
Comcast has repeatedly touted its rating from J.D. Power & Associates claiming the company has been cited for the most improvement of any cable operator scored by the survey firm. That isn’t saying very much when one takes a closer look.
 In fact, since 2010 Comcast has achieved very little improvement in its abysmal score. J.D. Power & Associates reports that over the last four years, Comcast has only managed to boost its TV satisfaction score 92 points and Internet satisfaction 77 points… on a 1,000-point scale.[1]
In fact, since 2010 Comcast has achieved very little improvement in its abysmal score. J.D. Power & Associates reports that over the last four years, Comcast has only managed to boost its TV satisfaction score 92 points and Internet satisfaction 77 points… on a 1,000-point scale.[1]
Comcast also continues to have below-average scores in all four regions for both television and broadband, with the exception of Internet service in the north-central region, where it faces competition from DSL offered by telephone company CenturyLink.
Other consumer satisfaction surveys are far less charitable to Comcast.
Consumer Reports ranked Comcast 15th out of 17 large cable companies and called their service and customer relations mediocre. In a survey conducted in April, the consumer group found 56% of the public opposed to the merger, 11% supported it, and 32% offered no opinion. The survey found 74% believing the merger will result in higher prices and fewer choices for consumers.[2]
“A merger combining these two huge companies would give Comcast even greater control over the cable and broadband Internet markets, leading to higher prices, fewer choices, and worse customer service for consumers,” Delara Derakhshani, policy counsel in Consumers Union’s D.C. office, said in a statement.[3]
Nearly every year, Comcast CEO Brian Roberts acknowledges the problems with customer service and promises improvements.[4] But according to the American Consumer Satisfaction Index, those improvements never arrive. Perhaps they need the expertise of professionals like those virtual assistants to turn things around.
In 2004, ACSI noted it added cable television to its index in 2000, and since that time, “customer satisfaction has gone from bad to worse, and there is no improvement in sight:”[5]
 Among cable providers, Time Warner has the highest score of 60. Both Comcast and Charter Communications register at 56. For the private as well as public sector, including the IRS, this is the lowest level of customer satisfaction of any organization in ACSI. Consumer complaints are also much more common relative to any other measured industry. Almost half of all cable customers have registered complaints about one thing or another.
Among cable providers, Time Warner has the highest score of 60. Both Comcast and Charter Communications register at 56. For the private as well as public sector, including the IRS, this is the lowest level of customer satisfaction of any organization in ACSI. Consumer complaints are also much more common relative to any other measured industry. Almost half of all cable customers have registered complaints about one thing or another.
When buyers have meaningful choice alternatives, this level of customer (dis)satisfaction is neither competitive nor sustainable. Cable is the only industry to score below 60 in ACSI. With the satellite companies removed, the weighted average for the cable industry is 59.
Under normal competitive conditions, there would be mass customer defections. The reason this is not the case for the cable industry is due to local monopoly power, which means that in most markets, the dissatisfied customer has nowhere to go.
In 2007, ACSI foreshadows what a merger between two giant cable companies is likely to mean for customers as the two companies eventually attempt to integrate their disparate computer systems and management:[6]
After a minor gain in 2006, the first ever for the industry, satisfaction among subscribers to cable and satellite TV service drops 2% to 62, the lowest level of customer satisfaction among all industries covered by ACSI. None of the providers has improved on customer satisfaction this year. Comcast (down 7% to 56), DirecTV (down 6% to 67) and Time Warner Cable (down 5% to 58) tumble. High system loads causing problems with reliability and pricing were major culprits. Both Comcast and Time Warner have acquired many new subscribers in their deal to divide up troubled cable provider Adelphia Communications – integrating these acquisitions often leads to short-term problems with customer satisfaction.
 In 2008, things deteriorated further for Comcast customers, according to this ACSI assessment:[7]
In 2008, things deteriorated further for Comcast customers, according to this ACSI assessment:[7]
Comcast is down 4% to 54, an all-time low for the largest cable provider in the country. Rapid growth may have contributed to difficulties in operations as Comcast continues to add cable subscribers, often through acquisitions of companies in smaller markets.
[…] As is often the case, small is often better in terms of being able to provide good customer service. Cablevision, for example, with some 3 million subscribers, is barely 1/8th the size of Comcast. These companies don’t generally seek to expand quickly beyond their geographic footprints and are often targets of acquisition by larger firms, companies that may be able to withstand depressed customer satisfaction in the short term as operations of the smaller providers are integrated.
This year, both Comcast and Time Warner Cable fell even further according to ACSI:[8]
Cable giants Comcast and Time Warner Cable have the most dissatisfied customers. Comcast falls 5% to 60, while Time Warner registers the biggest loss and plunges 7% to 56, its lowest score to date.
“Comcast and Time Warner assert their proposed merger will not reduce competition because there is little overlap in their service territories,” says David VanAmburg, ACSI Director. “Still, it’s a concern whenever two poor-performing service providers combine operations. ACSI data consistently show that mergers in service industries usually result in lower customer satisfaction, at least in the short term. It’s hard to see how combining two negatives will be a positive for consumers.”
ACSI also scored Internet Service Providers this year and found even worse news:[9]
High prices, slow data transmission and unreliable service drag satisfaction to record lows, as customers have few alternatives beyond the largest Internet service providers. Customer satisfaction with ISPs drops 3.1% to 63, the lowest score in the Index.
[…] Cable-company-controlled ISPs languish at the bottom of the rankings again. Cox Communications is the best of these and stays above the industry average despite a 6% fall to 64. Customers rate Comcast (-8% to 57) and Time Warner Cable (-14% to 54) even lower for Internet service than for their TV service. In both industries, the two providers have the weakest customer satisfaction.
Comcast claims the transaction will allow the two companies to invest in their networks, improve customer service with a topnotch phone answering service, and enhance the products available to Time Warner Cable customers.
In reality, Comcast’s largest investment will be in a $17 billion share buyback to benefit their stockholders.[10] Time Warner Cable’s current CEO has secured for himself a golden parachute package of $78 million dollars for just two months on the job as CEO of Time Warner Cable.[11]
With that kind of money on the table, it is no surprise Comcast has invested in 76 lobbyists from 24 different lobbying firms and is spending millions trying to convince regulators, including the NY PSC that this transaction is a good deal for New York. The more than 2,700 New Yorkers that have filed comments with the PSC, largely in strong opposition to this merger, disagree. Their voices should speak louder than out of state groups that have been urged by Comcast to send letters supporting this transaction.
—
[1]http://variety.com/2014/biz/news/comcast-time-warner-cable-remain-among-most-hated-tv-providers-survey-1201145921/
[2]http://variety.com/2014/biz/news/comcast-time-warner-cable-merger-poll-shows-majority-oppose-1201224277/
[3]http://consumersunion.org/
[4]http://www.dslreports.com/shownews/Comcast-CEO-Makes-His-Yearly-Promise-to-Improve-Customer-Service-128206
[5]http://www.theacsi.org/component/content/article/30-commentary-category/86-acsi-quarterly-commentaries-q1-2004
[6]http://www.theacsi.org/component/content/article/30-commentary-category/169-acsi-quarterly-commentaries-q1-2007
[7]http://www.theacsi.org/component/content/article/30-commentary-category/179-acsi-quarterly-commentaries-q1-2008
[8]http://www.theacsi.org/news-and-resources/press-releases/press-2014/press-release-telecommunications-and-information-2014
[9]http://www.theacsi.org/news-and-resources/press-releases/press-2014/press-release-telecommunications-and-information-2014
[10]http://www.cleveland.com/business/index.ssf/2014/02/comcast_agrees_to_purchase_of.html
[11]http://www.usatoday.com/story/money/business/2014/03/20/four-months-as-time-warner-cables-ceo--80-million/6658083/
 Staff attorneys that have reviewed details of the Time Warner Cable/Comcast merger proposal are prepared to make a recommendation as early as next week that the Department of Justice should block the deal because it is anti-competitive and anti-consumer.
Staff attorneys that have reviewed details of the Time Warner Cable/Comcast merger proposal are prepared to make a recommendation as early as next week that the Department of Justice should block the deal because it is anti-competitive and anti-consumer. Under consideration by the Justice Department:
Under consideration by the Justice Department:

 Subscribe
Subscribe In a major victory for consumers and public interest groups, the Federal Communications Commission this week will unveil fundamental changes in the oversight of high-speed Internet service, regulating it in the public interest as a public utility.
In a major victory for consumers and public interest groups, the Federal Communications Commission this week will unveil fundamental changes in the oversight of high-speed Internet service, regulating it in the public interest as a public utility. With millions at stake charging content producers extra for guaranteed fast lanes on the Internet, some lobbyists will go to almost any length to throw up roadblocks in opposition to Net Neutrality.
With millions at stake charging content producers extra for guaranteed fast lanes on the Internet, some lobbyists will go to almost any length to throw up roadblocks in opposition to Net Neutrality.
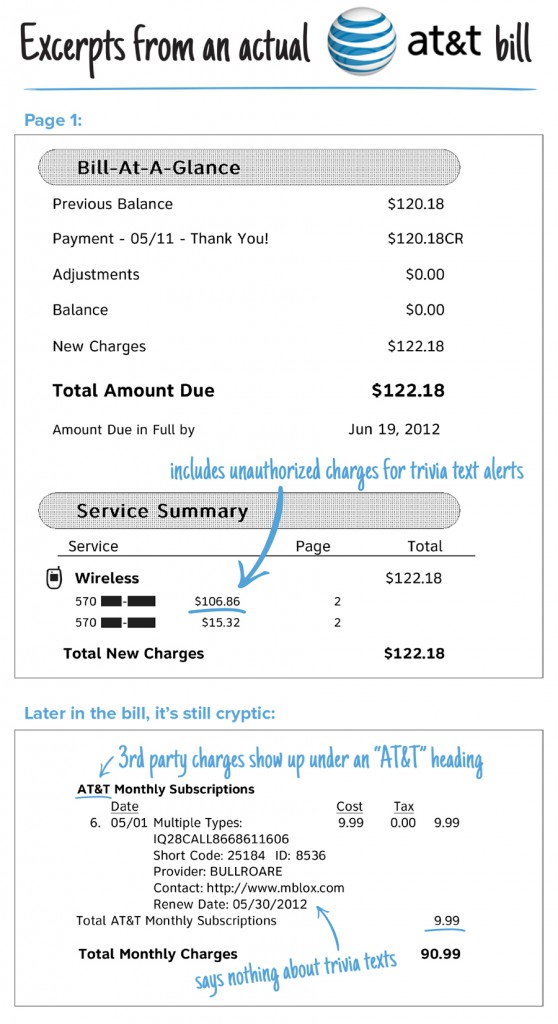

 In fact, since 2010 Comcast has achieved very little improvement in its abysmal score. J.D. Power & Associates reports that over the last four years, Comcast has only managed to boost its TV satisfaction score 92 points and Internet satisfaction 77 points… on a 1,000-point scale.[1]
In fact, since 2010 Comcast has achieved very little improvement in its abysmal score. J.D. Power & Associates reports that over the last four years, Comcast has only managed to boost its TV satisfaction score 92 points and Internet satisfaction 77 points… on a 1,000-point scale.[1] Among cable providers, Time Warner has the highest score of 60. Both Comcast and Charter Communications register at 56. For the private as well as public sector, including the IRS, this is the lowest level of customer satisfaction of any organization in ACSI. Consumer complaints are also much more common relative to any other measured industry. Almost half of all cable customers have registered complaints about one thing or another.
Among cable providers, Time Warner has the highest score of 60. Both Comcast and Charter Communications register at 56. For the private as well as public sector, including the IRS, this is the lowest level of customer satisfaction of any organization in ACSI. Consumer complaints are also much more common relative to any other measured industry. Almost half of all cable customers have registered complaints about one thing or another. In 2008, things deteriorated further for Comcast customers, according to this ACSI assessment:[7]
In 2008, things deteriorated further for Comcast customers, according to this ACSI assessment:[7]