Frontier can boost speeds on its acquired fiber to the home networks, which offer almost unlimited capacity upgrades.
Frontier Communications is America’s feast or famine broadband provider, today announcing speed upgrades for its acquired Frontier FiOS and Vantage Fiber service areas while the company continues to pile up hundreds of complaints about poor quality DSL service in the northern U.S. where fiber upgrades are unlikely to ever happen.
Frontier today announced gigabit service (1,000/1,000 Mbps) is now available in its FiOS (California, Texas, Florida, and parts of the Pacific Northwest and Indiana) and Vantage Fiber (primarily Connecticut) service areas. The company also unveiled new plans offering 200/200 and 300/300 Mbps speed options in Indiana, Oregon, and Washington.
“Frontier is pleased to now offer a 200/200 Mbps service, the fastest, most efficient introductory broadband service available in our markets, plus eye-popping speed and capacity with our FiOS Gigabit for the home,” said John Maduri, executive vice president and chief customer officer at Frontier Communications. “Speed and reliability are hallmarks of FiOS Fiber broadband service. Two-way speeds over our all-fiber network make Internet tasks faster and more efficient, regardless of the time of day, while also enabling the many connected devices and streaming services in the home to work simultaneously and smoothly.”
Frontier’s fiber networks are only found in certain regions of the country, including 1.4 million homes in the Tampa Bay/six-county region along the central west coast of Florida, parts of Southern California, Dallas, and individual communities in Indiana, Oregon, and Washington that used to be served by Verizon.
Frontier’s Vantage Fiber network was largely acquired from AT&T’s U-verse service area in Connecticut, with more recent limited rollouts in North Carolina and Minnesota. Life for the unfibered masses in the rest of Minnesota is less sunny, with nearly 500 complaints against Frontier filed by frustrated consumers stuck with a company they feel has forgotten about them.
City Pages notes no company affirms the notoriety of a bad phone company like Frontier Communications, which still relies on a deteriorating copper wire network in most of its original (a/k/a “legacy”) service areas. Complaints about mediocre internet access, missing in action repair crews, and Soviet era-like delays to get landline service installed are as common as country roads.
The grievances read like a cannonade of frustration. They speak of no-show repairmen. Endless waits on hold. Charges for services never rendered. Outages that last for days.
“I have never dealt with a more incompetent company than Frontier,” writes one customer on Google Reviews. “I have no other choice for internet or phone service in my area…. It took me over three months just for Frontier to get to my house to even connect my service…. They also canceled multiple times for installation without calling. They just didn’t show up.”
These maladies aren’t exclusive to the outbacks. They also extend to Watertown Township, in the exurbs of Carver County.
“Frontier Communications is my only option for internet,” Kathleen McCann wrote state regulators. “My internet service is worse than dial-up…. As a dentist, I am not able to email dental X-rays. It took me 47 minutes to upload one small photo to Facebook recently.”
 Frontier vice president Javier Mendoza at least admits most rural Minnesotans will be waiting for upgrades forever.
Frontier vice president Javier Mendoza at least admits most rural Minnesotans will be waiting for upgrades forever.
“The economic reality is that upgrading broadband infrastructure in the more rural parts of the state is not economically viable,” he says.
That leaves customers hoping some other entity will step up and serve the critical digital needs of one of America’s most important agricultural states. If not, the future is dismal.
“Those people are screwed,” Christopher Mitchell of the Institute of Local Self-Reliance, a Minneapolis nonprofit, tells the newspaper. “People who make business or real estate decisions are not going to move to that area.”
With that bleak assessment, several rural Minnesota communities are doing something remarkable — building their own public broadband networks. Even more surprising is that many of those towns are led by hardcore Republican local governments that have very different views about municipal broadband than the national party.
Life is rougher for Frontier’s legacy customers that depend on the company’s decades-old copper wire networks.
Some have joked they could change the mind of big city Republicans that are openly hostile to the concept of public broadband by making them spend two weeks without adequate internet access.
In the Minnesota backcountry, in the heart of Trumpland, broadband is about as bipartisan an issue you can find. Ten cities and 17 townships in Renville and Sibley counties went all-out socialist for suitable, super high-speed fiber optic broadband. RS Fiber, the resulting co-op, delivers superior internet access with fewer complaints than the big phone and cable companies offer in Minneapolis-St. Paul.
Public broadband is no more a “big government” takeover than municipal co-ops were when they were formed to bring electric and phone service to rural farms during the days of FDR. Waiting for investor-owned utilities to find adequate profits before breaking ground came second to meeting the public need for reliable power and phone service.
Today, part of that need is still there, even with an incumbent phone company delivering something resembling service. Frontier DSL is internet access that time forgot, with customers comparing it to the days of dial-up. Speed tests often fail to break 1 Mbps. Cable companies won’t come anywhere near most of these communities, many inconveniently located between nothing and nowhere.
As long as Frontier remains “checked out” with make-due internet access, rural Minnesota won’t ever benefit from the kinds of fiber fast speeds Frontier is promoting on the fiber networks that other companies originally built. Frontier is not in the business of constructing large-scale fiber networks itself. It prefers to acquire them after they are built. That makes Frontier customers in legacy service areas still served with copper envious of the kind of speeds available in California, Texas, and Florida.
Investors continue to pressure Frontier to reduce spending and pay down its debts, piled up largely on the huge acquisitions of Verizon and AT&T landline customers Frontier effectively put on its corporate credit card. For Wall Street, the combination of debt repayments and necessary upgrade expenses are bad news for Frontier’s stock. The company already discontinued its all-important dividend, used for years to lure investors. A growing number of analysts suspect Frontier will face bankruptcy reorganization in the next five years, if only to restructure or walk away from its staggering debts.


 Subscribe
Subscribe A Rochester, N.Y.-based broadband company founded by an ex-president of Time Warner Cable and a former top executive at Rochester Telephone is bringing broadband competition to thousands of residents in Connecticut and Pennsylvania through its fiber-to-the-home network.
A Rochester, N.Y.-based broadband company founded by an ex-president of Time Warner Cable and a former top executive at Rochester Telephone is bringing broadband competition to thousands of residents in Connecticut and Pennsylvania through its fiber-to-the-home network.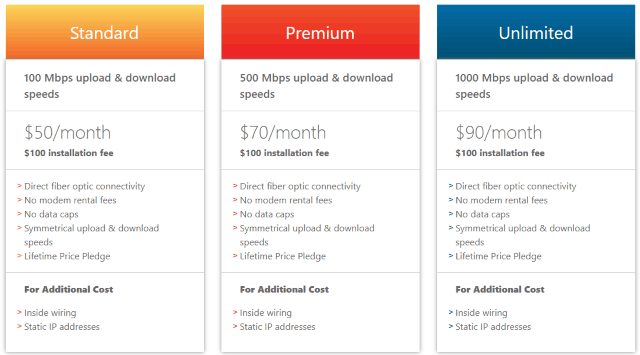
 News 12 The Bronx/Brooklyn (shared studios/talent, but branded individually to each borough)
News 12 The Bronx/Brooklyn (shared studios/talent, but branded individually to each borough)
 Connecticut’s telecommunications regulator has effectively banned public broadband in the state, ruling that municipalities cannot use their reserved space on utility poles if it means competing with the state’s dominant telecom companies — Comcast, Altice, and Frontier Communications.
Connecticut’s telecommunications regulator has effectively banned public broadband in the state, ruling that municipalities cannot use their reserved space on utility poles if it means competing with the state’s dominant telecom companies — Comcast, Altice, and Frontier Communications. The law stood as written until 2013, when the legislature clarified exactly who could benefit from the use of “municipal gain.” Where the original law effectively protected reserved pole space for “municipal” use, the language was broadened in 2013 to read “for any purpose.”
The law stood as written until 2013, when the legislature clarified exactly who could benefit from the use of “municipal gain.” Where the original law effectively protected reserved pole space for “municipal” use, the language was broadened in 2013 to read “for any purpose.”
