilities
Kristi Izzo, Secretary
44 South Clinton Avenue, 9th Floor
P.O. Box 350 Trenton, NJ 08625-0350
Email: [email protected]
Re: In the Matter of Verizon New Jersey, Inc. Docket# TO 12020155
Dear Secretary Izzo:
I want to alert you to an urgent matter pending before the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities. Pursuant to a 1993 law called Opportunity New Jersey, Verizon NJ was obligated to upgrade New Jersey’s “copper wire” network by 2010. To fund the Opportunity New Jersey expansion, Verizon NJ was permitted to collect excess charges from their customers and received lucrative tax breaks from the State. These charges and tax breaks began in the 1990s and are still being collected today.
Verizon failed to meet its timeframe requirements under the Opportunity New Jersey agreement to New Jersey residents. As a result of Verizon’s failures, on March 12, 2012, the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities initiated a legal action against Verizon NJ. The Board and Verizon NJ have now entered into a proposed settlement agreement which I believe is inadequate and not in the best interests of myself and other New Jersey residents who have paid for this service that was not fully delivered.
I oppose the Board’s proposed settlement agreement and demand that The Board of Public Utilities hold Verizon to the original Opportunity New Jersey agreement which requires Verizon to expand broadband services to every customer in the State. The proposed settlement has the potential of costing myself and other residents even more money than I have already paid for the last 21 years. The Board of Public Utilities should not allow Verizon to flagrantly disregard the stipulations which are the framework for the charges and tax breaks that Verizon has enjoyed for 21 years.
I am asking the Board of Public Utilities to be my advocate and investigate where our dollars were spent and to require Verizon to give me what I was originally promised under Opportunity New Jersey agreement of 1993.
Sincerely,
[Your Name, Address, Phone Number]

 Despite the success of FiOS, Verizon’s senior management continues to devote more attention to its highly profitable Verizon Wireless division, spending an even larger proportion of its total capital investments on wireless services.
Despite the success of FiOS, Verizon’s senior management continues to devote more attention to its highly profitable Verizon Wireless division, spending an even larger proportion of its total capital investments on wireless services.

 Subscribe
Subscribe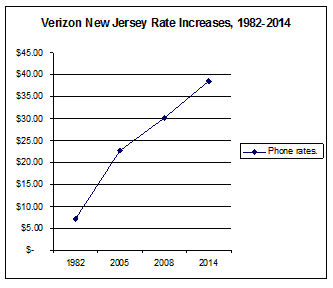 After adding up various other surcharges, Kushnick’s bill increased a lot.
After adding up various other surcharges, Kushnick’s bill increased a lot.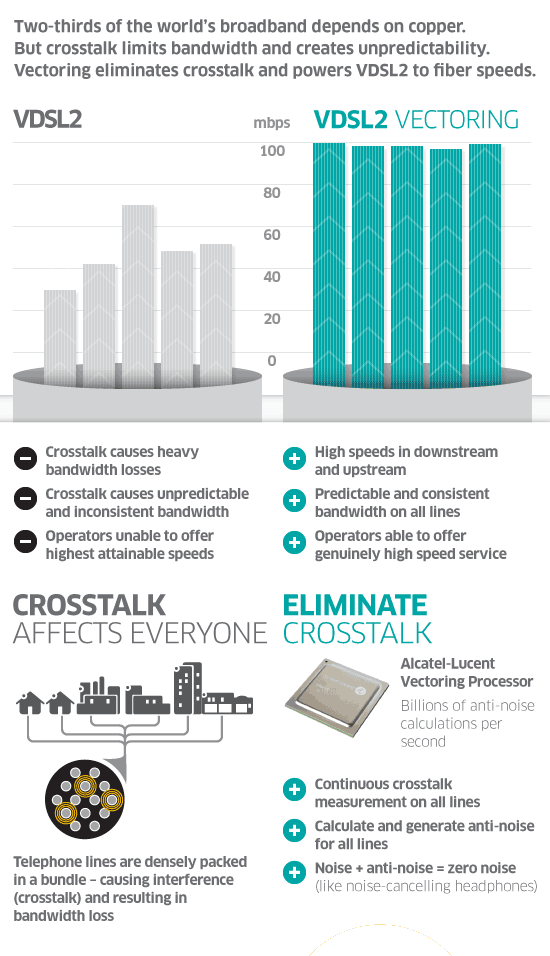 Alcatel-Lucent reported this month next generation DSL technology is a success for the company, with more than
Alcatel-Lucent reported this month next generation DSL technology is a success for the company, with more than  Cincinnati Bell
Cincinnati Bell 
 “Our business has been in decline for five or six years,” Torbeck
“Our business has been in decline for five or six years,” Torbeck  Last year, Cincinnati Bell had passed 184,000 homes with fiber optics – a 28 percent market share. But only 52,000 homes subscribed to Fioptics — Cincinnati Bell’s fiber brand. Time Warner Cable had managed to keep many of its wavering 446,000 customers loyal to the cable company with aggressive discounting and customer retention offers. But now that many of those discounts have since expired, Torbeck wants to reach 650,000-700,000 homes in its service area covering southwestern Ohio and northern Kentucky and convince 50% of those customers to switch to fiber optics.
Last year, Cincinnati Bell had passed 184,000 homes with fiber optics – a 28 percent market share. But only 52,000 homes subscribed to Fioptics — Cincinnati Bell’s fiber brand. Time Warner Cable had managed to keep many of its wavering 446,000 customers loyal to the cable company with aggressive discounting and customer retention offers. But now that many of those discounts have since expired, Torbeck wants to reach 650,000-700,000 homes in its service area covering southwestern Ohio and northern Kentucky and convince 50% of those customers to switch to fiber optics. The company’s unique position as the last remaining independent phone company that still bears the name of the telephone’s inventor may make the company a target for a takeover before Torbeck’s vision is realized. One analyst thinks Cincinnati Bell would be a natural target for Google, which has a recent record of repurposing fiber networks built by other companies as a cost-saving measure to further deploy Google Fiber.
The company’s unique position as the last remaining independent phone company that still bears the name of the telephone’s inventor may make the company a target for a takeover before Torbeck’s vision is realized. One analyst thinks Cincinnati Bell would be a natural target for Google, which has a recent record of repurposing fiber networks built by other companies as a cost-saving measure to further deploy Google Fiber. Cincinnati Bell has already spent about $300 million on Fioptics and plans to spend an extra $80 million this year on expansion. Before the network is complete, the phone company is likely to spend as much as $600 million on fiber upgrades. But the payoff has been higher revenue — $100 million last year alone, and a stabilizing business model that has reduced losses from landline cord-cutting. Telecom analyst Nicholas Puncer offers support for the investment, something rare for most Wall Street advisers.
Cincinnati Bell has already spent about $300 million on Fioptics and plans to spend an extra $80 million this year on expansion. Before the network is complete, the phone company is likely to spend as much as $600 million on fiber upgrades. But the payoff has been higher revenue — $100 million last year alone, and a stabilizing business model that has reduced losses from landline cord-cutting. Telecom analyst Nicholas Puncer offers support for the investment, something rare for most Wall Street advisers.




