
Franken
Sen. Al Franken (D-Minn.) has turned over much of his campaign website to expressing concern about the merger of Time Warner Cable and Comcast.
Franken has maintained a comparatively low profile since arriving in the U.S. Senate and rarely grants interviews to reporters outside of Minnesota, but after the announced $45 billion merger deal between the two largest cable companies in the country, he started making exceptions.
Franken has repeatedly tangled with Comcast, the dominant cable operator in his home state, since being elected. He favors Net Neutrality/Open Internet policies, strongly opposed Comcast’s purchase of NBCUniversal, and believes cable rates are too high and service quality is too low.
Although the senator claims he remains undecided about the merger, his public comments suggest he is likely going to oppose the deal.
“We need more competition, not less,” said Franken, who mocked Comcast’s claim that the two cable companies never compete with each other. “This is going exactly in the wrong direction. Consumers, I am very concerned, are going to pay higher bills and get even worse service and less choice.”
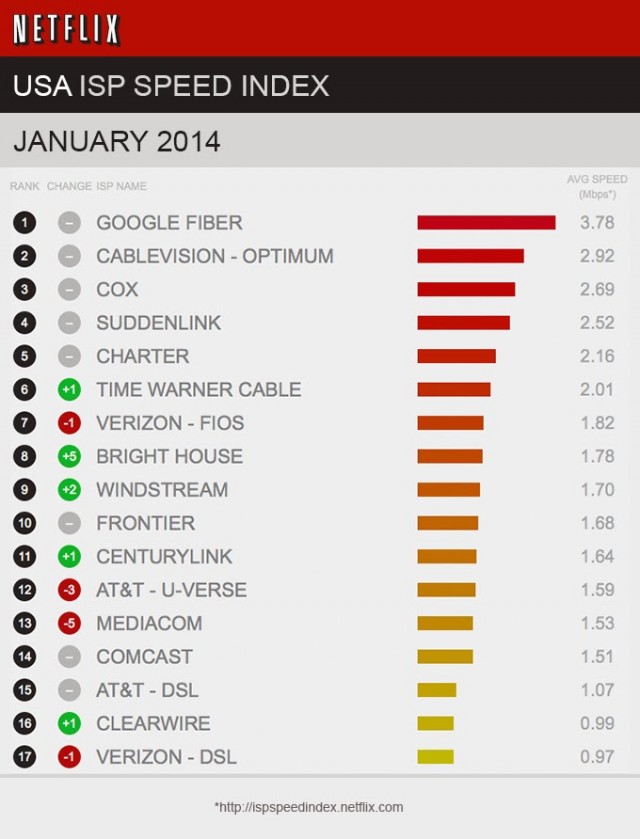
Although the merger will leave the combined company serving nearly one in three households, Comcast says it plans to keep its total nationwide broadband market share under 30%. But Franken points out Comcast isn’t just a cable company. It also owns a major television network and has ownership interests in nearly three dozen cable networks and television stations around the country — many in America’s largest cities.
Franken mass e-mailed his campaign supporters to express concern about the current state of the cable and broadband business and asked consumers what they thought about their cable company. More than 60,000 have shared their mostly negative views so far.
Minnesota Public Radio takes a closer look at why Sen. Al Franken is interested in the merger of Time Warner Cable and Comcast. Feb. 24, 2014 (4:32)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.
 That may prove to be smart politics for Franken, seen as a polarizing figure in the left-right divide. The near-universal loathing among consumers for both Comcast and Time Warner Cable threaten to rise above traditional partisan politics. Republican lawmakers have kept largely quiet about the merger deal, and some are even openly questioning it. Franken may tapped into a re-election issue that voters across Minnesota are likely to support — especially older Republican-leaning independents.
That may prove to be smart politics for Franken, seen as a polarizing figure in the left-right divide. The near-universal loathing among consumers for both Comcast and Time Warner Cable threaten to rise above traditional partisan politics. Republican lawmakers have kept largely quiet about the merger deal, and some are even openly questioning it. Franken may tapped into a re-election issue that voters across Minnesota are likely to support — especially older Republican-leaning independents.
Franken claims his survey is trying to level the playing field by getting consumers involved in the issue. For Washington regulators accustomed to only hearing from company lobbyists and various third party groups often financially tied to merger advocates, it could be a game-changer.
Comcast’s connections in Washington are legendary. Former Republican FCC commissioner Meredith Attwell Baker wasted no time taking a job as a senior Comcast lobbyist shortly after voting in favor of Comcast’s buyout of NBCUniversal. Former Republican FCC chairman Michael Powell today heads the National Cable and Telecommunications Association (NCTA), the cable industry’s largest lobbying group and supporter of the merger.
The merger deal’s regulatory review will be conducted by current FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler, a past president of the NCTA and former cable and wireless industry lobbyist. Bill Baer is in charge of the Antitrust Division that will examine the merger at the U.S. Department of Justice. His last job was leading the law firm that represented NBC in support of the Comcast-NBCUniversal merger.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CNN Al Franken Talks With CNN About TWC-Comcast Merger 2-13-14.flv[/flv]
Sen. Al Franken spoke to CNN’s Jake Tapper earlier this month about the Time Warner Cable-Comcast merger. Tapper admitted he dropped Comcast because he was dissatisfied with their service. (7:45)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 “Look, the amount of decision makers, which is so surprisingly small in the industry in general, is potentially getting smaller,” Steve Krakauer, TheBlaze’s vice president of digital content told POLITICO. “Keeping up the fight is so important.”
“Look, the amount of decision makers, which is so surprisingly small in the industry in general, is potentially getting smaller,” Steve Krakauer, TheBlaze’s vice president of digital content told POLITICO. “Keeping up the fight is so important.”

 Gizmodo
Gizmodo 
 Comcast will announce later this morning it has reached an agreement to acquire all of Time Warner Cable in an all-stock deal worth $44 billion.
Comcast will announce later this morning it has reached an agreement to acquire all of Time Warner Cable in an all-stock deal worth $44 billion. Time Warner Cable management offered no clues they were negotiating with Comcast and delivered a presentation to shareholders last week promising major upgrades for Time Warner customers and future success as a standalone cable operator. All of those plans are now in doubt.
Time Warner Cable management offered no clues they were negotiating with Comcast and delivered a presentation to shareholders last week promising major upgrades for Time Warner customers and future success as a standalone cable operator. All of those plans are now in doubt. Consumer groups hope the deal gets derailed as soon as possible.
Consumer groups hope the deal gets derailed as soon as possible.