 Conditions recommended by Stop the Cap! to protect New York consumers after a merger of Charter Communications and Time Warner Cable are expected to cost the two cable companies almost one billion dollars and will guarantee statewide adoption of Time Warner Cable’s Maxx upgrade, guaranteeing all customers receive speed upgrades ranging from 60-300Mbps.
Conditions recommended by Stop the Cap! to protect New York consumers after a merger of Charter Communications and Time Warner Cable are expected to cost the two cable companies almost one billion dollars and will guarantee statewide adoption of Time Warner Cable’s Maxx upgrade, guaranteeing all customers receive speed upgrades ranging from 60-300Mbps.
On Friday, the N.Y. Public Service Commission announced its conditional approval of the merger transaction, but only if Charter agrees to a series of wide-ranging conditions to guarantee that New York customers receive tangible benefits as a result of the merger:
The Commission agrees that in order for the proposed merger to be in the public interest, the Petitioners must agree to make concrete and enforceable commitments to modernize their cable system and services, expand access, address the digital divide and improve customer service. To this end, we find that with the acceptance by the Petitioners of the enforceable conditions, as discussed in the body of this Order and Appendix A, the proposed merger is in the public interest. These conditions are designed to help ensure a near ubiquitous world-class communications network that meets the needs of all New Yorkers. Absent acceptance of these conditions, the public interest standard cannot be met, and the petition for transaction approval is denied.
Stop the Cap! was quoted and footnoted extensively in the PSC order. We provided the PSC with insight beyond the public relations machine of Charter and Time Warner Cable. We exposed the fact Charter’s promised service improvements were actually more modest than what Time Warner Cable has undertaken on its own through its Maxx upgrade program. We educated regulators about the inadequacy of Charter’s initial commitment to offer low-cost Internet access for low-income families. We questioned the consumer benefits of certain upgrades that could actually increase costs for consumers because of additional equipment fees. We alerted the PSC that Charter would discontinue Time Warner’s affordable $14.99 Internet offer. We strongly recommended the PSC consider making rural broadband expansion a part of this transaction. We also sought additional protections from any future compulsory usage caps or usage-based billing.
 Although Stop the Cap! was opposed to the transaction from the outset, doubting it was in the public interest, we recognized the chances for approval were greater than the Comcast-TWC merger that was eventually withdrawn. Therefore, we made it a priority to outline multiple conditions we felt should be imposed on Charter if the deal was to be approved.
Although Stop the Cap! was opposed to the transaction from the outset, doubting it was in the public interest, we recognized the chances for approval were greater than the Comcast-TWC merger that was eventually withdrawn. Therefore, we made it a priority to outline multiple conditions we felt should be imposed on Charter if the deal was to be approved.
Our constituency is ordinary consumers and ratepayers. Too often these kinds of mergers are approved with token conditions that only benefit minority or special interests, favored non-profit or government entities, or those with vested business interests (programmers, equipment manufacturers, etc.) It was important to us that any approval bring something beyond free Internet service for schools or community centers, agreements to continue carrying certain cable networks, or a temporary discount or low value coupon that ends up in the mailboxes of customers a year or two from now.
We know what Time Warner Cable customers in New York want: better service, faster speeds, no data caps, no gotcha fees, affordable Internet options, and job protection.
It appears New York regulators understand that as well and intend to force Charter to offer customers a better deal.
Despite publicly saying little about the merger, just a few hours after the PSC’s decision, Gov. Andrew Cuomo’s office issued a press release taking credit for the merger conditions and unveiling the “tenth signature proposal of his 2016 agenda: dramatically expanding and improving access to high-speed Internet in communities statewide.” Once again, the governor will try to entice providers like Time Warner Cable, Frontier Communications, and Verizon to expand rural broadband in New York using public dollars.
Although lacking a catchy title, the “New New York Broadband Program” includes a $500 million solicitation for private sector partners to subsidize rural broadband expansion with state dollars. The key goals of the 2016 program include:
 Access to broadband at speeds of at least 100Mbps; 25Mbps in the most remote areas of the State.
Access to broadband at speeds of at least 100Mbps; 25Mbps in the most remote areas of the State.- Public-private partnerships with a required 50 percent match in private sector investment targeted across the program.
- Priority for projects that improve broadband Internet access in unserved areas, libraries and educational opportunity centers.
- Applications will be chosen through a “reverse-auction” process, which will award funding to bidders seeking the lowest State investment.
- Auctions to be held within each Regional Economic Development Council region to ensure statewide allocations of funding.
Much of the funding from earlier years ended up going to Time Warner Cable for modest expansion of its cable service, especially in eastern upstate New York. Likely applicants in 2016 include Time Warner Cable, Frontier Communications, community-owned/co-op broadband providers and rural wireless ISPs. Verizon and Cablevision are unlikely to apply.
Despite the governor’s efforts, most New York homes and businesses will be more affected by the Charter-Time Warner Cable merger, if it wins federal approval.

Gov. Cuomo
The Public Service Commission took its role very seriously, issuing a 93-page decision that took recommendations from consumer groups including Stop the Cap! very seriously. It did not share the industry’s belief that telecommunications providers in New York are heavily competitive.
“Time Warner serves close to 50% of New York State and we have a legitimate interest in ensuring that, when a company of this size provides customers with a service so affected by the public interest, as is communications, that real benefits accrue to consumers as a result of a given transaction,” the PSC wrote.
The PSC had an easier time sorting through comments about this merger, which generated considerably less interest than Comcast’s failed attempt to buy Time Warner.
“Generally, comments supporting the proposed transaction assert that, among other things, the merger will create jobs and provide better products at more affordable rates,” the PSC concluded in its ruling. “Those opposing the transaction state that the merger will inevitably lead to higher rates and potential data caps on broadband services in the future.”
The PSC took a very skeptical approach to Charter’s promised benefits, often finding them vague, questionable, or likely to have occurred with or without Charter’s involvement.
 For example, the PSC questioned Charter’s promised network investments and upgrades:
For example, the PSC questioned Charter’s promised network investments and upgrades:
Petitioners, however, decline to specify where in the national footprint of Charter, TWC and BHN these investments will be made or to identify the decisional factors to be used to channel these capital resources to specific areas or customers. There is no analysis to indicate that a reasonable proportion of these investments will be to systems in New York or for the benefit of New York customers. Similarly, there is no proposal by the Petitioners to describe the specific commitments that are being made or the specific enforcement mechanisms that would be used in the event the Petitioners’ implementation fell short of their commitments. Further, in order for these investments to be characterized as part of a net public benefit, Staff concludes, and we agree, that Petitioners would have to establish that these investments would not have been made in the absence of the proposed merger.
In the absence of a demonstration that there is “a tangible commitment to make new investments or invest beyond Time Warner’s current capital investment budgets,” it is difficult to characterize these capital expenditures as a certain benefit to New York customers or a satisfaction of the public interest under the New York statutes.
One of Stop the Cap!’s core arguments in our comments to the PSC was that Charter’s upgrade commitments were not particularly meaningful because Time Warner Cable was gradually upgrading its own systems to a level of service superior to what Charter plans to offer. The PSC clearly understood this and our warning that Charter’s commitments lacked specificity:
Public Benefit Assessment Staff and several commenters suggest that the proposed merger, as described in the Joint Petition and Petitioners’ Reply Comments, does not have sufficient net benefits to warrant a finding that the transaction is in the public interest. We concur. Many of the asserted benefits from the proposed transaction are events triggered by actions taken independently from the merger, and others are likely to be undertaken by TWC in any event, should the merger not be approved. Further, many asserted benefits are only described on a national scale and there is no way to determine if the investments or expenditures will occur in New York. Similarly, many of the projected benefits are described in terms that are too indefinite to permit us to assume that the benefits will occur as described to make a meaningful contribution to the transaction’s net benefits.
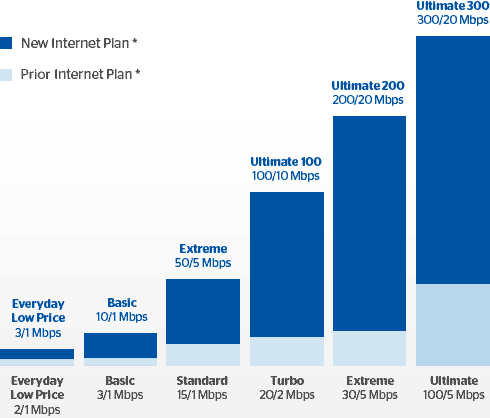
Time Warner Cable Maxx speed improvements.
As a result, the PSC has looked more closely at Time Warner Cable’s Maxx program to be the benchmark for New York, not Charter’s proposed upgrades. They have adopted our recommendation that every Time Warner Cable customer in New York get the same kind of service upgrade residents in New York City enjoy today.
Another argument made by Stop the Cap! dealt with affordable Internet access. Time Warner Cable’s Everyday Low Price Internet ($14.99/mo for 2Mbps) is not fast, but it is affordable and free of the kind of revenue-protecting pre-conditions usually placed on Internet access for the poor. Time Warner’s plan is available to every customer at any time with no restrictions or contracts. In contrast, Charter’s originally proposed affordable Internet program required participants have school-age children, enroll only in the late summer, not have current cable broadband service (or be willing to forego it for 60 days), and not have any prior balance. As with Comcast, pre-conditions like this limit participation. The PSC agreed and now customers will be able to keep their more affordable Internet plans without jumping through artificial hoops launched by Charter.
The days of rural New Yorkers being quoted $20,000 to install Time Warner Cable service are also going to be a thing of the past. In addition to a commitment to pay for line extensions reaching 145,000 unserved or underserved customers, Charter is now required to work with New York’s Broadband 4 All program to receive supplementary funding, as available, to complete service extensions to eventually reach every customer that lives within a franchise area and wants cable service.
There are several other benefits outlined below that make this a better (although not great) deal, at least for New Yorkers. If any other state regulator manages to get an even better deal for that state’s residents, New Yorkers will automatically benefit because of a “most favored state clause” in the PSC’s order, which requires Charter to share those benefits with New York residents.
 All in all, the New York State Public Service Commission has lived up to its reputation as a consumer-protective body that is responsive to the needs of the public. This is in great contrast to many other states where regulators seem themselves as a business facilitator (and occasionally come directly from the businesses being regulated). In these states, the merger won approval with few, in any, preconditions.
All in all, the New York State Public Service Commission has lived up to its reputation as a consumer-protective body that is responsive to the needs of the public. This is in great contrast to many other states where regulators seem themselves as a business facilitator (and occasionally come directly from the businesses being regulated). In these states, the merger won approval with few, in any, preconditions.
We were delighted to have been extensively quoted and footnoted in the PSC’s order, having proven our case the Charter-Time Warner deal didn’t offer very much for New York. But we’re not happy the PSC punted on data caps. While recognizing they are a concern, the PSC seemed satisfied a three-year guarantee of no data caps was adequate. We disagree. As an increasing number of Comcast customers can attest, data caps are anti-competitive, anti-consumer, and unnecessary. Whatever benefits faster speeds can deliver can be easily curtailed by a data cap. So can online video competition. With much of upstate New York totally dependent on a single provider – Time Warner or Charter – for broadband speeds above 10Mbps, there is plenty of room for mischief that would otherwise be controlled by competitive forces. The PSC saw fit to avoid using its power of approval to get creative on keeping flat rate Internet affordable and available. That is a mistake we predict will be back to haunt us in the future.
Here are the specific conditions, most advocated by Stop the Cap!, that Charter Communications must agree to as a condition of the deal’s approval in New York:
Rural Broadband Access [$355 Million Value]
In addition to the goals accomplished by Gov. Cuomo’s New New York Broadband Program, Charter must agree to unilaterally build-out its network to reach an additional 145,000 “unserved” and “underserved” homes and businesses within four years. This will be an easy target for Charter to reach because the PSC defines “underserved” as any home with less than 100Mbps service. That represents much of upstate New York bypassed by TWC Maxx, so a speed upgrade in just one upstate city will achieve this requirement.
However, the PSC also included a second condition. Subject to the final terms and conditions of the Broadband 4 All Program being comparable to the Connect New York Program, Charter will be required to bid for Broadband 4 All Program funding to offer line extensions to any remaining unserved and underserved home across its entire New York service territory, which means every New Yorker within a cable franchise service area that wants service will be able to get it without being quoted tens of thousands of dollars for construction costs.
This will finally help would-be customers like Stop the Cap! reader Jesse Walser in Jamesville who has tried to get wired broadband in his home for over a decade. Verizon won’t upgrade its network and Time Warner Cable quoted him between $5,900 and $26,000 for installation of a line extension to reach his home.
All Digital Cable System Upgrade
Charter must convert their existing New York systems to an all-digital network (including upgrading the Columbia County Charter cable system to enable broadband communications) capable of delivering faster broadband speeds.
In Columbia County, residents are currently better served by smaller local providers. Both Germantown Telephone and Mid-Hudson Cable offer high-speed access throughout their territories. Berkshire Telephone has almost 100% DSL coverage, and Taconic Telephone has expanded DSL service to much of their huge service territory. Frontier Communications offers some DSL in southern Columbia County. The biggest problem providers are Verizon, which has no plans for DSL service in the area, and Charter Cable, which still runs a basic cable television-only system in the county.
In New York, Charter now provides cable television and other communication services to a relatively small number of customers, from two cable system clusters in and around Plattsburgh (14,000 customers) and Columbia County (2,500 customers). Plattsburgh gets television, phone and broadband service from Charter, but Columbia County is still served by a now-ancient, cable television only system.
Network Modernization and Speed Increases [$305 Million Value]
Charter must convert all of its systems in New York to all-digital within 30 months of the closing of the merger transaction. Charter is also required to offer broadband speeds up to 100Mbps to all customers by the end 2018 and match TWC Maxx speeds of 300Mbps by the end of 2019.
Charter’s all digital upgrade in upstate New York will facilitate faster broadband service, but it will also mean a set-top box or other similar device for every cable connected television in the home.
Broadband Affordability [$250 Million Value]
Despite Charter’s simplified menu of options (two broadband speed tiers and one video package), the PSC has required Charter to allow customers to keep their current plans, at least for the next several years:
- Charter is required to maintain and advance its commitment to an affordable standalone Internet offering through the continuation of the Time Warner Everyday Low Price $14.99
service throughout the Time Warner New York territory for up to two years and allow existing customers to keep the service for three years. - Charter is required to offer its 60Mbps standalone broadband product throughout New York at uniform national pricing. [$125 million value]
- Charter is required to allow existing Time Warner customers to retain, without material changes that have the intent to discourage, the standalone and bundled broadband services they subscribe to at the close of the transaction for three years from the date of the closing.
- Charter is required to provide a low-income broadband offering to eligible customers throughout its New York footprint. The PSC-ordered plan will offer 30Mbps for $14.99 a month to any household eligible for the National School Lunch Program and senior citizens 65 years and older eligible for the federal Supplemental Security Income program. No credit check shall be required and conditions requiring current broadband customers to wait 60 days to qualify and cover any past due bills have been deleted.
Customer Service [$55 Million Value]
Within two years after the close of the proposed transaction, Charter shall invest a minimum of $50 million in service improvement programs.
Charter is required to show a 35% reduction in Time Warner Cable’s 2014 cable PSC Complaint Rate by the end of 2020, with a 17.5% reduction due by the end of 2018. If they don’t achieve that, Charter must invest an additional $2.5 million in its service for each failure.
Job Protection
For the next four years, Charter cannot cut the number of customer facing jobs in New York.


 Subscribe
Subscribe


 If you are living with a Comcast data cap and want to see it gone, you can do something about it. Consider organizing your own local movement by tapping fellow angry customers and recruiting local activist groups to the cause. In Rochester, there was no shortage of angry college students and groups ready to protest. Google local progressive political groups, technology clubs, and technology-dependent organizations in your immediate area. Some are likely to be a good resource for building effective public protests, sign-making, and other TV-friendly protest techniques. Contact town governments, the mayor’s office of your city, technology-oriented newspaper columnists, radio talk show/computer support show hosts, etc., to build a mailing list for coordinated announcements about your efforts. Many local officials also oppose data caps.
If you are living with a Comcast data cap and want to see it gone, you can do something about it. Consider organizing your own local movement by tapping fellow angry customers and recruiting local activist groups to the cause. In Rochester, there was no shortage of angry college students and groups ready to protest. Google local progressive political groups, technology clubs, and technology-dependent organizations in your immediate area. Some are likely to be a good resource for building effective public protests, sign-making, and other TV-friendly protest techniques. Contact town governments, the mayor’s office of your city, technology-oriented newspaper columnists, radio talk show/computer support show hosts, etc., to build a mailing list for coordinated announcements about your efforts. Many local officials also oppose data caps.

 Comcast is inviting controversy launching a new live streaming TV service targeting cord-cutters while exempting it from its own data caps.
Comcast is inviting controversy launching a new live streaming TV service targeting cord-cutters while exempting it from its own data caps.
 Comcast claims it is reasonable to exempt Stream TV from its 300GB data cap being tested in a growing number of markets.
Comcast claims it is reasonable to exempt Stream TV from its 300GB data cap being tested in a growing number of markets.
 Time Warner Cable customers who purchased their own cable modems to avoid the company’s $8 monthly rental fee will effectively be forced to indirectly pay those fees once again if Charter Communications wins approval to buy the cable operator.
Time Warner Cable customers who purchased their own cable modems to avoid the company’s $8 monthly rental fee will effectively be forced to indirectly pay those fees once again if Charter Communications wins approval to buy the cable operator. Zoom wants Charter to be required to offer consumers that own their own equipment a tangible monthly discount for broadband service as a condition of any merger approval.
Zoom wants Charter to be required to offer consumers that own their own equipment a tangible monthly discount for broadband service as a condition of any merger approval.