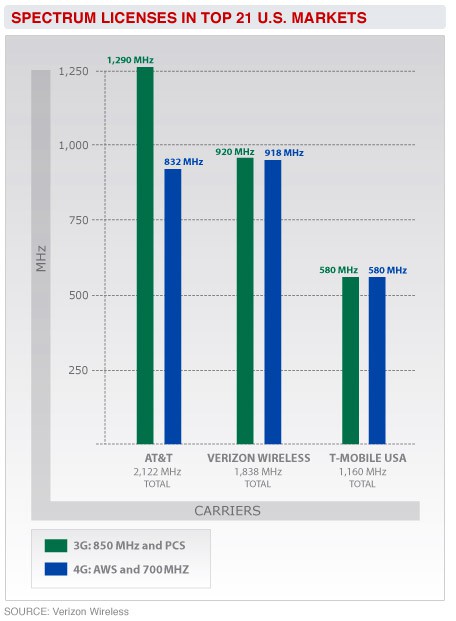
Verizon Wireless provides evidence AT&T already has more spectrum than any other carrier -- spectrum they are not using.
AT&T’s alternate reality of the wireless universe is on full display as the company makes statements promoting its proposed merger with T-Mobile that, in some cases, retreat from the facts or otherwise distort them.
AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson has been visiting with journalists, often from the business press, to talk up the merger’s potential. The company has supplemented those PR tours with a 400-page filing with the Federal Communications Commission that has won converts among some non-profit groups, many of which receive direct funding from AT&T.
Stop the Cap! felt a fact check was in order, so we reviewed Stephenson’s recent claims made in an interview with USA Today:
Claim: In the last four years, the volume of (traffic on) these (wireless broadband) networks is up 8,000%. We believe that we’re going to go up, in five years, eight to 10 times from where we are today. We don’t have the spectrum position to accomplish that. T-Mobile’s spectrum is very compatible with ours. In cities like New York, we put the two companies together, and we get a very quick lift in capacity of about 30%. That means fewer dropped calls, better service quality, and it gives us a path to do something that neither one of us could do independently, and that is deploy fourth-generation mobile broadband to 95% of the U.S.
Fact: Although wireless broadband traffic is up, AT&T holds more wireless spectrum than any other carrier, a good deal of it unused. In fact, some of AT&T’s competitors and critics suggest the company is hoarding spectrum, and its insatiable appetite for more could get fulfilled if the company can sell Congress on its “shortage theory.” Although some of that spectrum is being reserved for the company’s future LTE network, critics contend AT&T spent a lower percentage of its revenue on network expansion (despite being the exclusive holder of the Apple iPhone during the period) than its competitors.
Between 2008 and 2010, AT&T’s FCC filing said it spent $21.1 billion in capital expenditures to upgrade its wireless network. That’s less than the $22.1 billion spent by Verizon Wireless over the same period. As a percentage of revenue, AT&T’s total was a little higher, at 13%, to Verizon’s 12.8%. Even so, given its congestion problems, AT&T should have spent significantly more. Complaints about congestion were apparent at least two years ago, yet in 2009 AT&T increased wireless capital expenditures by only 1% to Verizon’s 10%.
AT&T has admitted it has faced congestion issues in several large cities — an especially serious problem for a company using GSM technology, which combines voice and data traffic onto a single wireless pipe. When the network gets overcongested, data sessions fail and voice calls drop. CDMA networks like Verizon and Sprint have two virtual pipes, one for data and one for calls. If one gets congested, it doesn’t necessarily harm the other.
Additionally, although T-Mobile will provide some additional capacity in selected urban markets, some of their towers are remarkably close to AT&T’s own towers, effectively making them redundant. Because T-Mobile uses different spectrum, in some cases AT&T customers will see no benefit from the combination of the two networks, unless they buy new equipment capable of accessing both.
AT&T using T-Mobile as the key to deploying fourth-generation mobile broadband is more than a little hard to believe, considering the German-owned carrier is dwarfed by AT&T.
Claim: Anybody who opens the newspaper or watches TV sees this as a fiercely competitive industry — maybe the most competitive in the United States. The large majority of Americans, when they go to buy cellphone service, have a choice of at least five providers. In 18 of the top 20 markets, the customer has a choice of five different competitors. It’s a fiercely competitive market today. It will be a fiercely competitive market after this deal is done. We don’t see that changing.

Free Press characterizes AT&T's claims of more competition by absorbing a competitor to be the equivalent of chucking your smartphone down the rabbit hole.
Fact: If ad purchases were evidence of a robust, competitive market, we could say phone and cable companies were hot competitors. Both advertise heavily, but charge similar prices for similar service — a classic case of duopoly market pricing power. In the cell phone business, the overwhelming majority of Americans subscribe to either AT&T or Verizon Wireless. Sprint is a distant third at around 12%. After T-Mobile, all other carriers represent just 1-2% of the remaining market share. Many cities don’t have access to smaller providers like Cricket, US Cellular, or MetroPCS, either. In those areas, the choices are usually AT&T, Verizon, and perhaps Sprint.
How does this marketplace concentration impact customers? Loss of innovation. Typically, smaller carriers have to innovate to attract attention and compete successfully with larger providers. AT&T and Verizon have long track records of locking up access to the most innovative phones, so smaller providers have to create unique service plans, offer lower prices, or provide attractive bundles. Sprint sells unlimited access in a marketplace full of restrictive data caps or calling minute allowances. T-Mobile provided some of the least expensive plans around, especially for families. Cricket offers pay-per-day prepaid calling plans that can make a wireless phone affordable for anyone. US Cellular has stellar customer service.
All competitors are not equal. Anyone who lives or visits rural areas understands the implications of relying on Cricket, MetroPCS, or even Sprint for cell phone service well off the main highway. With coverage being a major factor, many quickly decide there are only two realistic choices for robust service — AT&T and Verizon.
AT&T’s myopia aside, eliminating T-Mobile, one of the market’s most fiercely innovative providers, will do nothing to benefit consumers.
Q&A Claims:
Q: There are small companies in the market, but one commentator said that they’re like grocery stores trying to compete with Walmart.
A: Everybody has their analysis. We can evaluate the numbers nine ways to Sunday. At the end of the day, the Justice Department will do the fact gathering and data gathering and will evaluate it market by market, then make those determinations. Based on our analyses, this is a deal that should be approved.
Q: If the market is so competitive, why might two companies have 70% of the business?
A: We all make technology decisions. We all put marketing plans into place. We all make decisions that drive how effective we are in the marketplace. I think we’ve done pretty well. I think Sprint has done a remarkable job over the last couple of years and will do very well tomorrow.
Q: Consumers only have two places where they can get an iPhone.
A: But there are RIM (BlackBerry) devices. There are Windows (Phone) 7 devices. Android devices tend to be doing very well throughout the market — in fact, we are having a lot of success with Android. Metro PCSand a lot of our competitors are having a lot of success there. So there are plenty of options for the customer.
Q&A Facts:
- AT&T’s in-house analysis decides what is best for AT&T, not for individual American consumers. The Justice Department and the Federal Communications Commission are subject to political pressure and are not independent arbiters of competitive fairness.
- Sprint has lost customers for years and is only now attracting some of them back. While charitable to Sprint, Stephenson’s remarks are not welcomed by them. They consider this deal anti-consumer and anti-competitive.
- Perhaps with the exception of the Evo, available first from Sprint, almost every other cutting-edge phone launches exclusively with AT&T and/or Verizon. Other carriers get to sell these popular phones much later, or sell stripped down models that don’t deliver the same features. Just review the phones available to Cricket and MetroPCS customers and compare them with what is on offer from Verizon and AT&T.
Claim: History tells you that prices in this industry have come down for 10 years. In the last 10 years, there’s been a significant number of business combinations in this industry, and prices have come down by 50%. And prices continue to come down. We have a history, when we acquire one of these companies, we map their rate plans into AT&T. So if somebody chooses to stay on that rate plan, those rate plans are available. I don’t see why we would change it for this case. It’s just a customer-friendly thing to do.
 Fact: More and more customers are no longer simply buying voice plans, on which Stephenson’s claims are based. Instead, they are upgrading to smartphones, where they discover carriers’ mandatory add-on fees for data services. Although prices for voice plans have not increased, rates for text messaging, data, and other add-ons have. That can add $25 a month or more per phone. Many carriers are reducing their discounts on new phones while adding new “junk fees” to their bills to cover “regulatory costs” as well.
Fact: More and more customers are no longer simply buying voice plans, on which Stephenson’s claims are based. Instead, they are upgrading to smartphones, where they discover carriers’ mandatory add-on fees for data services. Although prices for voice plans have not increased, rates for text messaging, data, and other add-ons have. That can add $25 a month or more per phone. Many carriers are reducing their discounts on new phones while adding new “junk fees” to their bills to cover “regulatory costs” as well.
AT&T also doesn’t specifically promise to retain T-Mobile’s innovative rate plans. Instead, they propose to grandfather existing customers on those plans until they purchase new phones or switch carriers. That does not mean existing AT&T customers can jump to a T-Mobile plan. It also doesn’t mean those plans will still be available for new customers.
AT&T has a track record of not being particularly customer-friendly, either.
Claim: T-Mobile will continue to operate their business exactly like they have. They’ve demonstrated that they’ve had a lot of success. They market directly against AT&T. I envision them to continue marketing against AT&T in the marketplace.
Fact: T-Mobile is so successful, they have been shopping around for a buyer for some time to allow them to exit the business. A success story that is not.
Claim: Q. If the deal goes through, would you offer all of the AT&T handsets to T-Mobile? A: Of course. If you’re a T-Mobile customer, that’s one of the great advantages. The handset selection that AT&T offers would become available to T-Mobile customers.
Fact: This proves our point T-Mobile customers do not have access to the latest and greatest equipment available to AT&T customers.
AT&T has also claimed the deal will create new jobs and stimulate economic growth. Tell that to the T-Mobile employees who will be collecting unemployment shortly after being deemed redundant by AT&T. Virtually all of T-Mobile’s current service areas overlap AT&T.
Free Press’ Tim Karr compares the consolidation of the cellular industry to the railroad mergers of the 19th century. By locking up competition, carriers can raise prices and call the shots in the marketplace. While a handful of competitors could eke out their 1-2% market share in such a duopoly, all will be starved for capital and considered a risky bet in light of the domination by AT&T and Verizon.
Karr is asking Americans to put their elected officials on notice they don’t want this anti-consumer merger:
So should it be left to Washington and one exceedingly powerful company to decide the fate of our communications? (If you’re thinking “no,” you can help stop this merger by contacting the members of the Antitrust Subcommittee and urging them to grill AT&T next Wednesday.)
If Congress, the FCC and Department of Justice hear from enough people like you and me, they can muster the courage to ask the right questions of AT&T.
Next Wednesday’s hearing on the Hill is our first chance to expose this merger for the nightmare that it is, and save our smartphones from following AT&T down the rabbit hole.


 Subscribe
Subscribe












