Verizon customers in New York are paying artificially higher telephone rates justified to encourage Verizon investment in FiOS fiber to the home upgrades most New York State communities will never receive.
Starting in 2006, the New York Public Service Commission granted Verizon rate increases for residential flat-rate and message-rate telephone service and a 2009 $1.95 monthly increase for certain residence local exchange access lines to encourage Verizon’s investments to expand FiOS fiber to the home Internet across New York State.
“We are always concerned about the impacts on ratepayers of any rate increase, especially in times of economic stress,” said then-Commission chairman Garry Brown in June 2009. “Nevertheless, there are certain increases in Verizon’s costs that have to be recognized. This is especially important given the magnitude of the company’s capital investment program, including its massive deployment of fiber optics in New York. We encourage Verizon to make appropriate investments in New York, and these minor rate increases will allow those investments to continue.”
After Verizon announced it was suspending further expansion of its FiOS project a year later, the company continued to pocket the extra revenue despite reneging on the investments the PSC considered an important justification for the rate increases.
“The commission allowed Verizon rate increases in 2006 and 2008 based, in significant part, upon the assumption that the revenue from the higher rates would lead Verizon to invest in fiber optic lines, presumably for the benefit of wireline customers,” argues a coalition of state legislators, consumer groups, and unions. “Serious questions exist regarding the extent to which funds may instead have been used to build out the network for the benefit of wireless customers. Publicly available reports, while fragmentary, suggest that Verizon may have included construction costs for significant benefit of its wireless affiliate to be included in the costs of the Verizon New York wireline company, thus adding to its costs and tax losses.”
 Almost a decade later, Verizon is still receiving the extra revenue while some public officials complain Verizon is not meeting its commitments even in cities where Verizon has introduced FiOS service.
Almost a decade later, Verizon is still receiving the extra revenue while some public officials complain Verizon is not meeting its commitments even in cities where Verizon has introduced FiOS service.
Last week New York City Mayor Bill de Blasio ordered all future city contracts with Verizon be reviewed and authorized by City Hall. City officials complain Verizon promised in 2008 it would make FiOS available to every city resident no later than mid-2014. A year later, the service is still not available in some areas.
Verizon has blamed access issues and uncooperative landlords for most of the delays, but city officials are not happy with Verizon’s explanations.
“They [Verizon] have to demonstrate to us that they are good corporate actors if they want us to use our discretion in ways that benefit them,” the mayor’s counsel, Maya Wiley, told the New York Post.
Meanwhile, upstate New York residents now indefinitely bypassed by Verizon FiOS want a refund for the rate increases that were supposed to inspire Verizon to keep expanding fiber optics.
“Verizon has made at least $250 from me and every other upstate customer for nine years of broken promises,” said Penn Yan resident Mary Scavino. “Not only don’t they offer us fiber optics, we cannot even qualify for DSL service from them. If you can’t get Time Warner Cable in the Finger Lakes, you often don’t have broadband at all. It is them or nothing. Where did our money go?”
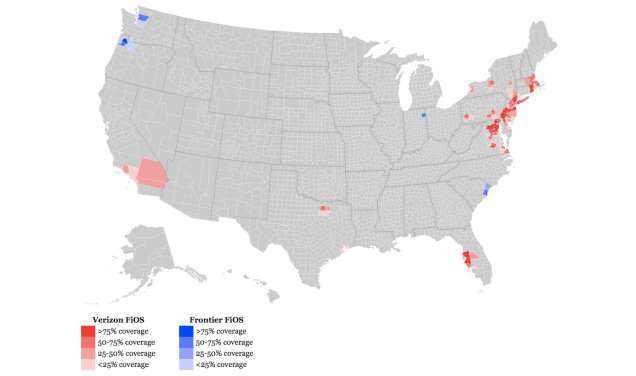
And, we’re done. Verizon FiOS availability map also showing areas later sold to Frontier.
Fred, a Stop the Cap! reader in the city of Syracuse, thinks the PSC should immediately revoke the rate increases and force Verizon to refund the money to customers who will not get upgraded service.
“It’s not like Verizon cannot make money in a city like Syracuse,” writes Fred. “It’s clear the CEO thinks even more money can be made off Verizon Wireless customers off the backs of landline customers, and the PSC continues to look the other way while they do it.”
Verizon claims it has lost money on its copper wireline network for years, something the PSC seems to accept in its 2009 press release announcing rate increases:
The rate increases will generate much needed additional short-term revenues as the company faces the dual financial pressures created by competitive access line losses and the significant capital it is committing to its New York network. For 2008, Verizon reported an overall intrastate return of negative 6.7 percent and a return on common equity of negative 48.66 percent. The current trend in the market is toward bundled service offerings, and Verizon believes the proposed price changes to its message rate residential service will encourage the migration of customers towards higher-value service bundles.
That migration costs New York ratepayers even more for telephone service. Verizon’s website prompts customers seeking new landline service to bundle a package of long distance discounts and calling features that costs in excess of $50 a month before taxes, fees, and surcharges. Bundling broadband costs even more. Verizon does not tell customers ordering online they qualify for a bare bones landline with no calling features and pay-per-call billing for less than half the cost of Verizon’s recommended bundle.

This Verizon discount calling program known as “Message Rate B” is only available to Washington, D.C. residents who have been threatened with disconnection or have an outstanding balance owed to Verizon. It costs $7.29 a month and includes 75 local calls.
More than three dozen New York State legislators also question whether Verizon’s “losses” are actually the result of Verizon’s purposeful “misallocation of costs” — moving expenses to the landline business even if they were incurred to benefit Verizon’s more profitable wireless division.
“The result has been massive cost increases for consumers, especially for the garden-variety dial tone service at the bottom of the technological ladder,” argues their 2014 petition. “For example, in New York City […] since 2006 the price of residential ‘dial tone’ service (one line item on the bill) went up 84%, while other services, such as inside wire maintenance, went up 132%.”
The petitioners claim there is evidence to dispute Verizon’s assertion its legacy copper network is as big of a money loser as the company suggests, thanks to “cooking the books” with accounting tricks. The petitioners want the PSC to order a review of Verizon’s books to be certain consumers are not being defrauded or manipulated.

Community leaders were arrested in 2013 during a protest outside Verizon’s NYC headquarters (at 140 West Street at the West Side Highway) to out the company for its history of avoiding taxes. (Image: Vocal NY)
From 2009-2013, Verizon New York reported losses of over $11 billion dollars, with an income tax benefit to Verizon Communications of $5 billion, and significant tax revenue losses for state, city and federal governments. Verizon New York has apparently paid no state, city or federal income tax for the last five years or more.
If Verizon is using accounting tricks to inflate the cost of legacy landline service while reducing costs to its wireless service, it could prove a win-win for Verizon and a lose-lose to ratepayers. Verizon could use its “losses” to argue for greater rate increases for landline customers while further reducing its tax obligations. On the wireless side, Verizon would enjoy praise from Wall Street analysts and shareholders pleased by the company’s apparently effective cost controls.
The best evidence of these techniques in action are the statements of company officials which suggest wireless costs are being paid by wireline customers.
Verizon’s chief financial officer, Fran Shammo, indicated to investors that Verizon wireline construction budgets are charged for expenses related to wireless service.
“The fact of the matter is wireline capital — and I won’t get the number but it’s pretty substantial — is being spent on the wireline side of the house to support the wireless growth,” Shammo told investors at Verizon at Goldman Sachs Communacopia Conference, Sept. 20, 2012. “So the IP backbone, the data transmission, fiber to the cell, that is all on the wireline books but it’s all being built for the wireless company.”
“It seems to me Verizon Wireless, already considered the Cadillac of wireless companies, doesn’t need a hidden subsidy from Verizon paid for by ratepayers all over the state,” Fred argues. “It seems very curious to me Verizon pioneered a large regional fiber optic upgrade that just a few years later it considers too costly to continue expanding, even as AT&T, Google, Comcast, and other companies are now entering the fiber business. A Public Service Commission that wants better broadband for New Yorkers ought to get to the bottom of this because it just doesn’t look right.”



 Subscribe
Subscribe Frontier Communications continues to face challenges keeping customers in its legacy copper wire service areas, where only modest investments in network upgrades have proved insufficient to stop customers shopping around for better service.
Frontier Communications continues to face challenges keeping customers in its legacy copper wire service areas, where only modest investments in network upgrades have proved insufficient to stop customers shopping around for better service. Consumer groups and New York State Attorney General Eric Schneiderman are expressing concern over the performance of the New York Public Service Commission in its year-long review of telecommunications services in New York.
Consumer groups and New York State Attorney General Eric Schneiderman are expressing concern over the performance of the New York Public Service Commission in its year-long review of telecommunications services in New York.
 Whether there is adequate competition for broadband service throughout the various regions of New York State, and whether there are any areas that are still essentially cable monopolies;
Whether there is adequate competition for broadband service throughout the various regions of New York State, and whether there are any areas that are still essentially cable monopolies;

 Almost a decade later, Verizon is still receiving the extra revenue while some public officials complain Verizon is not meeting its commitments even in cities where Verizon has introduced FiOS service.
Almost a decade later, Verizon is still receiving the extra revenue while some public officials complain Verizon is not meeting its commitments even in cities where Verizon has introduced FiOS service.





